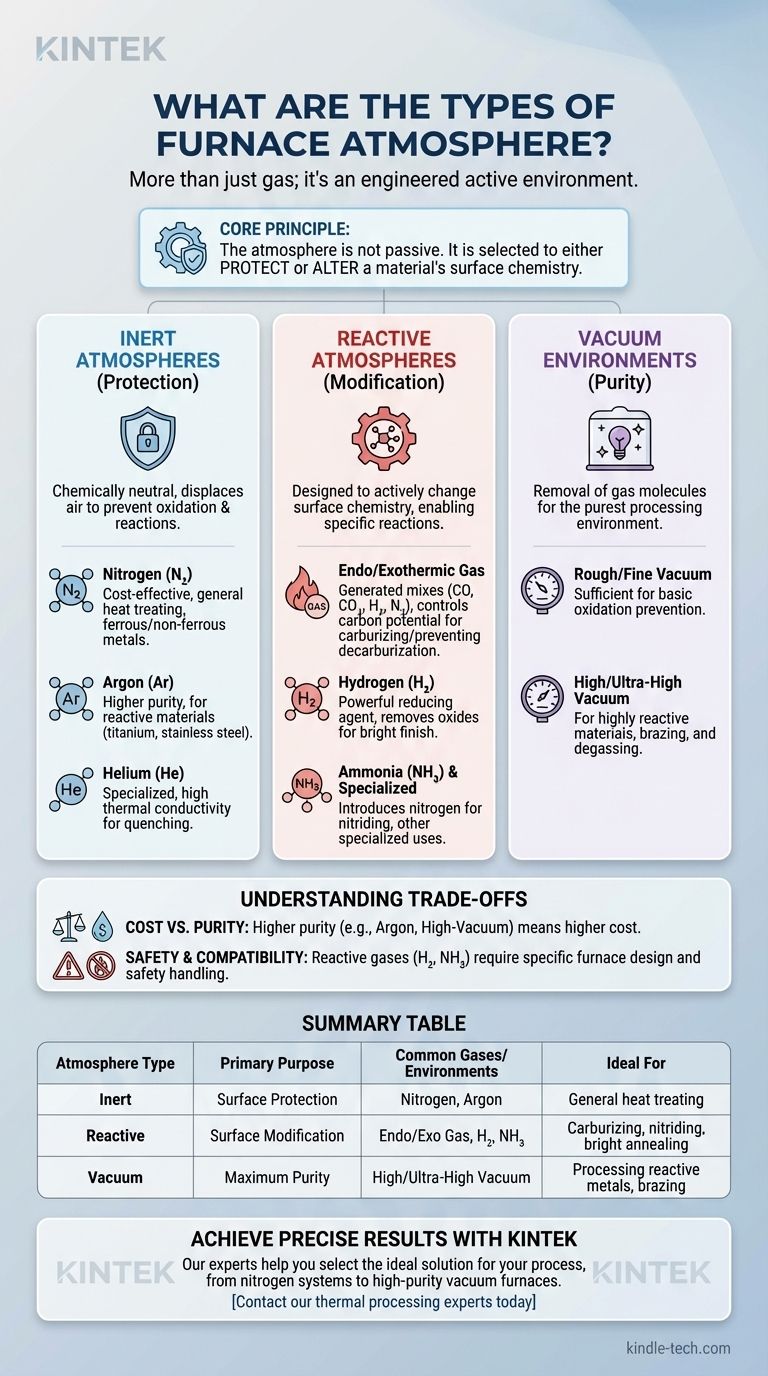
A furnace atmosphere is far more than just the gas inside a chamber; it is an active, engineered environment critical to the outcome of any thermal process. The primary types are broadly categorized as inert gas atmospheres (like nitrogen or argon), reactive atmospheres (such as endothermic or exothermic gases), and vacuum environments, each designed to achieve a specific chemical or physical result on the material being heated.
The core principle to understand is that the furnace atmosphere is not passive. It is a fundamental process variable you must select to either protect a material's surface from change or to deliberately and precisely alter its surface chemistry.

The Purpose of a Controlled Atmosphere
A controlled atmosphere is introduced into a furnace to replace the ambient air, which is approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases. The removal of reactive oxygen is often the primary, but not the only, goal.
Preventing Unwanted Reactions
The most common function of a furnace atmosphere is surface protection. At high temperatures, most metals will readily react with oxygen, leading to scaling and oxidation.
By purging the chamber with an inert gas or creating a vacuum, you can prevent these detrimental reactions from occurring. This is also critical for avoiding decarburization, a process where carbon leaches from the surface of steel, softening it.
Enabling Specific Reactions
Conversely, some processes require a specific chemical reaction to occur on the material's surface. These are known as reactive atmospheres.
These atmospheres contain specific gases designed to introduce elements into the workpiece. This allows for surface modification treatments like carburizing (adding carbon) or nitriding (adding nitrogen) to harden the surface of steel parts.
Key Types of Furnace Atmospheres
The selection of an atmosphere is dictated entirely by the process goal. The main categories are defined by their chemical interactivity with the workpiece.
Inert Atmospheres (Protection)
These atmospheres are chemically neutral to the workpiece. Their sole purpose is to displace air, primarily oxygen, to prevent oxidation and other unwanted reactions.
- Nitrogen (N₂): The most common and cost-effective inert atmosphere. It is suitable for a wide range of heat-treating applications for ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
- Argon (Ar): More inert than nitrogen and used for materials that can react with nitrogen at high temperatures, such as titanium or certain stainless steels. It is denser than air and provides excellent protection but is more expensive.
- Helium (He): An inert gas used in specialized applications, often valued for its high thermal conductivity in vacuum furnace quenching processes.
Reactive Atmospheres (Modification)
These atmospheres are designed to actively change the surface of the material.
- Endothermic/Exothermic Gas: These are generated gases, often from the partial combustion of natural gas. They are carefully controlled mixtures of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and nitrogen. Their primary use is to control the "carbon potential" to prevent decarburization or to perform carburizing on steel.
- Hydrogen (H₂): A powerful reducing agent. It is used to actively remove oxides from a material's surface, creating a bright, clean finish. It is often mixed with nitrogen (forming gas) to reduce flammability.
- Ammonia (NH₃) & Other Specialized Gases: Gases like ammonia are used to introduce nitrogen for nitriding. Other gases, like sulfur dioxide, are used for highly specialized applications.
Vacuum Environments (Purity)
A vacuum is not the absence of an atmosphere, but rather a type of atmosphere itself. By removing almost all gas molecules, a vacuum furnace provides the purest processing environment possible.
Different vacuum levels are used for different purposes:
- Rough/Fine Vacuum: Sufficient for preventing basic oxidation.
- High/Ultra-High Vacuum: Required for processing highly reactive materials or for applications like brazing and degassing, where removing all trapped gases from the material itself is the goal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Choosing an atmosphere involves balancing process requirements with practical constraints. There is no single "best" option.
Cost vs. Purity
The level of purity required directly impacts cost. Nitrogen is an economical workhorse for many applications, while high-purity Argon is significantly more expensive but necessary for reactive metals. A high-vacuum furnace represents a major capital investment but offers unparalleled versatility and purity.
Safety and Handling
Reactive and combustible gases introduce safety challenges. Hydrogen is extremely effective as a reducing agent but is highly flammable and requires specialized handling and safety systems. Ammonia is effective for nitriding but is toxic and corrosive.
Equipment Compatibility
Not all furnaces are created equal. A standard air furnace cannot simply be used with a hydrogen atmosphere. The furnace must be designed with the proper seals, materials, and safety interlocks to handle the specific gas or vacuum level required for the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection must be driven by a clear understanding of your end goal for the material being treated.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation on common steels: A nitrogen atmosphere is typically the most effective and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is hardening the surface of a steel part: A reactive atmosphere, such as an endothermic gas for carburizing or dissociated ammonia for nitriding, is required.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals like titanium or achieving maximum cleanliness for brazing: A high-vacuum environment is the superior and often necessary choice.
Ultimately, mastering the furnace atmosphere gives you precise control over the final properties and quality of your material.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Primary Purpose | Common Gases/Environments | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmospheres | Surface Protection (Prevent Oxidation) | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar) | General heat treating of steels, non-ferrous metals |
| Reactive Atmospheres | Surface Modification (Alter Chemistry) | Endothermic/Exothermic Gas, Hydrogen (H₂), Ammonia (NH₃) | Carburizing, nitriding, bright annealing |
| Vacuum Environments | Maximum Purity & Cleanliness | High/Ultra-High Vacuum | Processing reactive metals (titanium), brazing, degassing |
Achieve Precise Results with the Right Furnace Atmosphere
Selecting the correct furnace atmosphere is critical to the success of your thermal process, whether you need to protect a material's surface, deliberately alter its chemistry, or achieve ultimate purity. The wrong choice can lead to scrap parts, failed brazes, and inconsistent quality.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts understand the nuances of furnace atmospheres and can help you select the ideal solution for your specific application and materials, from cost-effective nitrogen systems to high-purity vacuum furnaces.
Let us help you master your process. Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your requirements and ensure your next heat treatment is a success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a high-temperature atmosphere sintering furnace in MOF-derived catalysts? | Precision Pyrolysis
- What is the role of a precision heat treatment furnace in the annealing of nanostructured eutectic steel?
- What gases are used in brazing? Optimize Your Brazing Process with the Right Atmosphere
- What is used to provide an inert atmosphere for welding? Master the Shield for Perfect Welds
- What is the function of a high-purity argon environment during in-situ ceramicization? Ensure Hardened Ceramic Phases
- What is the specific function of a tube atmosphere furnace in nano-tungsten synthesis? Optimize Your Powder Production
- How do carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbon monoxide (CO) function in furnace atmospheres? Master Carbon Potential for Perfect Heat Treatment
- What is the role of a hydrogen atmosphere furnace in diamond/copper composites? Enhance Your Material Purity



















