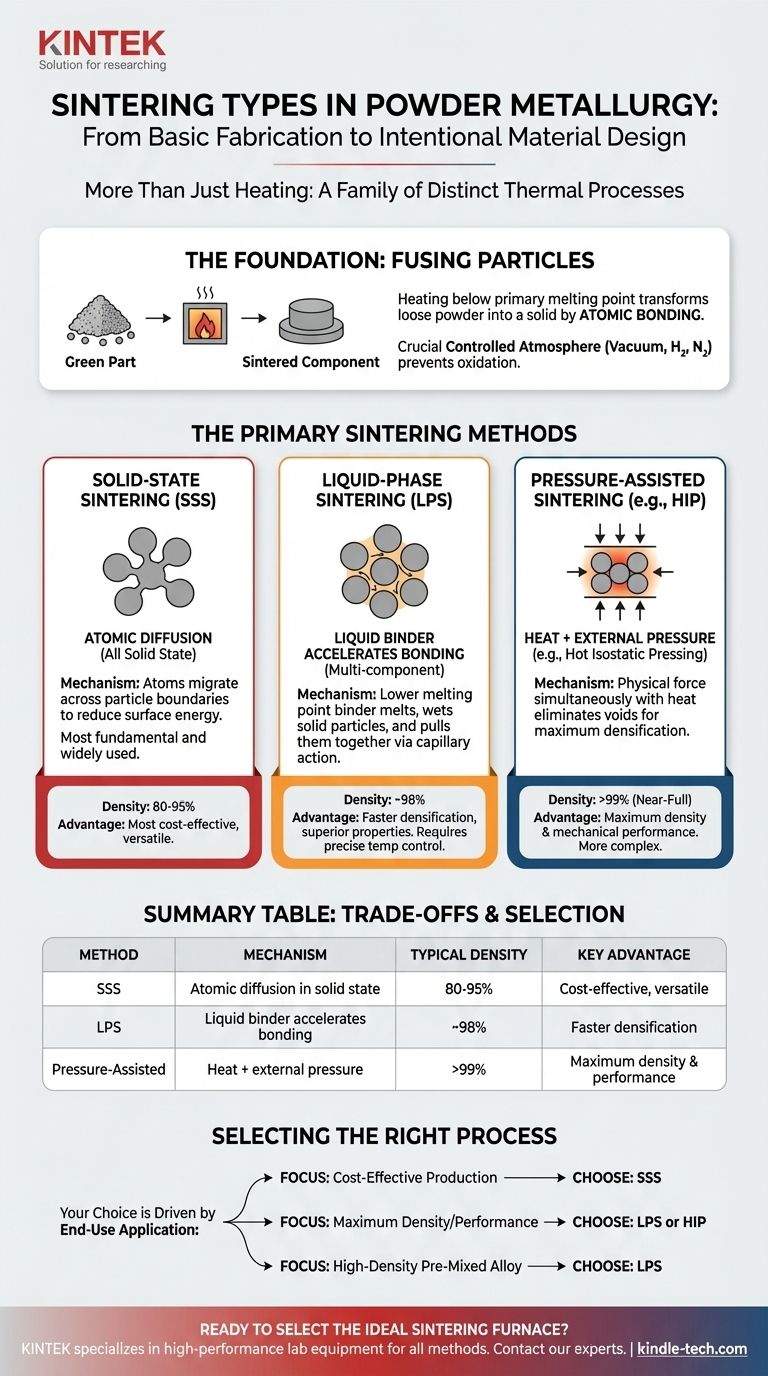
While often spoken of as a single step, sintering in powder metallurgy is actually a family of distinct thermal processes. The primary types are Solid-State Sintering (SSS), where particles bond without melting, Liquid-Phase Sintering (LPS), where a portion of the material melts to act as a binder, and Pressure-Assisted Sintering, which uses external force during heating to achieve superior densification.
The core takeaway is that the choice of sintering method is not arbitrary. It is a critical engineering decision that directly controls the final density, mechanical properties, and cost of a powder metallurgy part. Understanding the difference between these methods is essential for moving from basic fabrication to intentional material design.

The Foundation: What Sintering Achieves
Sintering is the crucial heat treatment step that transforms a loosely compacted "green" part made of metal powder into a solid, functional component. This is accomplished by heating the part in a controlled-atmosphere furnace.
The Goal: Fusing Particles
The process heats the material to a temperature below its primary melting point. At this elevated temperature, atoms at the contact points between powder particles diffuse across the boundaries, effectively welding the particles together.
This atomic bonding dramatically increases the part's strength, hardness, and structural integrity, turning a fragile compact into a durable engineering component.
The Role of Atmosphere
Sintering is almost always performed in a controlled atmosphere, such as a vacuum, hydrogen, or nitrogen-based mixture. This is critical to prevent the formation of oxides on the metal particles, which would inhibit proper bonding and compromise the final part's properties.
The Primary Sintering Methods
While the goal of bonding particles is universal, the mechanism used to achieve it defines the type of sintering.
Solid-State Sintering (SSS)
This is the most fundamental and widely used form of sintering. The entire process occurs while all materials remain in a solid state.
Particle bonding relies solely on atomic diffusion, a relatively slow process where atoms migrate across particle boundaries to reduce surface energy. It is the standard method for single-component metal powders like iron or copper.
Liquid-Phase Sintering (LPS)
This method is used for multi-component powder mixtures where one component has a lower melting point than the others. The furnace temperature is raised above the melting point of this "binder" element but kept below the melting point of the primary structural metal.
This creates a small amount of liquid phase that wets the solid particles. Capillary action from the liquid pulls the solid particles together, rapidly accelerating densification and closing pores more effectively than solid-state diffusion alone.
Pressure-Assisted Sintering
This category involves applying external mechanical pressure simultaneously with heat. This force physically aids in closing the voids between particles, leading to densities that are difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional methods.
A prominent example is Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), where the part is heated in a high-pressure inert gas environment. The uniform pressure from all directions eliminates internal porosity, resulting in a fully dense component with superior mechanical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sintering method involves balancing performance requirements against process complexity and cost.
Density vs. Cost
Solid-State Sintering is the most cost-effective method but typically results in parts with 80-95% of theoretical density.
Liquid-Phase Sintering and Pressure-Assisted Sintering (like HIP) can achieve densities of 98% to nearly 100%. This performance comes at the cost of more complex material systems, tighter process control, and more expensive equipment.
Material & Shape Limitations
LPS is only suitable for alloy systems with components that have distinctly different melting points. Pressure-assisted methods can be limited by part geometry and the complexity of the required tooling or pressure vessels. SSS is more versatile for a wider range of simple materials.
Process Control
SSS is relatively straightforward to control. LPS, however, requires extremely precise temperature management. If the temperature is too low, no liquid forms; if it's too high, the entire part could melt, losing its shape and dimensional accuracy.
Selecting the Right Sintering Process
Your choice of method should be driven by the end-use application of the component.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production for standard applications: Solid-State Sintering is the industry default and provides excellent value for a wide range of parts.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and superior mechanical properties: Liquid-Phase Sintering or a pressure-assisted method like HIP is required for high-performance components.
- If your primary focus is creating a high-density part from a pre-mixed alloy powder: Liquid-Phase Sintering is the most effective route to accelerate densification and achieve exceptional final properties.
Mastering these techniques allows you to purposefully engineer the microstructure and performance of your final component.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Method | Primary Mechanism | Typical Density | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-State Sintering (SSS) | Atomic diffusion in solid state | 80-95% | Most cost-effective and versatile |
| Liquid-Phase Sintering (LPS) | Liquid binder accelerates bonding | ~98% | Faster densification, superior properties |
| Pressure-Assisted Sintering | Heat + external pressure (e.g., HIP) | >99% (near-full) | Maximum density and mechanical performance |
Ready to select the ideal sintering process for your powder metallurgy components? The right sintering furnace is critical to achieving your target density, strength, and cost-efficiency.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and equipment for all sintering methods—from standard solid-state to advanced hot isostatic pressing (HIP). We provide the precise temperature control and controlled atmospheres your laboratory needs for reliable, repeatable results.
Contact our sintering experts today to discuss your application and find the perfect furnace solution for your research or production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology



















