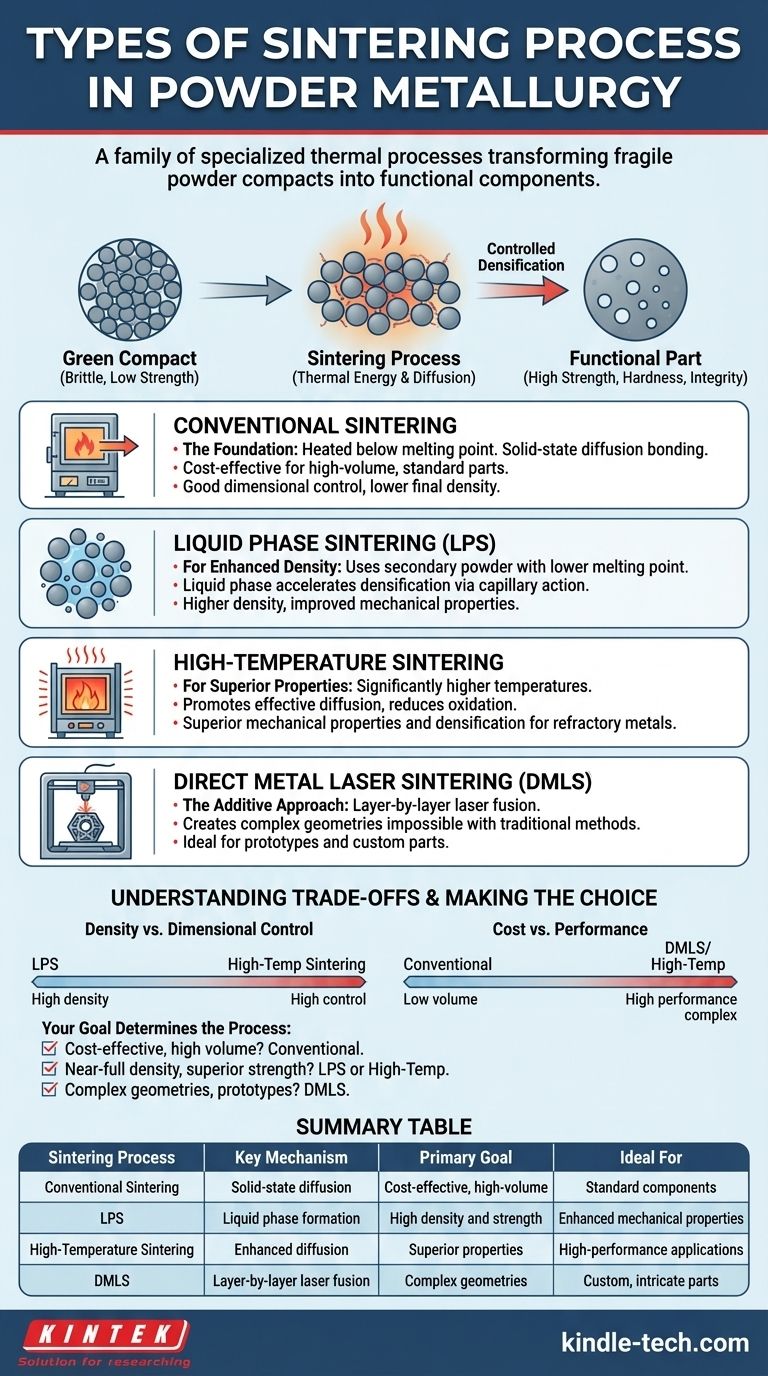
In powder metallurgy, sintering is not one single method but a family of specialized thermal processes. While all involve heating a compacted powder to bond its particles below the material's melting point, the specific techniques vary significantly based on the desired outcome. The primary types include conventional solid-state sintering, liquid phase sintering (LPS) for enhanced density, high-temperature sintering for superior performance, and direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) for additive manufacturing.
The core principle is that the choice of sintering method is a strategic engineering decision. It directly dictates the final part's density, mechanical properties, dimensional accuracy, and cost, transforming a fragile powder compact into a functional component.

The Role of Sintering in Powder Metallurgy
Sintering is the critical step that follows the pressing or compaction of metal powder. The initial compacted part, known as a "green compact," is brittle and has very low mechanical strength.
From a "Green" Compact to a Functional Part
The green compact is essentially a collection of powder particles held together by mechanical interlocking from the pressing stage. It has no metallurgical bonds.
Sintering introduces thermal energy, which activates diffusion mechanisms at the contact points between powder particles. This process creates strong metallurgical bonds, effectively fusing the particles together and giving the component its strength, hardness, and structural integrity.
The Goal: Controlled Densification
During sintering, the voids (porosity) between the powder particles are reduced, causing the component to shrink and become denser. The degree of densification is a key metric controlled by the sintering process parameters.
Key Types of Sintering Explained
Each sintering technique offers a different approach to achieving particle bonding and densification, tailored for specific materials and applications.
Conventional Sintering: The Foundation
This is the most common and traditional method. The green compact is simply heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace to a temperature below the melting point of the primary metal.
Bonding occurs entirely in the solid state through diffusion. It is a reliable and cost-effective process for a wide range of general-purpose components.
Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS): For Enhanced Density
In LPS, a small amount of a secondary powder with a lower melting point is mixed with the primary metal powder. During heating, this secondary component melts, creating a liquid phase that wets the solid particles.
The liquid accelerates densification dramatically through capillary action, pulling the solid particles closer together and providing a fast path for material transport. This results in higher density and improved mechanical properties compared to conventional sintering.
High-Temperature Sintering: For Superior Properties
As the name implies, this process uses significantly higher temperatures than conventional sintering, often for materials with extremely high melting points like refractory metals or certain high-strength steels.
The higher thermal energy promotes more effective diffusion, reducing surface oxidation and resulting in superior mechanical properties and better densification. However, it requires more advanced and costly furnace technology.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): The Additive Approach
DMLS is a type of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, and differs fundamentally from the other methods. It does not start with a pre-formed green compact.
Instead, a high-power laser selectively sinters thin layers of metal powder on a build plate, one on top of the other, to construct the part from the ground up. This allows for the creation of highly complex geometries that are impossible to produce with traditional pressing and sintering.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sintering process involves balancing competing factors. No single method is best for every application.
Density vs. Dimensional Control
Processes that achieve high density, like LPS and high-temperature sintering, often result in more significant and sometimes less predictable part shrinkage. Conventional sintering offers better dimensional control but at the cost of lower final density and more residual porosity.
Cost vs. Performance
Conventional sintering is the most economical process for high-volume production. High-temperature sintering increases costs due to higher energy consumption and the need for specialized furnaces. DMLS is the most expensive per part, but it unlocks unparalleled geometric freedom and is ideal for prototyping and low-volume, high-complexity components.
Process Complexity and Material Limitations
LPS requires careful control of the liquid phase to avoid part distortion. DMLS is a complex digital process that is only compatible with specific, often expensive, atomized metal powders. Conventional sintering is the most straightforward and versatile for a wide range of standard PM materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's requirements will determine the optimal sintering process.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production of standard parts: Conventional sintering is the industry standard and most efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving near-full density and superior mechanical strength: Liquid phase sintering or high-temperature sintering are the necessary approaches.
- If your primary focus is creating complex geometries, custom parts, or rapid prototypes: Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) is the only viable option.
Understanding these distinct processes allows you to select the precise thermal treatment required to transform metal powder into a high-performance component.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Process | Key Mechanism | Primary Goal | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Sintering | Solid-state diffusion | Cost-effective, high-volume production | Standard components |
| Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS) | Liquid phase formation | High density and strength | Enhanced mechanical properties |
| High-Temperature Sintering | Enhanced diffusion | Superior properties for refractory metals | High-performance applications |
| Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) | Layer-by-layer laser fusion | Complex geometries and prototypes | Custom, intricate parts |
Ready to optimize your powder metallurgy process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your sintering needs. Whether you're working with conventional furnaces or exploring additive manufacturing with DMLS, our expertise ensures you achieve the precise density, strength, and dimensional accuracy your components require.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and results. Get in touch via our contact form and let's build high-performance parts together!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance
- What technical advantages does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace provide? Enhance Fe-Ni/Zr2P2WO12 Composite Density
- What is the pressure for vacuum sintering? Achieve Optimal Material Purity and Density
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al



















