At its core, a laboratory furnace is a high-temperature oven used to fundamentally alter the physical and chemical properties of a material through precisely controlled thermal processing. These instruments are indispensable in fields ranging from materials science and metallurgy to electronics and ceramics. They are used for a wide range of applications, including synthesizing new materials, strengthening metals, and preparing samples for analysis.
The primary purpose of a laboratory furnace isn't just to heat things up. It is a sophisticated tool for executing specific thermal processes—like sintering, annealing, or ashing—that require precise control over temperature, time, and sometimes atmosphere to achieve a desired material transformation.

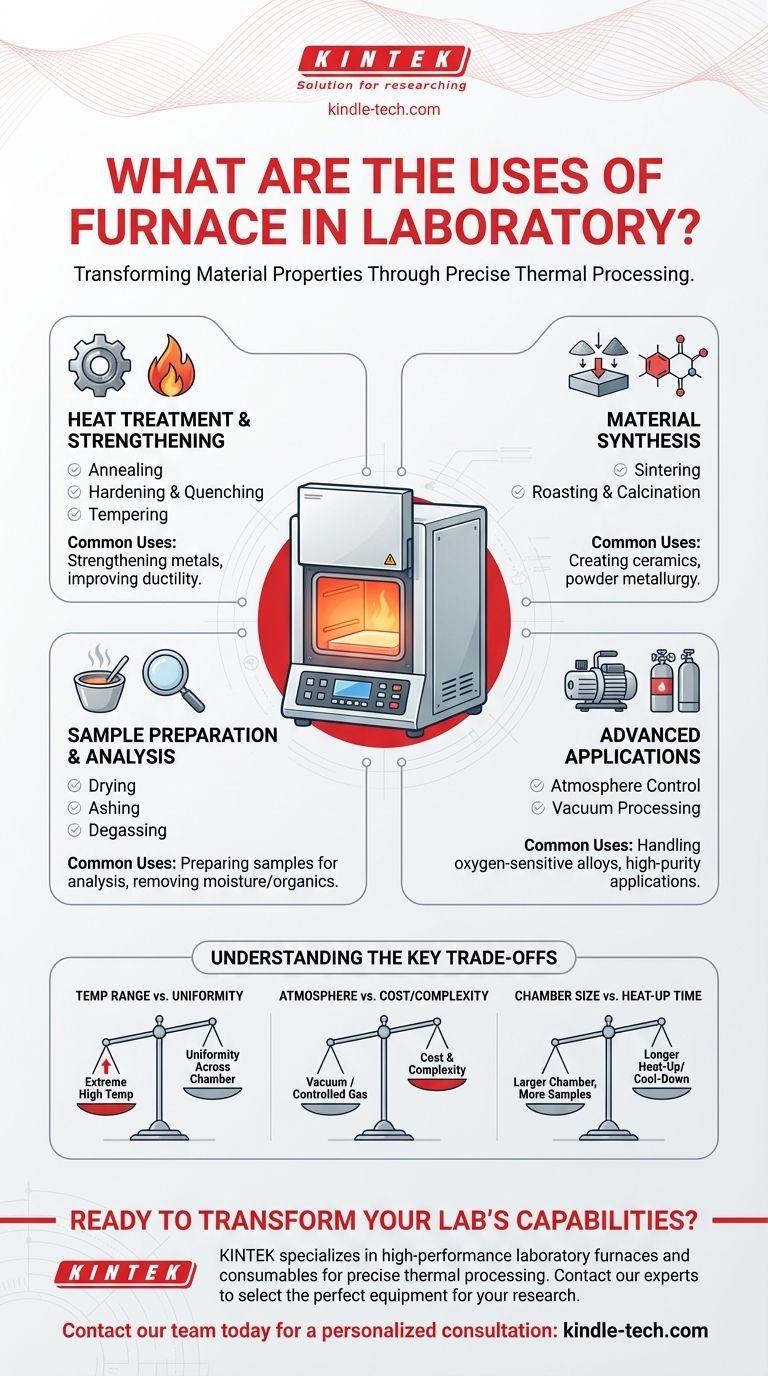
Core Functions: Transforming Material Properties
The most common applications of a laboratory furnace involve intentionally modifying a material's internal structure or composition. These processes are foundational to both academic research and industrial quality control.
Heat Treatment and Strengthening
This category of processes primarily applies to metals and alloys, where heat is used to alter mechanical properties like hardness and ductility.
- Annealing: Involves heating a material and then cooling it slowly. This process removes internal stresses and makes the material softer and more workable.
- Hardening & Quenching: Involves heating a metal to a critical temperature and then cooling it rapidly. This locks in a crystalline structure that significantly increases its hardness and strength.
- Tempering: A secondary process performed after hardening. The material is reheated to a lower temperature to reduce brittleness and improve its toughness.
Sintering and Material Synthesis
These processes are used to create solid, coherent objects from powders without melting them. This is a cornerstone of ceramics and powder metallurgy.
- Sintering: Heating a compressed powder to just below its melting point. At this temperature, the particles fuse together, creating a dense, solid part. This is how most technical ceramics are made.
- Roasting & Calcination: Thermal treatments used to cause a chemical change, such as removing water, carbon dioxide, or other volatile substances from a sample.
Sample Preparation and Analysis
In many scientific workflows, a furnace is a preparatory tool used to ready a sample for further testing or analysis.
- Drying: Gently heating a sample at a relatively low temperature to remove moisture without altering its chemical composition.
- Ashing: A high-temperature process that burns off all organic matter in a sample, leaving only the inorganic components (ash) for analysis. This is common in materials and environmental testing.
- Degassing: Heating a material, often under vacuum, to remove trapped or dissolved gases from its structure.
Advanced Applications in Controlled Environments
For materials that are sensitive to oxygen or require extreme purity, standard furnaces are insufficient. Specialized furnaces provide precise atmospheric control.
Atmosphere Control for Sensitive Materials
An atmosphere furnace allows the user to replace the air inside the chamber with a specific gas.
This is critical for processes like brazing or annealing metals that would otherwise oxidize (rust) at high temperatures. Using an inert gas like argon or nitrogen creates a protective environment, ensuring the material's surface remains clean and unaltered.
Vacuum Processing for Purity and Performance
A vacuum furnace removes nearly all the air and other gases from the chamber before heating.
This is the gold standard for high-performance applications, such as treating components for the aerospace industry or in advanced electronics. Vacuum heat treatment prevents any surface reactions, yielding materials with superior purity and performance characteristics.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing or using a furnace involves balancing several factors. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for selecting the right tool for your specific application.
Temperature Range vs. Uniformity
Furnaces capable of reaching extremely high temperatures (above 1500°C) may sometimes sacrifice temperature uniformity across the entire chamber. For sensitive processes, ensuring every part of the sample experiences the same temperature is paramount.
Atmosphere Control vs. Cost and Complexity
A simple furnace that operates in ambient air is relatively straightforward and affordable. Introducing vacuum or controlled gas capabilities adds significant cost, complexity, and maintenance requirements. This advanced control is only necessary when working with reactive materials.
Chamber Size vs. Heat-Up Time
A larger furnace chamber can process more or bigger samples at once, but it also has a greater thermal mass. This means it will take significantly longer to heat up to the target temperature and cool back down, which can impact laboratory throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective dictates which furnace process is most appropriate.
- If your primary focus is creating ceramic parts from powder: Your key processes are sintering and calcination.
- If your primary focus is altering the strength of a metal part: You need to perform heat treatments like annealing, hardening, and tempering.
- If your primary focus is determining the inorganic content of a sample: The correct procedure is ashing.
- If your primary focus is treating an oxygen-sensitive alloy: You must use an atmosphere or vacuum furnace to prevent oxidation.
Ultimately, the laboratory furnace is a fundamental tool for the controlled creation and refinement of materials.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering | Strengthening metals, improving ductility |
| Material Synthesis | Sintering, Calcination, Roasting | Creating ceramics, powder metallurgy |
| Sample Preparation | Ashing, Drying, Degassing | Preparing samples for analysis, removing moisture/organics |
| Advanced Processing | Atmosphere Control, Vacuum Heat Treatment | Handling oxygen-sensitive alloys, high-purity applications |
Ready to transform your lab's capabilities? KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory furnaces and consumables designed for precise thermal processing. Whether you need a standard furnace for annealing or an advanced atmosphere-controlled system for sensitive materials, our experts can help you select the perfect equipment to meet your research and quality control goals.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can enhance your material science workflows.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the use of a digital muffle furnace? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the thermal debinding process? A Guide to Safe Binder Removal for MIM & Ceramics
- What is the purpose of a laboratory furnace? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is an electric muffle furnace? Achieve Unmatched Thermal Purity and Uniformity
- What is the difference between a furnace and an oven in a laboratory? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Heat Needs



















