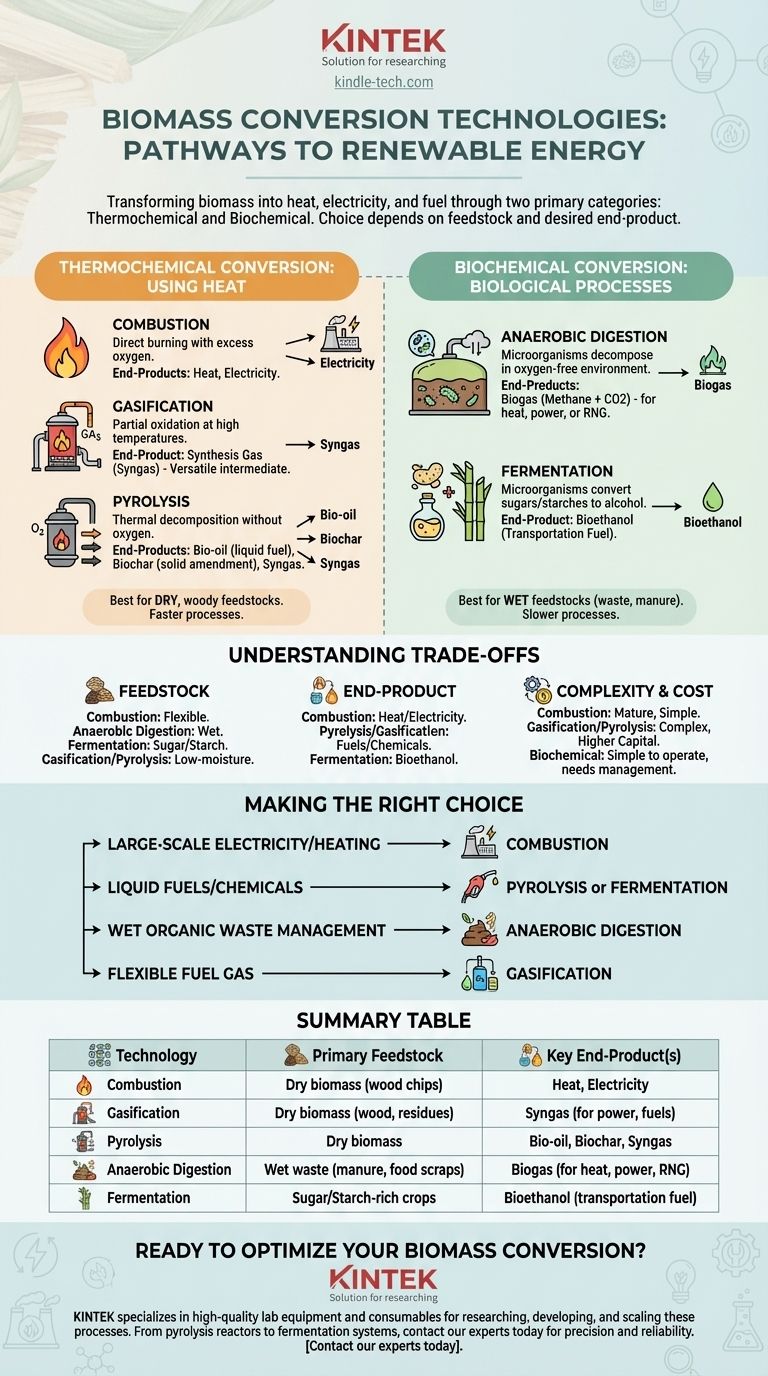
The primary methods for converting biomass fall into two main categories: thermochemical and biochemical. Thermochemical technologies like combustion, gasification, and pyrolysis use heat to break down biomass, while biochemical methods like anaerobic digestion and fermentation use microorganisms to decompose the organic material. Each pathway is designed to transform raw organic matter into more valuable forms like heat, electricity, or fuel.
The optimal biomass conversion technology is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The choice fundamentally depends on two factors: the type of biomass feedstock available (e.g., dry wood vs. wet manure) and the desired end-product (e.g., direct heat vs. liquid fuel).

Thermochemical Conversion: Using Heat to Transform Biomass
Thermochemical pathways rely on heat and chemical processes to decompose the complex structures within biomass. These methods are generally faster than biological processes and are well-suited for dry, woody feedstocks.
Combustion: The Direct Approach to Heat and Power
Combustion is the most common and straightforward biomass technology. It is the simple process of burning biomass in the presence of excess oxygen to release heat.
This heat can be used directly for industrial processes or space heating. It can also be used to boil water, creating high-pressure steam that drives a turbine to generate electricity.
Gasification: Creating a Versatile Fuel Gas
Gasification involves heating biomass at high temperatures with a limited amount of oxygen. This partial oxidation doesn't burn the material completely.
Instead, it converts the solid biomass into a combustible gas mixture known as synthesis gas, or syngas. Syngas (primarily hydrogen and carbon monoxide) is a versatile intermediate that can be burned to generate electricity or further processed into liquid fuels and chemicals.
Pyrolysis: Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is the process of heating biomass to high temperatures in the complete absence of oxygen. This prevents combustion and causes the material to thermally decompose into different products.
Depending on the process speed, pyrolysis yields three primary products: a liquid called bio-oil (or pyrolysis oil), a solid charcoal-like substance called biochar, and a portion of syngas. Bio-oil can be upgraded into transportation fuels, while biochar is a valuable soil amendment.
Biochemical Conversion: Leveraging Biological Processes
Biochemical, or biological, conversion uses enzymes, bacteria, and other microorganisms to break down biomass. These methods are ideal for feedstocks with high moisture content, such as agricultural waste, manure, and municipal solid waste.
Anaerobic Digestion: Producing Biogas from Wet Waste
This process uses microorganisms to decompose wet organic materials in an oxygen-free environment. It is essentially a controlled version of the natural decomposition that occurs in swamps or landfills.
The primary output is biogas, which is mostly methane and carbon dioxide. This biogas can be captured and burned to generate heat and electricity, or it can be purified into renewable natural gas (RNG) for injection into pipelines.
Fermentation: Creating Biofuels like Ethanol
Fermentation uses microorganisms, typically yeast, to convert the carbohydrates (sugars and starches) in biomass into alcohol.
This is the same fundamental process used to make alcoholic beverages. In the context of energy, it is the primary method for producing bioethanol from crops like corn and sugarcane to be used as a transportation fuel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single technology is universally superior. The selection process requires a clear understanding of the inherent compromises between feedstock, complexity, and output.
Feedstock Flexibility
Different technologies are optimized for different types of biomass. Combustion is highly flexible and can handle many forms of dry biomass. Anaerobic digestion, conversely, requires wet feedstocks to function efficiently.
Fermentation is even more specific, requiring feedstocks rich in sugars or starches. Gasification and pyrolysis work best with low-moisture feedstocks like wood chips or agricultural residues.
End-Product Versatility
The desired final product heavily influences the choice of technology. If the only goal is heat or electricity, direct combustion is often the most cost-effective path.
However, if the goal is to produce liquid transportation fuels or valuable chemicals, pyrolysis or gasification offer pathways to create these more complex products.
Process Complexity and Cost
Combustion is a mature, relatively simple, and well-understood technology. In contrast, gasification and pyrolysis systems are more technically complex and can have higher capital costs.
Biochemical processes like anaerobic digestion can be simpler to operate at a small scale (e.g., on a single farm) but require careful management of biological conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate technology requires aligning the process with your specific resources and objectives.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, cost-effective electricity or district heating: Direct combustion of dry biomass is the most established and reliable solution.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid transportation fuels or valuable bio-chemicals: Pyrolysis to produce bio-oil or fermentation to produce ethanol are the targeted pathways.
- If your primary focus is managing wet organic waste (e.g., manure, food scraps): Anaerobic digestion is the ideal technology to convert this waste into biogas.
- If your primary focus is creating a flexible fuel gas for multiple applications: Gasification provides a versatile syngas intermediate that can be used for power, heat, or synthesis.
By understanding these core conversion pathways, you can effectively evaluate and select the optimal biomass technology for any specific energy objective.
Summary Table:
| Technology | Primary Feedstock | Key End-Product(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Combustion | Dry biomass (wood chips) | Heat, Electricity |
| Gasification | Dry biomass (wood, residues) | Syngas (for power, fuels) |
| Pyrolysis | Dry biomass | Bio-oil, Biochar, Syngas |
| Anaerobic Digestion | Wet waste (manure, food scraps) | Biogas (for heat, power, RNG) |
| Fermentation | Sugar/Starch-rich crops | Bioethanol (transportation fuel) |
Ready to select and implement the optimal biomass conversion technology for your lab or project? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for researching, developing, and scaling these processes. Whether you need reactors for pyrolysis studies, gas analyzers for syngas, or fermentation systems, our solutions ensure precision and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your biomass conversion goals and enhance your laboratory's efficiency and success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
People Also Ask
- What role do laboratory autoclaves play in pectin extraction? Optimize Prebiotic Yield from Citrus and Apple Biomass
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing
- What is the primary function of a laboratory autoclave in the pre-treatment of medical plastic waste for liquid fuel?
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam



















