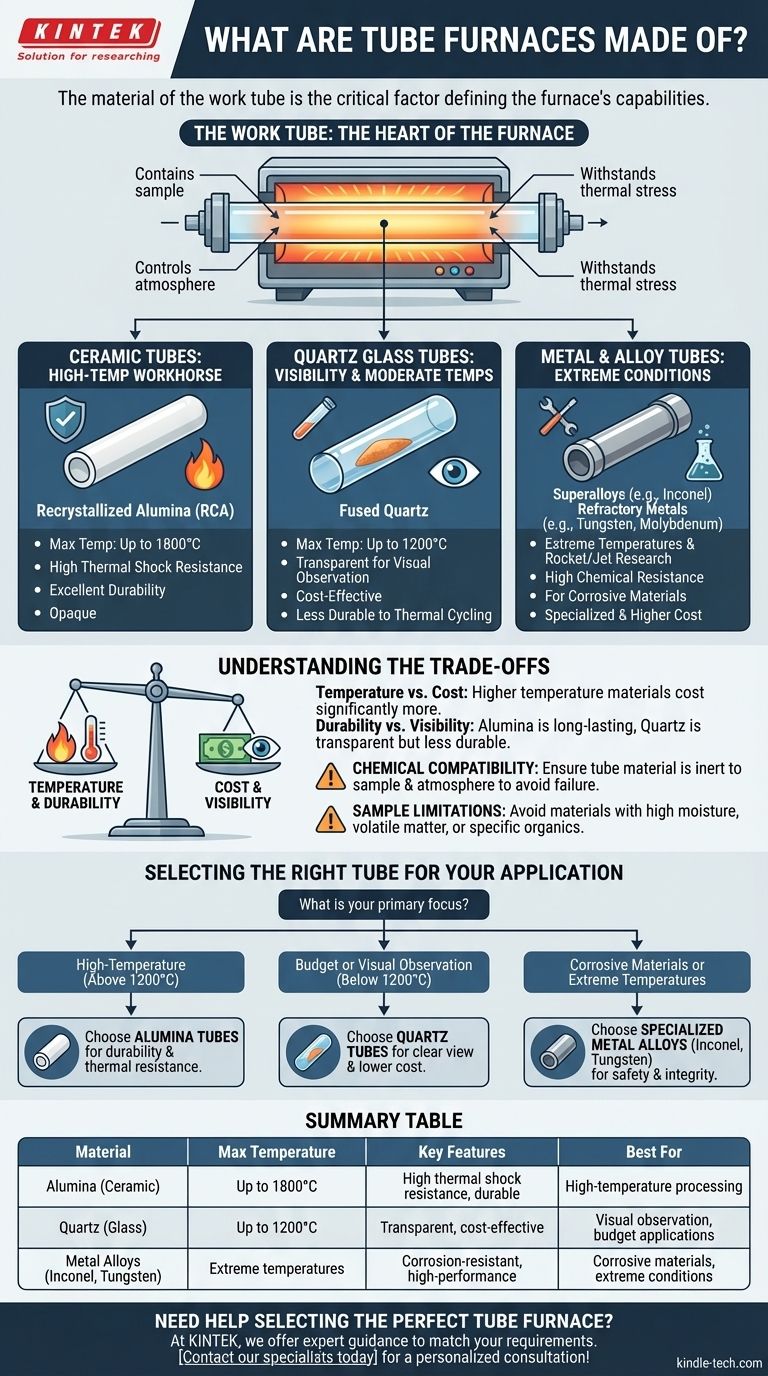
The material of a tube furnace's work tube is not a minor detail; it is the single most critical factor defining the furnace's capabilities. The central tube is typically constructed from one of three material classes: ceramics like alumina, glass such as quartz, or specialized metals and superalloys like Inconel or tungsten. Each material is chosen to meet specific requirements for temperature, chemical inertness, and durability.
The choice of a work tube material is a strategic decision dictated by your experiment's maximum temperature, chemical environment, and budget. Understanding the trade-offs between materials is essential for achieving reliable and accurate results.

Why the Work Tube Material is Critical
The work tube is the heart of the furnace. It contains the sample, controls the processing atmosphere, and must withstand extreme thermal stress.
Therefore, the tube's material properties directly constrain the furnace's operational limits, including its maximum temperature and the types of materials you can safely process.
A Breakdown of Common Tube Materials
Each material offers a distinct profile of performance, durability, and cost. The selection process involves matching your specific application needs to the right material.
Ceramic Tubes: The High-Temperature Workhorse
The most common high-performance ceramic is recrystallized alumina (RCA). These tubes are the standard for applications requiring high temperatures and long-term durability.
Alumina tubes can operate at temperatures up to 1800°C. They are highly resistant to thermal shock and can endure many heating and cooling cycles, making them a long-lasting and reliable choice. Their primary drawback is that they are opaque.
Quartz Glass Tubes: For Visibility and Moderate Temperatures
Fused quartz is a popular and cost-effective option for processes that do not exceed 1200°C.
The key advantage of quartz is its transparency, which allows for direct visual observation of the sample during processing. However, quartz is more susceptible to thermal shock and generally cannot withstand as many heat-cool cycles as alumina, making it less durable over time.
Metal and Alloy Tubes: For Extreme or Corrosive Conditions
For the most demanding applications, metal tubes are required. Superalloys like Inconel are custom options used for extreme temperatures, such as those found in rocket and jet engine research.
For processing highly corrosive materials, refractory metals like tungsten or molybdenum are used. These materials provide the necessary chemical resistance to prevent the tube from degrading and contaminating the sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a tube material is an exercise in balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate one for a given task.
Temperature vs. Cost
There is a direct correlation between a material's temperature rating and its cost. Quartz is the most budget-friendly option for temperatures up to 1200°C, while alumina and specialized superalloys represent a significant increase in investment for their higher temperature capabilities.
Durability vs. Visibility
You must often choose between the long operational life of an alumina tube and the observational benefits of a transparent quartz tube. If you need to see your sample, quartz is the only option, but you must accept its lower durability.
Chemical Compatibility is Non-Negotiable
Ignoring the chemical interaction between your sample and the work tube can lead to failed experiments, damaged equipment, and contaminated results. Always verify that the tube material is inert to the chemicals and atmosphere being used in your process.
Sample Limitations
Be aware that tube furnaces are not suitable for all samples. Materials containing high moisture, volatile matter, or certain organic compounds can release substances that damage the tube or create unsafe conditions and should generally be avoided.
Selecting the Right Tube for Your Application
Your final choice should be guided by a clear understanding of your experimental goals.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing (above 1200°C): Alumina tubes are the standard due to their exceptional durability and thermal resistance.
- If your primary focus is budget-conscious applications or visual observation (below 1200°C): Quartz tubes offer a clear view of your sample and a lower initial cost.
- If your primary focus is processing corrosive materials or reaching extreme temperatures: Specialized metal alloys like Inconel, tungsten, or molybdenum are necessary to ensure safety and experimental integrity.
By understanding these material properties, you can confidently select a tube furnace that aligns perfectly with your specific scientific or industrial goals.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Ceramic) | Up to 1800°C | High thermal shock resistance, durable | High-temperature processing |
| Quartz (Glass) | Up to 1200°C | Transparent, cost-effective | Visual observation, budget applications |
| Metal Alloys (e.g., Inconel, Tungsten) | Extreme temperatures | Corrosion-resistant, high-performance | Corrosive materials, extreme conditions |
Need help selecting the perfect tube furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance to match your specific temperature, chemical, and budget requirements.
Let us help you achieve reliable and accurate results with the right tube material. Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What is the difference between a tubular furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Application



















