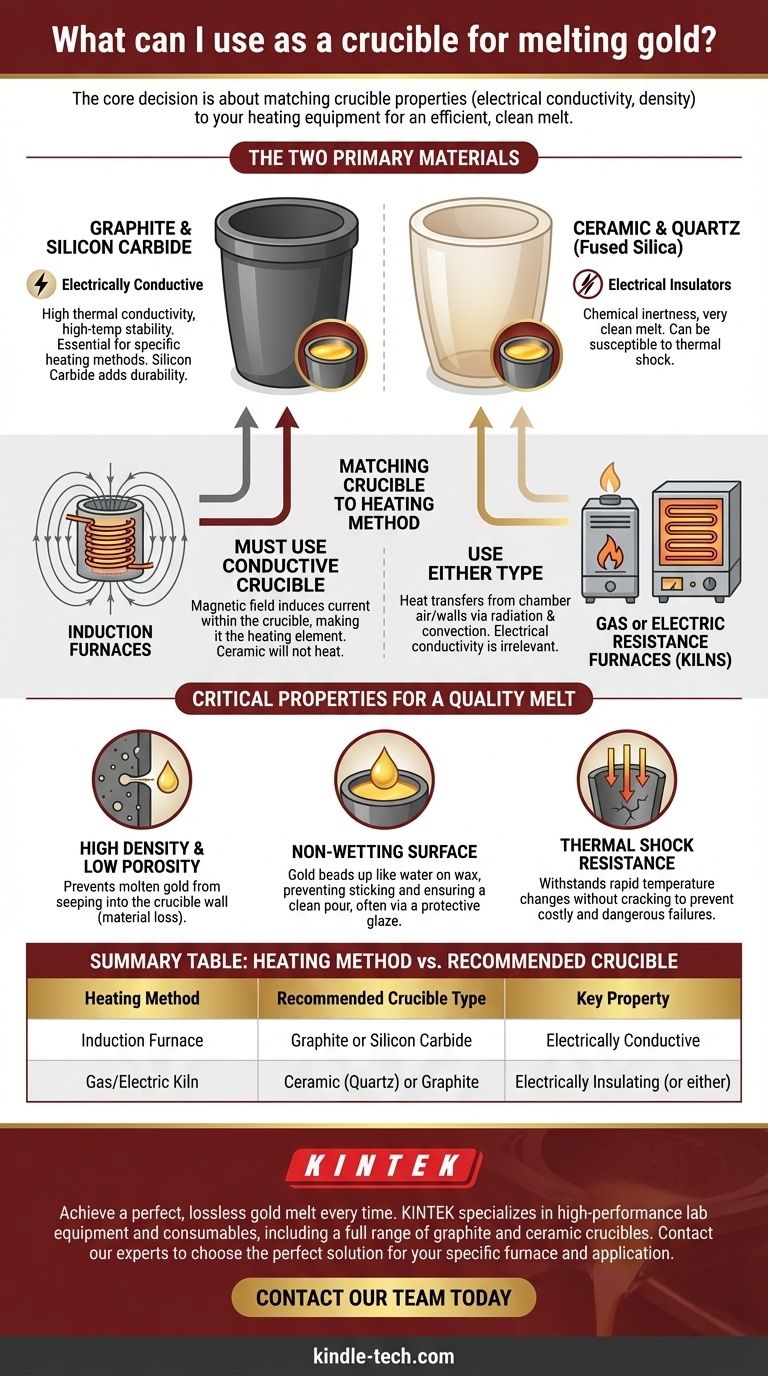
For melting gold, the most common and effective crucibles are made from either graphite or a ceramic material like fused silica (quartz) or clay graphite. The best choice depends directly on your heating method and the specific properties required for a clean melt.
The core decision is not just about finding a material that can withstand gold's melting point. It's about matching the crucible's properties—specifically its electrical conductivity and material density—to your heating equipment to ensure an efficient, clean, and lossless melt.
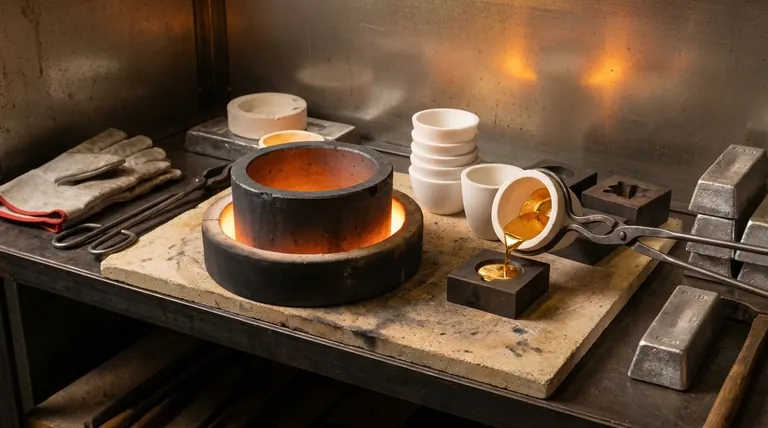

The Two Primary Materials for Gold Melting
The choice between crucible materials fundamentally comes down to how you plan to apply heat. Each material interacts with heat differently, making one more suitable than the other depending on your setup.
Graphite & Silicon Carbide Crucibles
Graphite is a highly effective and widely used material for melting gold and other precious metals. It is known for its excellent thermal conductivity and high-temperature stability.
These crucibles are electrically conductive. This property is not just incidental; it is essential for certain heating methods. Silicon carbide is another conductive material often used for its superior durability.
Ceramic & Quartz Crucibles
Ceramic crucibles, typically made from fused silica (often called quartz) or clay-graphite composites, are the other primary option.
Unlike pure graphite, these materials are generally electrical insulators. They are valued for their chemical inertness and ability to provide a very clean melt, though they can be more susceptible to cracking under rapid temperature changes.
Matching Your Crucible to Your Heating Method
The most common mistake is choosing a crucible without considering the furnace type. The physics of how your furnace generates heat dictates the type of crucible you must use.
For Induction Furnaces
Induction furnaces work by creating a powerful magnetic field that induces an electric current within the crucible itself, causing it to heat up rapidly from the inside out.
For this to work, you must use a conductive crucible. A graphite or silicon carbide crucible is required, as it will react to the magnetic field and become the heating element. A ceramic crucible will not heat up in an induction furnace.
For Gas or Electric Resistance Furnaces (Kilns)
These furnaces heat a chamber using external gas burners or electric coils. The heat transfers from the air and furnace walls to the crucible through radiation and convection.
In this setup, you can use either a ceramic/quartz crucible or a graphite crucible. Because the heat is external, the crucible simply needs to absorb it efficiently and hold the metal, making its electrical conductivity irrelevant.
Critical Properties for a Quality Melt
Beyond the base material, certain characteristics are non-negotiable for preventing the loss or contamination of your gold.
High Density and Low Porosity
Molten gold can seep into a porous crucible, resulting in material loss that is difficult to recover. A high-quality crucible must have a very dense material structure to prevent this absorption.
Non-Wetting Surface
A "non-wetting" surface means the molten gold will bead up, much like water on a waxed car. It will not stick to the crucible walls.
This is often achieved with a durable protective glaze. This property is critical for ensuring a clean pour and recovering every possible gram of your metal.
Thermal Shock Resistance
The crucible will undergo extreme temperature changes. Thermal shock resistance is its ability to withstand rapid heating and cooling without cracking. A failure here can be both costly and dangerous.
Making the Right Choice for Your Melt
Your choice should be guided by your equipment and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is melting with an induction furnace: You must use a conductive graphite or silicon carbide crucible, as the furnace heats the crucible directly.
- If your primary focus is melting in a gas or electric kiln: You have the flexibility to use either an insulating ceramic/quartz crucible or a conductive graphite crucible.
- If your primary focus is preventing material loss: Prioritize a high-density crucible with a smooth, non-wetting interior glaze, regardless of the base material.
Selecting the correct crucible is the foundation for a safe, efficient, and successful precious metal melt.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Recommended Crucible Type | Key Property |
|---|---|---|
| Induction Furnace | Graphite or Silicon Carbide | Electrically Conductive |
| Gas/Electric Kiln | Ceramic (Quartz) or Graphite | Electrically Insulating |
Achieve a perfect, lossless gold melt every time. Selecting the right crucible is critical for efficiency and safety. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of graphite and ceramic crucibles designed for precise precious metal melting. Our experts can help you choose the perfect crucible for your specific furnace and application. Contact our team today to discuss your needs and ensure a successful melt.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between VAR and ESR? A Guide to Understanding Tail Risk in Financial Modeling
- What is deposition in environmental chemistry? Understanding How Air Pollution Harms Ecosystems
- How can different materials have different heat capacity? Unlocking the Microscopic Secrets of Energy Storage
- Does higher heat capacity mean higher melting point? Unraveling the Critical Difference
- What are sputtering systems used for? A Guide to Advanced Thin-Film Deposition



















