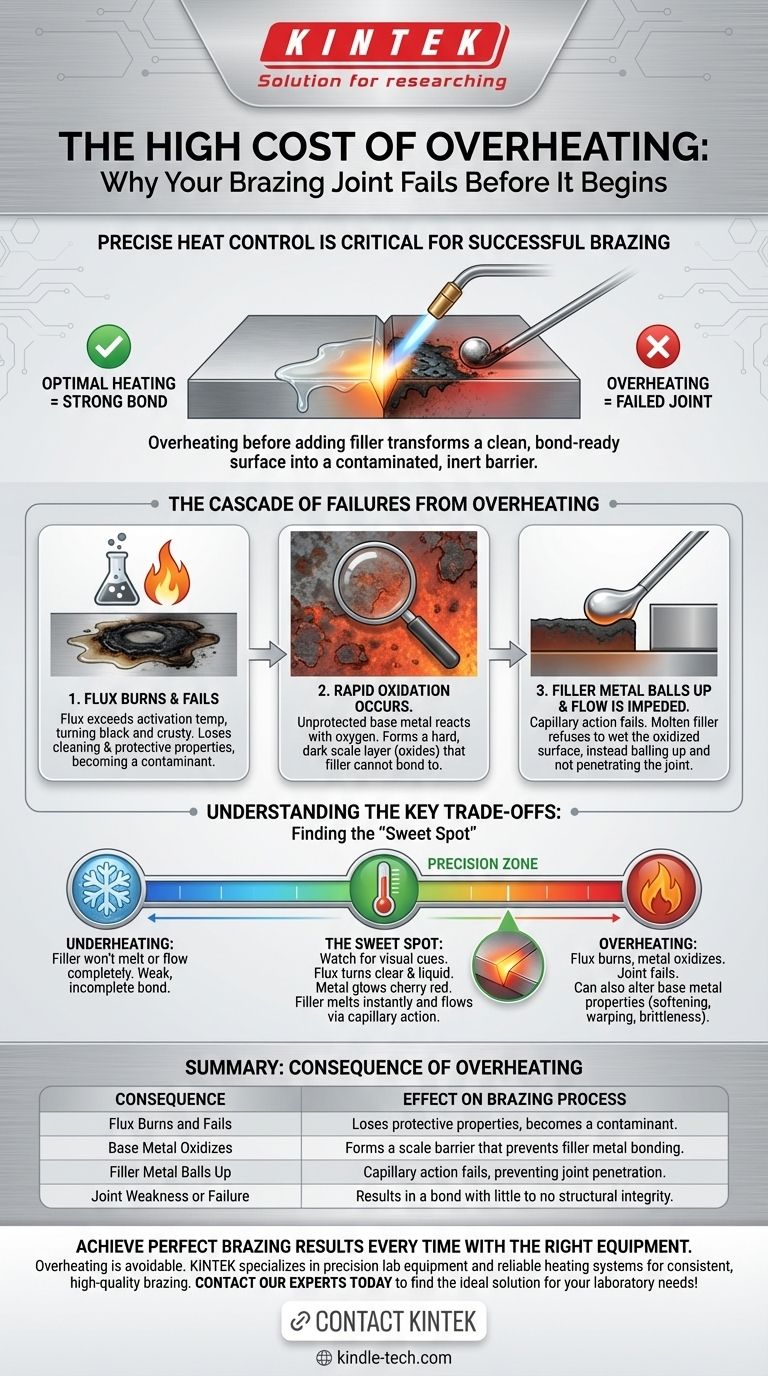
In short, overheating a brazing joint before adding filler metal is one of the most common and critical mistakes in the process. It will cause the protective flux to burn and fail, the base metal to oxidize, and ultimately prevent the filler metal from flowing into the joint, resulting in a weak or completely failed bond.
Overheating transforms the joint from a clean, chemically active surface ready for bonding into a contaminated, inert barrier. The core principle of brazing relies on drawing filler metal into a joint via capillary action, and overheating destroys the very conditions that make this possible.

The Cascade of Failures from Overheating
When you apply too much heat too early, a series of predictable failures occurs. Each problem compounds the next, making a successful braze nearly impossible.
Failure 1: The Flux Burns and Becomes Ineffective
Flux is a chemical compound with a specific activation temperature range. Its job is to clean the metal and shield it from oxygen during heating.
When you overheat the joint, you exceed this range. The flux becomes "burnt"—it will turn black or crusty, losing its protective and cleaning properties entirely. A burnt flux is worse than no flux at all, as it becomes a contaminant itself.
Failure 2: Rapid Oxidation of the Base Metal
Once the flux has failed, the now-unprotected, red-hot base metal is exposed to oxygen in the air. This causes a rapid formation of a hard, dark layer of oxides, often called scale.
Brazing filler metal cannot bond to oxides. The process, known as wetting, requires the filler to flow over and metallurgically bond with a pure, clean metal surface. The oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing this bond from ever forming.
Failure 3: Impeded Filler Metal Flow and Capillary Action
When you finally introduce the filler rod to the overheated and oxidized joint, it will not flow smoothly. Instead, the filler will likely ball up on the surface and refuse to be drawn into the gap.
This is a failure of capillary action, the primary force that pulls molten filler metal into a tight-fitting joint. Capillary action only works on a clean, wetted surface. With burnt flux and a layer of scale in the way, the path is blocked.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
The goal isn't just to avoid overheating; it's to achieve the precise temperature required for the specific filler alloy you are using. Both too little and too much heat will result in a failed joint.
The Danger of Underheating
Conversely, if the base metal is not hot enough, the filler metal will not melt properly or flow completely. It may solidify before penetrating the full depth of the joint, creating a weak bond that looks acceptable on the outside but has no internal strength.
Finding the "Sweet Spot": Reading the Visual Cues
The key is to heat the base metal, not the filler rod. Watch the flux for your signal. As the base metal reaches the correct brazing temperature, the flux will become clear, watery, and fully liquid. This is the moment to gently touch the filler rod to the joint.
If the joint is at the right temperature, the filler will melt instantly and be pulled into the joint by capillary action, displacing the liquid flux. The color of the heated metal (often a dull to bright cherry red, depending on the alloy) is another crucial indicator.
The Impact on Base Metal Properties
For certain materials, especially heat-treated steels, some aluminum alloys, and hardened copper alloys, overheating can have consequences beyond a failed joint. Excessive heat can permanently alter the metal's microstructure, causing it to soften (anneal), warp, or become brittle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your heating strategy should always be deliberate and focused on the specific needs of the joint and materials.
- If your primary focus is a strong, fully-penetrated joint: Heat the broader area of the base metals evenly, and watch the flux. When it turns clear and liquid, you know the metal is ready to accept the filler.
- If your primary focus is preventing leaks in a tube fitting: Concentrate on heating the entire circumference of the heavier/thicker part of the fitting first, allowing heat to conduct to the inner tube. This ensures the entire joint reaches temperature simultaneously for uniform capillary action.
- If your primary focus is preserving the base metal's integrity: Use temperature-indicating crayons and be disciplined about your heat input. Learn the specific visual cues for your metal to avoid exceeding its critical temperature.
Ultimately, successful brazing is a skill of precise observation and heat control, not an application of brute force.
Summary Table:
| Consequence of Overheating | Effect on the Brazing Process |
|---|---|
| Flux Burns and Fails | Loses protective properties, becomes a contaminant |
| Base Metal Oxidizes | Forms a scale barrier that prevents filler metal bonding |
| Filler Metal Balls Up | Capillary action fails, preventing joint penetration |
| Joint Weakness or Failure | Results in a bond with little to no structural integrity |
Achieve perfect brazing results every time with the right equipment. Overheating is a common but avoidable error. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, including reliable heating systems and temperature control tools designed for consistent, high-quality brazing. Let us help you enhance your process efficiency and joint reliability. Contact our experts today to find the ideal solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high vacuum furnace necessary for post-bond heat treatment (PBHT)? Enhance Your Diffusion-Bonded Joint Integrity
- How does a precision furnace affect 316LN phase transformation? Control Sigma Phase & Prevent Micro-Cracks
- What is the function of an annealing furnace in liquid metal photocatalysts? Unlock High-Performance Crystallization
- What is the temperature and holding time for sintering? Master the Variables for Optimal Results
- How can you determine when the temperature of a joint is hot enough to braze? Read the Flux for a Perfect Bond.
- What are the advantages of SPS furnaces for UHTCMCs? Achieve Superior Density and Microstructure
- What is the difference between hardening and vacuum hardening? Choose the Right Process for Superior Surface Finish
- Does hardening steel change dimensions? Mastering the Forces of Thermal and Metallurgical Change



















