At its core, an injection molding machine makes plastic products. These machines are the workhorses of modern manufacturing, responsible for creating an immense variety of the plastic parts we use every single day by injecting molten plastic into a precisely machined mold. You are almost certainly within reach of several items made by this process right now.
The true purpose of an injection molding machine is not just to make plastic parts, but to mass-produce them with exceptional speed, precision, and consistency. It is the definitive technology for creating complex plastic components at a very low cost per unit, once the initial investment is made.
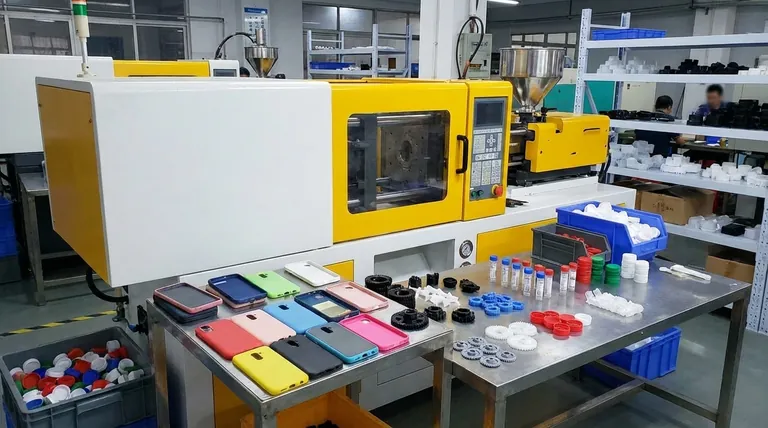

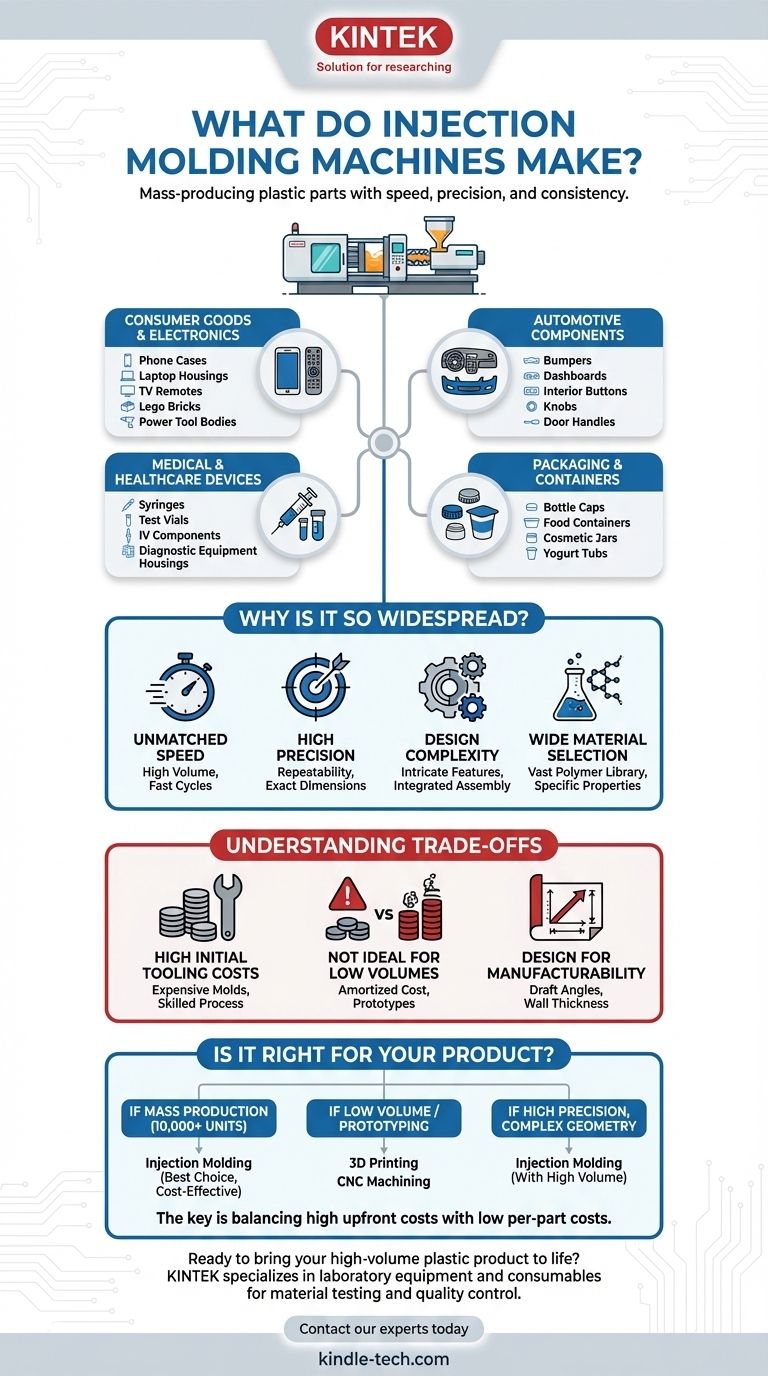
The Ubiquity of Injection Molded Parts
The sheer range of products is staggering. If a plastic item was made in high volumes and has a complex shape, it was almost certainly injection molded. We can group these items into several major categories.
Consumer Goods and Electronics
These are items where aesthetics and precise fit are critical. The cases for our phones, laptops, and TV remotes are prime examples.
Other common items include Lego bricks, computer keyboard keys, power tool housings, and the components inside appliances like coffee makers and vacuums.
Automotive Components
The automotive industry relies heavily on injection molding for its ability to produce durable, lightweight, and complex parts in massive quantities.
This includes large items like bumpers and dashboards, as well as smaller interior parts like buttons, knobs, door handles, and interior trim pieces.
Medical and Healthcare Devices
Precision and sterility are paramount in the medical field. Injection molding provides the required repeatability to produce millions of identical, reliable parts.
Syringes, test vials, IV components, and housings for medical diagnostic equipment are all produced through this sterile and highly controlled process.
Packaging and Containers
When cost-per-item and production speed are the main drivers, injection molding excels. This makes it ideal for single-use or high-volume packaging.
Think of bottle caps, food containers, cosmetic jars, and thin-walled tubs for products like yogurt and butter.
Why Is Injection Molding So Widespread?
The dominance of injection molding comes down to a unique combination of four key advantages that are difficult to match with other manufacturing processes.
Unmatched Speed for High Volume
Once the machine is set up, the cycle time to produce a finished part can be mere seconds. This allows for the production of hundreds, thousands, or even millions of parts from a single mold.
High Precision and Repeatability
The hardened steel mold acts as a perfect negative of the final part. This ensures that every single piece produced—from the first to the millionth—is virtually identical in its dimensions, finish, and features.
Design Complexity and Detail
The process allows for highly complex geometries to be molded directly into the part. This includes intricate features like reinforcing ribs, screw bosses for assembly, and snap-fit clips, eliminating the need for later assembly steps.
Wide Material Selection
A vast library of thermoplastic polymers can be used in injection molding. This allows engineers to select a material with the exact properties needed, whether it's flexibility, high strength, heat resistance, or optical clarity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its advantages, injection molding is not the right solution for every project. The process has fundamental trade-offs that must be considered.
High Initial Tooling Costs
The single biggest barrier to entry is the cost of the mold, also known as the "tool." Machining a high-precision, hardened steel mold is a highly skilled and expensive process that can cost anywhere from a few thousand to hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Not Ideal for Low Volumes
Because of the high upfront tooling cost, injection molding is not economically viable for prototypes or small production runs. The cost of the mold must be amortized over a very large number of parts to achieve a low per-unit price.
Design for Manufacturability
Parts must be carefully designed to be successfully molded and ejected from the tool. This involves considerations like maintaining uniform wall thickness, adding "draft angles" so the part can be removed, and managing features like undercuts that can complicate the mold.
Is Injection Molding Right for Your Product?
Choosing the correct manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's goals, particularly volume, budget, and design complexity.
- If your primary focus is mass production (10,000+ units): Injection molding is almost certainly the most cost-effective and efficient method to produce your parts.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or low-volume runs (1-1,000 units): You should look to alternatives like 3D printing (for early-stage prototypes) or CNC machining and urethane casting (for higher-fidelity, low-volume parts).
- If your primary focus is high precision in a complex geometry: Injection molding is a premier choice, but only if the production volume is high enough to justify the significant initial tooling investment.
Ultimately, understanding the relationship between the high upfront tooling cost and the extremely low per-part cost is the key to leveraging the power of injection molding.
Summary Table:
| Category | Examples of Products Made |
|---|---|
| Consumer Goods & Electronics | Phone cases, laptop housings, TV remotes, Lego bricks, power tool bodies |
| Automotive Components | Bumpers, dashboards, interior buttons, knobs, door handles |
| Medical & Healthcare Devices | Syringes, test vials, IV components, diagnostic equipment housings |
| Packaging & Containers | Bottle caps, food containers, cosmetic jars, yogurt tubs |
Ready to bring your high-volume plastic product to life? The precision and efficiency of injection molding are key to success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the laboratory equipment and consumables necessary for material testing and quality control in polymer processing. Whether you're developing a new material or ensuring your production meets strict standards, our solutions support the entire manufacturing lifecycle.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can equip your lab for innovation and ensure the quality of your next injection molded project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the manufacturing process of rubber molding? Injection, Compression, or Transfer Molding?
- What is the difference between injection molding and pressure molding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Process
- What is molding technique? A Guide to High-Volume, Complex Part Manufacturing
- What can you make with an injection moulding machine? Mass-Produce High-Quality Plastic Parts Efficiently
- What is the injection molding process? A Guide to High-Volume Part Production



















