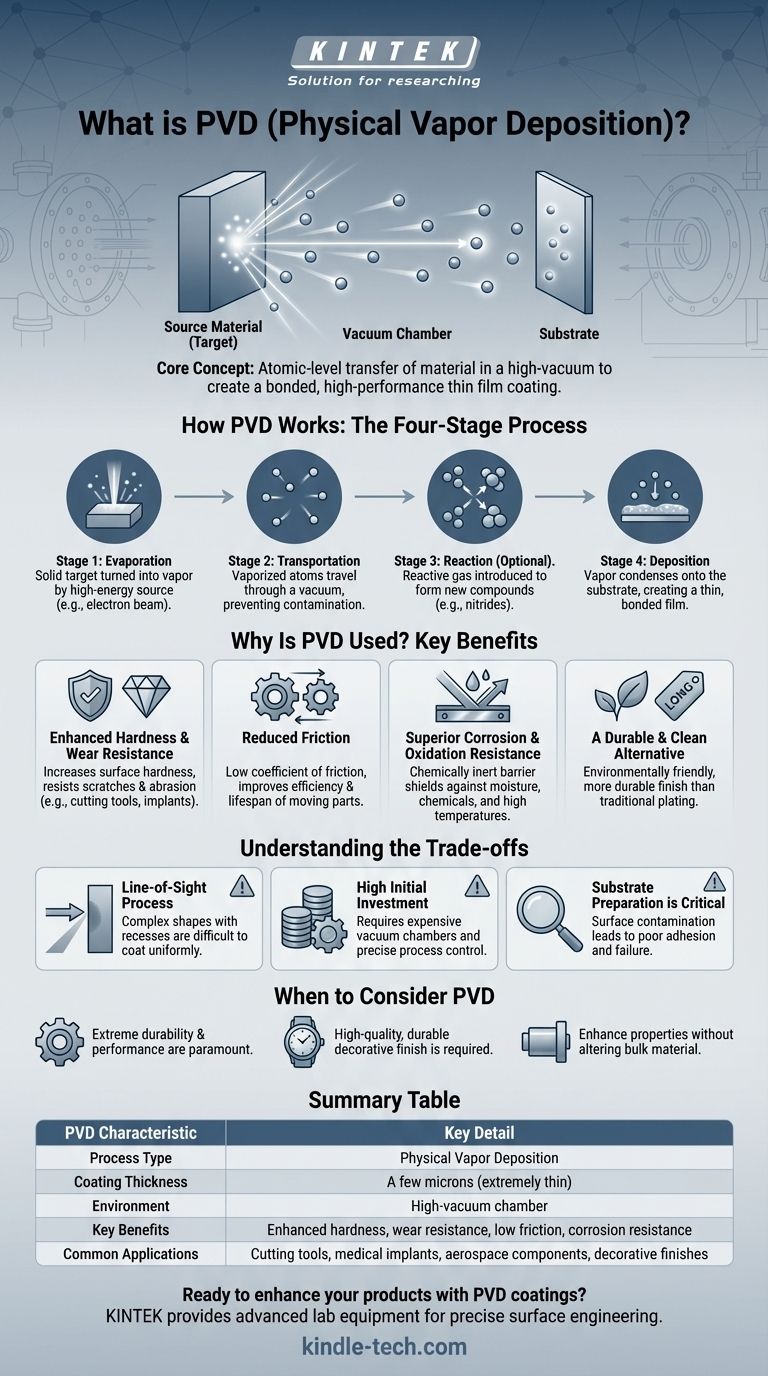
At its core, PVD stands for Physical Vapor Deposition. It is a sophisticated coating process that applies an exceptionally thin, durable film of material onto a surface, or "substrate," within a high-vacuum environment. Unlike painting or traditional electroplating, PVD transfers material on an atomic level to create a bonded, high-performance layer.
While the term sounds complex, PVD is fundamentally about turning a solid material into a vapor, transporting it atom by atom through a vacuum, and depositing it as a high-performance coating onto a target object. It's a method for enhancing a product's properties without changing its underlying structure.

How PVD Works: The Four-Stage Process
The PVD process is conducted inside a specialized vacuum chamber and can be broken down into four distinct stages. This atomic-level transfer is what gives the resulting coating its superior characteristics.
Stage 1: Evaporation
The process begins by turning a solid source material (the "target") into a vapor. This is accomplished by bombarding the target with a high-energy source, such as an electron beam or plasma, which dislodges atoms from the material's surface.
Stage 2: Transportation
Once vaporized, these atoms and molecules travel across the vacuum chamber. The vacuum is critical because it prevents these particles from colliding with air or other contaminants, ensuring a pure and direct path to the object being coated.
Stage 3: Reaction (Optional)
In some PVD processes, a specific gas (like nitrogen, oxygen, or an acetylene-based gas) is introduced into the chamber. The vaporized metal atoms react with this gas mid-flight to form new compounds like nitrides or oxides, which will have different properties than the original metal.
Stage 4: Deposition
Finally, the vaporized material—whether in its original form or as a new compound—condenses onto the target object (the "substrate"). This creates an extremely thin, hard, and strongly bonded film on the substrate's surface, often just a few microns thick.
Why Is PVD Used? Key Benefits
PVD is not just a coating; it's a material enhancement. It is chosen over other methods when performance and durability are paramount.
Enhanced Hardness and Wear Resistance
PVD coatings significantly increase the surface hardness of a component, making it far more resistant to scratches, abrasion, and general wear. This is critical for items like industrial cutting tools and medical implants.
Reduced Friction
The smooth, dense nature of PVD films creates a very low coefficient of friction. This property is vital for improving the efficiency and lifespan of moving parts in engines or other mechanical assemblies.
Superior Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
The deposited coating acts as a chemically inert barrier. It shields the underlying material from moisture, chemicals, salt, and high temperatures that would otherwise cause rust, tarnish, or degradation.
A Durable and Clean Alternative
PVD is an environmentally friendly process compared to traditional coating methods like electroplating, which often involve hazardous chemicals. It produces a finish that is more durable and resistant to chipping or fading.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD is a highly technical process with specific limitations that make it unsuitable for some applications.
It Is a Line-of-Sight Process
The vaporized material travels in a straight line. This means that complex shapes with deep recesses or internal surfaces can be very difficult to coat uniformly without sophisticated part rotation and fixturing.
High Initial Investment
PVD is not a simple procedure. It requires specialized, expensive vacuum chambers and precise control over the process, making the initial equipment and setup costs significant.
Substrate Preparation is Critical
The final quality of the PVD coating is highly dependent on the cleanliness and material of the substrate. Any surface contamination can lead to poor adhesion, causing the coating to peel or fail prematurely.
When to Consider PVD
PVD is not a one-size-fits-all solution, but it excels in specific scenarios where its benefits justify the complexity.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and performance: PVD is the superior choice for high-wear applications like cutting tools, engine components, or aerospace parts where failure is not an option.
- If your primary focus is a high-quality decorative finish: PVD offers a vast range of vibrant, tarnish-resistant colors that are far more durable than paint or traditional plating, making it ideal for watches, jewelry, and premium hardware.
- If you need to enhance an object's properties without altering its bulk material: PVD is ideal for applying a functional surface (like low friction or chemical resistance) onto a finished component.
Understanding PVD moves it from a complex term to a powerful tool for engineering a material's surface to meet a specific, demanding purpose.
Summary Table:
| PVD Characteristic | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical Vapor Deposition |
| Coating Thickness | A few microns (extremely thin) |
| Environment | High-vacuum chamber |
| Key Benefits | Enhanced hardness, wear resistance, low friction, corrosion resistance |
| Common Applications | Cutting tools, medical implants, aerospace components, decorative finishes |
Ready to enhance your products with PVD coatings? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise surface engineering. Our solutions help you achieve superior durability and performance for your laboratory applications. Contact us today to discuss how our PVD expertise can benefit your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















