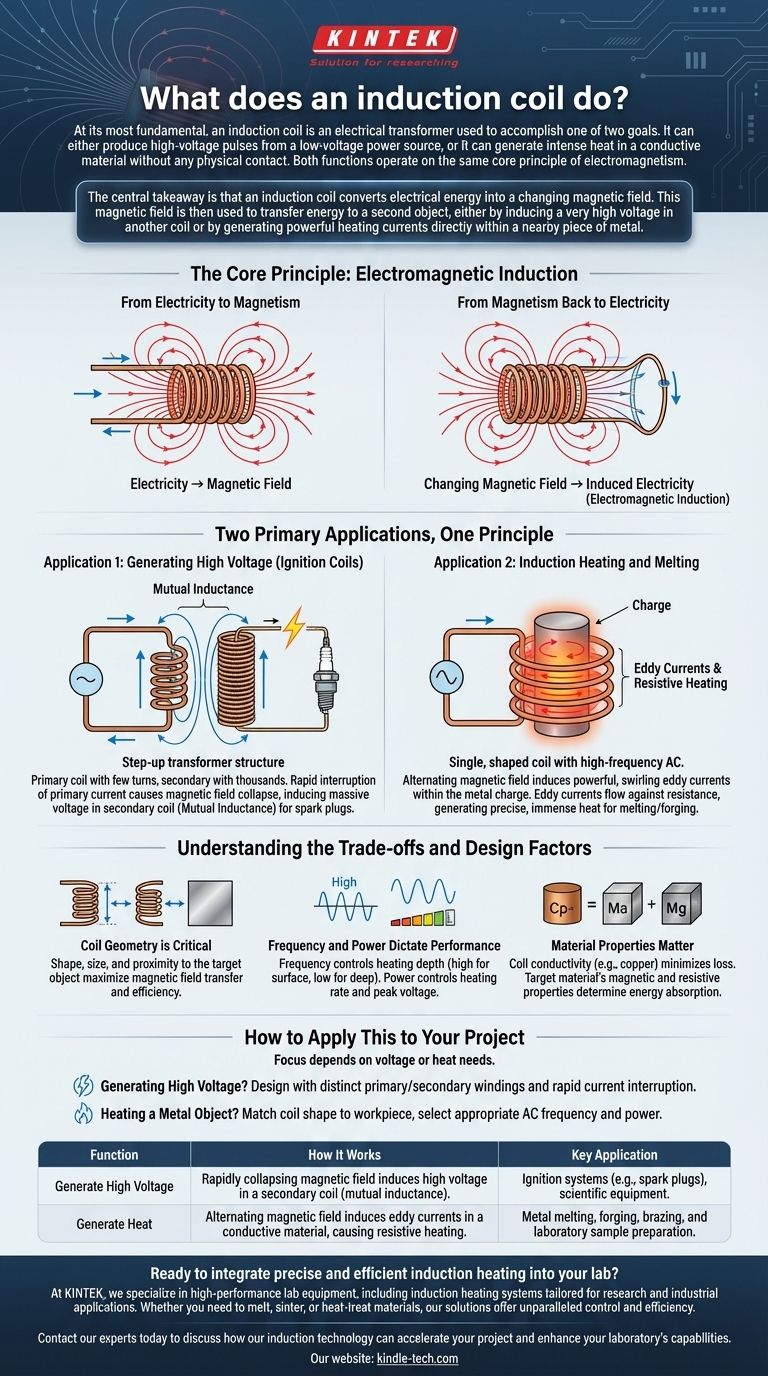
At its most fundamental, an induction coil is an electrical transformer used to accomplish one of two goals. It can either produce high-voltage pulses from a low-voltage power source, or it can generate intense heat in a conductive material without any physical contact. Both functions operate on the same core principle of electromagnetism.
The central takeaway is that an induction coil converts electrical energy into a changing magnetic field. This magnetic field is then used to transfer energy to a second object, either by inducing a very high voltage in another coil or by generating powerful heating currents directly within a nearby piece of metal.

The Core Principle: Electromagnetic Induction
The function of every induction coil is rooted in a fundamental law of physics: the relationship between electricity and magnetism.
From Electricity to Magnetism
When an electrical current flows through a conductor, such as a copper wire, it generates a magnetic field around that wire. Winding the wire into a coil concentrates these magnetic field lines, creating a much stronger and more usable magnetic effect.
From Magnetism Back to Electricity
The critical step is what happens next. When this magnetic field changes or oscillates, it can induce an electrical voltage or current in any other conductor placed within it. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction. This is the key to the coil's ability to transfer energy without touching.
Two Primary Applications, One Principle
While the principle is the same, the design of an induction coil is specialized for two very different outcomes: generating high voltage or generating heat.
Application 1: Generating High Voltage (Ignition Coils)
This type of coil is structured like a step-up transformer, with two distinct windings: a primary coil with few turns and a secondary coil with many thousands of turns.
It is used in applications like a gasoline engine's ignition system. A low-voltage current is passed through the primary coil, creating a magnetic field. When this current is suddenly interrupted, the magnetic field rapidly collapses.
This rapid change induces a massive voltage—often tens of thousands of volts—in the tightly wound secondary coil. This effect, called mutual inductance, creates a voltage high enough to jump the gap on a spark plug and ignite fuel.
Application 2: Induction Heating and Melting
For heating applications, the induction coil is typically a single, specially shaped winding connected to a high-frequency alternating current (AC) power supply. The metal to be heated (the "charge") is placed inside or near the coil.
The AC current creates a rapidly alternating magnetic field. This field, in turn, induces powerful, swirling electrical currents directly within the metal charge. These are known as eddy currents.
As these eddy currents flow against the metal's natural electrical resistance, they generate immense and precise heat, allowing the metal to be heated, forged, or even melted in a crucible.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Factors
The effectiveness of an induction coil is not automatic; it depends entirely on its design and how it is used. Understanding these factors is crucial for any application.
Coil Geometry is Critical
The shape, size, and proximity of the coil to the target object are paramount. For induction heating, the coil must be shaped to "couple" as closely as possible with the workpiece to ensure the maximum magnetic field is transferred, maximizing efficiency.
Frequency and Power Dictate Performance
The frequency of the alternating current is a key variable. Higher frequencies tend to heat the surface of a material, while lower frequencies can penetrate deeper. The amount of power (current) flowing through the coil directly controls the rate of heating or the peak voltage that can be achieved.
Material Properties Matter
The entire system is a two-way street. The electrical conductivity of the coil itself (usually copper, to minimize its own heat loss) is important. Likewise, the magnetic and resistive properties of the target material will determine how effectively it absorbs energy from the magnetic field.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your focus should depend entirely on whether you need voltage or heat.
- If your primary focus is generating high voltage: Concentrate on a design with distinct primary and secondary windings and a method for rapidly interrupting the primary current.
- If your primary focus is heating a metal object: Concentrate on matching the coil's shape to your workpiece and selecting an AC power supply with the appropriate frequency and power for your task.
Ultimately, understanding how an induction coil manipulates magnetic fields empowers you to select or design the right tool for your specific electrical task.
Summary Table:
| Function | How It Works | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Generate High Voltage | Rapidly collapsing magnetic field induces high voltage in a secondary coil (mutual inductance). | Ignition systems (e.g., spark plugs), scientific equipment. |
| Generate Heat | Alternating magnetic field induces eddy currents in a conductive material, causing resistive heating. | Metal melting, forging, brazing, and laboratory sample preparation. |
Ready to integrate precise and efficient induction heating into your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including induction heating systems tailored for research and industrial applications. Whether you need to melt, sinter, or heat-treat materials, our solutions offer unparalleled control and efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our induction technology can accelerate your project and enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- What is the lifespan of a mold? It's Immortal Unless You Control Moisture
- What are the critical performance requirements for hot pressing molds? Ensure Precision in Magnesium Alloy Processing
- Why are a laboratory hydraulic press and precision molds required for pressing MAX phase green bodies? - Expert Guide
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer



















