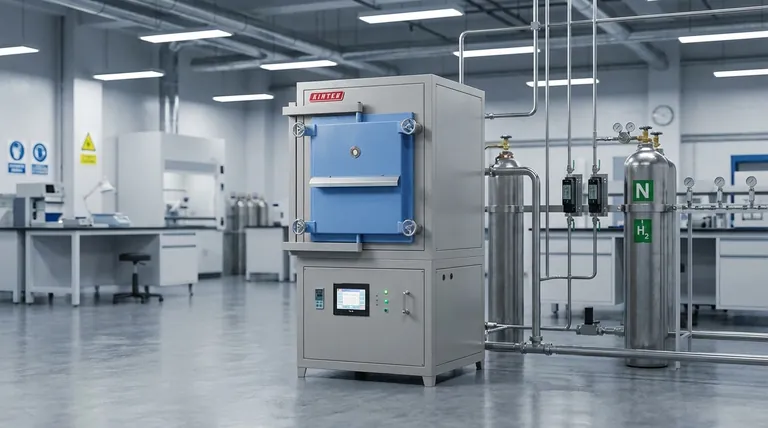
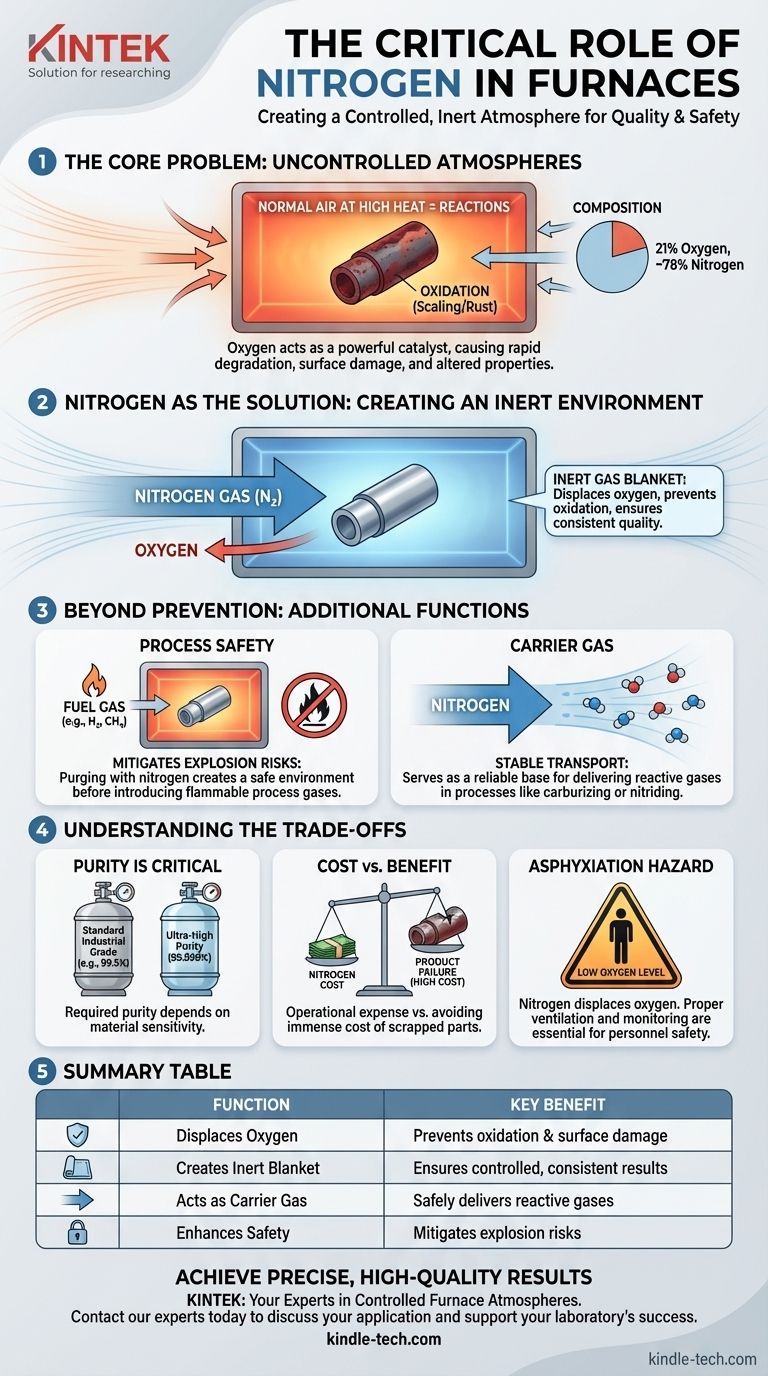
In a furnace, nitrogen's primary role is to create a controlled, inert atmosphere. It is pumped into the heating chamber to displace reactive gases, most importantly oxygen. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation (scaling or rust) on the surface of the material being processed, ensuring the final product maintains its intended quality and integrity.
The fundamental reason to use nitrogen in a furnace is to gain control over the environment. By replacing the reactive air with an inert gas, you protect the workpiece from damage, prevent fire or explosion hazards, and ensure the final product meets precise specifications.

The Core Problem: Uncontrolled Atmospheres
Why Normal Air is a Problem
At room temperature, the oxygen in the air is only mildly reactive. However, a furnace operates at extremely high temperatures, which act as a powerful catalyst for chemical reactions.
The air we breathe is approximately 21% oxygen. When a metal part is heated in the presence of this oxygen, the reaction is aggressive and rapid.
The Consequences of Oxidation
This high-temperature reaction with oxygen is called oxidation. On steel, it forms a dark, flaky layer known as mill scale. On other metals, it can cause severe discoloration and surface damage.
These effects are almost always undesirable. Oxidation can alter the dimensions of a precision part, ruin its surface finish, and in some cases, negatively impact the material's structural properties.
Nitrogen as the Solution: Creating an Inert Environment
Displacing Oxygen to Prevent Reactions
Nitrogen gas (N₂) is valued for being largely inert, meaning it does not readily react with other elements, even at high temperatures.
By continuously feeding nitrogen into a sealed furnace chamber, you can purge, or push out, the ambient air. This process, known as creating a nitrogen blanket or purge, effectively removes the oxygen from the equation. Without oxygen, the destructive oxidation reaction cannot occur.
Ensuring Process Safety
Many heat-treating processes introduce other flammable gases (like hydrogen or methane) to achieve specific results. An uncontrolled mixture of fuel gas and oxygen at high temperatures is the definition of an explosion hazard.
Nitrogen mitigates this risk. By first purging the chamber of oxygen, you create a safe environment into which flammable process gases can be introduced without the risk of combustion. Flowmeters and interlocks, as mentioned in control systems, are critical for managing this safety procedure.
Serving as a Carrier Gas
In more advanced processes, nitrogen is not just a passive blanket. It can also be used as a stable carrier gas.
For processes like carburizing (adding carbon) or nitriding (adding nitrogen in a reactive form), a precise atmosphere is required. Nitrogen can form the bulk of the atmosphere, carrying a small, controlled percentage of the "active" gas to the workpiece in a predictable way.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Purity is Critical
Not all nitrogen is the same. The required purity level depends entirely on the sensitivity of the material being heated.
For general-purpose annealing of a common steel, a standard industrial-grade nitrogen might suffice. For processing highly reactive metals like titanium or certain medical-grade stainless steels, an ultra-high purity (99.999%) nitrogen may be required, as even a few parts per million of oxygen can cause damage.
Cost vs. Benefit
Using nitrogen is an operational expense. The gas must be supplied from liquid tanks, high-pressure cylinders, or an on-site nitrogen generator.
This cost must be weighed against the immense cost of product failure. For high-value components, the cost of a controlled nitrogen atmosphere is negligible compared to the cost of scrapping a batch of parts due to oxidation.
The Asphyxiation Hazard
Safety for personnel is paramount. Nitrogen is not toxic, but it displaces oxygen. A leak from a furnace or supply line into an enclosed room can lower the oxygen level to a point that is immediately dangerous to human life, causing asphyxiation without warning. Proper ventilation and oxygen monitoring are non-negotiable safety requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to using nitrogen will depend entirely on your specific process and material.
- If your primary focus is simple annealing or stress-relieving common steels: A basic nitrogen purge to prevent heavy scaling and ensure a clean surface is often sufficient.
- If your primary focus is processing highly sensitive or reactive metals: You will require high-purity nitrogen and precise flow control to prevent even minor surface contamination.
- If your primary focus is a reactive process like carburizing or nitriding: Nitrogen serves as the safe, inert base gas that carries smaller, controlled amounts of active gases to the workpiece.
Ultimately, using nitrogen is about taking deliberate control over the furnace environment to achieve a predictable, high-quality result.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Displaces Oxygen | Prevents oxidation, scaling, and surface damage on materials. |
| Creates Inert Blanket | Ensures a controlled, predictable environment for consistent results. |
| Acts as Carrier Gas | Safely delivers reactive gases for processes like carburizing. |
| Enhances Safety | Mitigates explosion risks by removing oxygen before introducing flammable gases. |
Achieve precise, high-quality results with every heat treatment.
Whether you are annealing common steels or processing highly sensitive metals, controlling your furnace atmosphere is critical. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the solutions and expertise to help you implement safe, effective nitrogen atmospheres that protect your materials and ensure process reliability.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific furnace application and discover how we can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is nitrogen atmosphere for annealing? Achieve Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment
- What is the role of nitrogen in annealing process? Creating a Controlled, Protective Atmosphere
- How does a high-temperature furnace with atmosphere control optimize spinel coatings? Achieve Redox Sintering Precision
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality



















