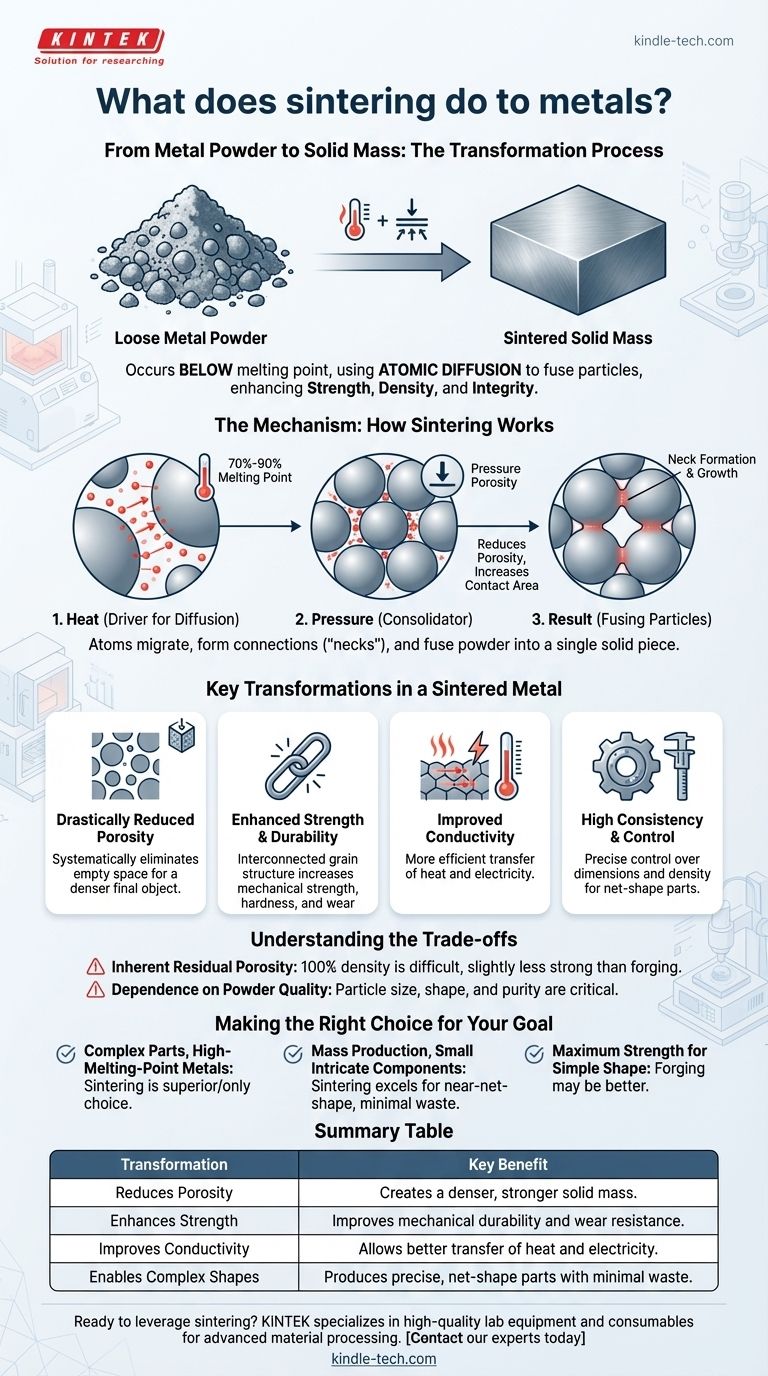
At its core, sintering transforms loose metal powder into a solid, coherent mass by applying heat and pressure. This process occurs below the metal's melting point, using atomic diffusion to fuse particles together, which fundamentally enhances the material's strength, density, and overall structural integrity.
Sintering is not about melting metal; it's about using controlled energy to persuade individual metal particles to bond together, reducing internal voids and creating a strong, dense component from a powder starting point.
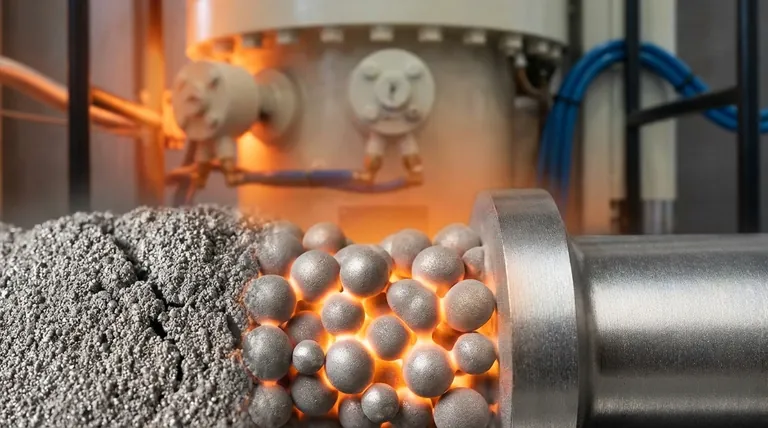

The Mechanism: How Sintering Works
Sintering is a thermal treatment that relies on a phenomenon called atomic diffusion. By heating the material to a high temperature—typically 70% to 90% of its melting point—the atoms gain enough energy to move.
Heat as the Driver for Diffusion
The applied heat energizes the atoms at the contact points between individual powder particles. These energized atoms begin to migrate across the boundaries, effectively building bridges between the particles.
Pressure as the Consolidator
While not always required, pressure is often used to press the metal powder particles into close contact. This initial compaction reduces the space, or porosity, between them and creates more surface area for atomic bonding to occur.
The Result: Fusing Particles into a Solid
As atoms diffuse, they form connections called "necks" at the particle contact points. Over time, these necks grow wider, pulling the particles closer, eliminating the pores between them, and ultimately fusing the powder into a single, solid piece.
Key Transformations in a Sintered Metal
The process of sintering imparts several critical changes to the material, transforming it from a loose powder into a functional engineering component.
Drastically Reduced Porosity
The most significant change is the reduction of empty space. The initial metal powder has a high degree of porosity, which is systematically eliminated as the particles fuse, leading to a much denser final object.
Enhanced Strength and Durability
By creating a solid, interconnected metallic grain structure, sintering significantly increases the component's mechanical strength, hardness, and resistance to wear. A denser part is inherently a stronger part.
Improved Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Fewer voids and more intimate contact between the metal grains allow for more efficient transfer of heat and electricity. Sintering improves these properties compared to the initial powder compact.
High Consistency and Control
Sintering allows for precise control over the final product's dimensions and density. This makes it an excellent method for mass-producing complex, net-shape or near-net-shape parts that require minimal finishing or machining.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is not the ideal solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Inherent Residual Porosity
Achieving 100% theoretical density is extremely difficult with sintering alone. Most sintered parts retain a small amount of residual porosity, which can make them slightly less strong than parts made from a fully molten process like forging.
Dependence on Powder Quality
The final properties of a sintered part are directly tied to the quality of the initial metal powder. Factors like particle size, shape, and purity are critical and must be tightly controlled for consistent results.
Suitability for High-Melting-Point Metals
Sintering is uniquely valuable for materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten or molybdenum. Casting these materials is often impractical or impossible, making sintering the primary manufacturing method.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for material, complexity, and performance.
- If your primary focus is creating complex parts from high-melting-point metals: Sintering is the superior, and sometimes only, viable choice.
- If your primary focus is mass production of small, intricate components with high precision: Sintering excels at producing near-net-shape parts efficiently and with minimal waste.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute maximum strength and toughness for a simple shape: A process like forging, which works the metal's grain structure, may be a better alternative.
Ultimately, sintering provides an indispensable tool for turning metal powders into strong, reliable components that are often difficult or too costly to produce any other way.
Summary Table:
| Transformation | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Reduces Porosity | Creates a denser, stronger solid mass. |
| Enhances Strength | Improves mechanical durability and wear resistance. |
| Improves Conductivity | Allows better transfer of heat and electricity. |
| Enables Complex Shapes | Produces precise, net-shape parts with minimal waste. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your laboratory or production needs? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for advanced material processing. Whether you're developing new metal components or optimizing your sintering process, our expertise and products are designed to support your success. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum environment system contribute to the hot pressing sintering of B4C-CeB6? Unlock Peak Ceramic Density
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve high-density NTC ceramics with superior stability.
- How does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace facilitate TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Achieve 100% Dense Titanium Composites
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context



















