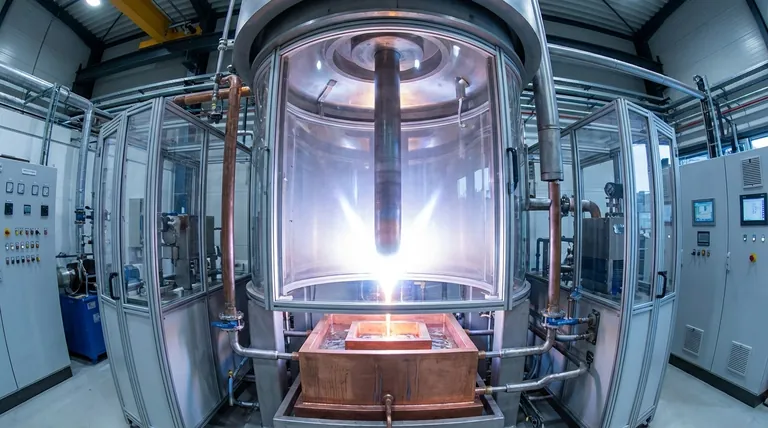
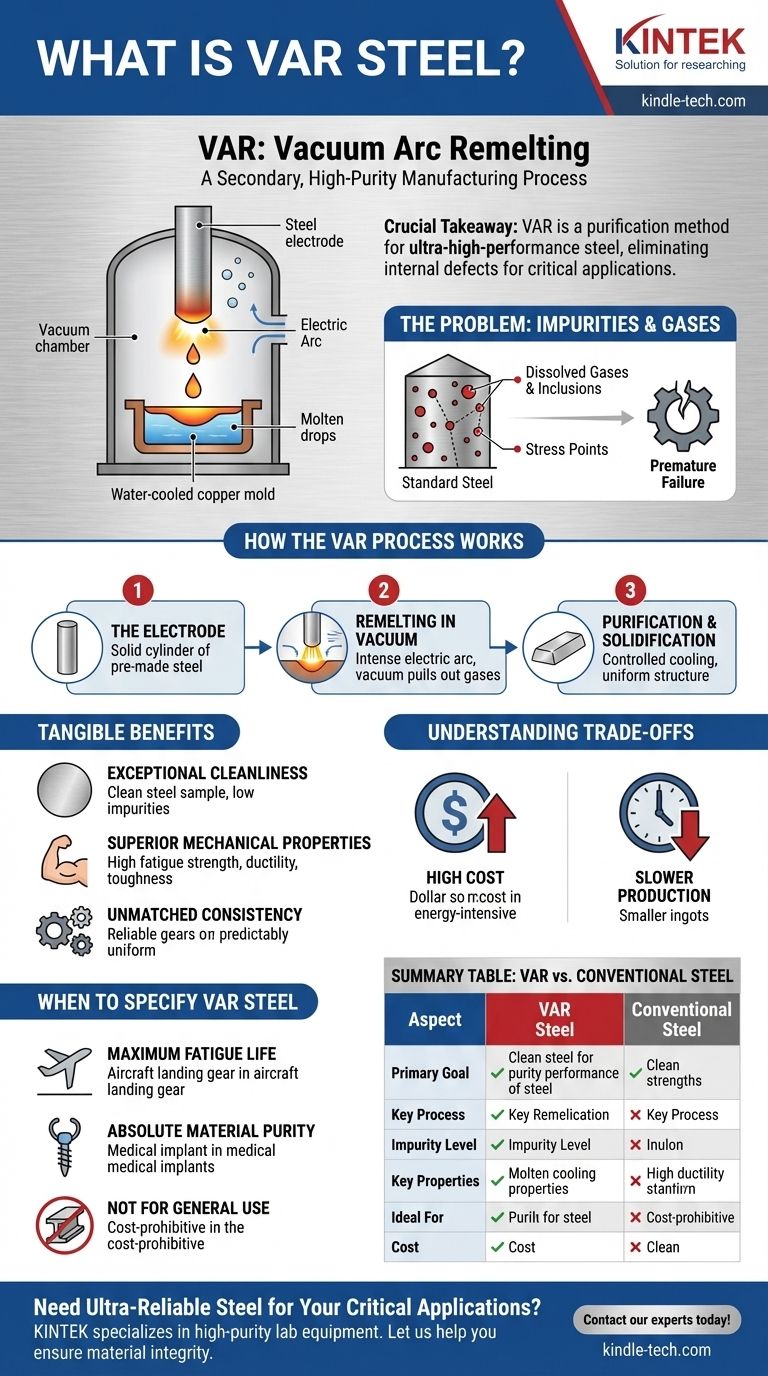
In short, VAR stands for Vacuum Arc Remelting. It is not a type of steel itself, but rather a secondary, high-purity manufacturing process. This process takes a standard, already-formed steel alloy and remelts it in a vacuum to remove dissolved gases and microscopic impurities, resulting in an exceptionally clean, strong, and reliable final product.
The crucial takeaway is that VAR is a purification method used to create ultra-high-performance steel for critical applications. Its purpose is to eliminate the internal defects that cause material failure under extreme stress, making it essential for industries like aerospace and medicine.

What Problem Does VAR Solve?
To understand the value of VAR, you must first understand the limitations of conventional steelmaking. The core problem is the presence of undesirable elements and structural inconsistencies.
The Enemy: Impurities and Gases
Standard steelmaking processes, while efficient for large volumes, inevitably leave behind impurities. These include dissolved gases like oxygen and nitrogen, as well as non-metallic "inclusions" such as oxides and sulfides.
The Consequence of Flaws
Even microscopic impurities act as stress points within the steel's crystal structure. When the material is subjected to repeated stress cycles (fatigue), these points are where cracks initiate and grow, leading to premature failure.
How the VAR Process Works
The VAR process is a methodical, controlled remelting designed specifically to remove the flaws inherent in primary steel production. It's a refinement process, not a creation process.
Step 1: The Electrode
The process begins with a solid cylinder of a pre-made, high-quality steel alloy, which is referred to as the electrode. This electrode is placed vertically inside a large, sealed vacuum chamber.
Step 2: Remelting in a Vacuum
An intense electric arc is struck between the bottom of the electrode and a water-cooled copper mold (or crucible) below it. The arc's heat progressively melts the tip of the electrode, causing molten metal to fall drop by drop into the mold.
Step 3: Purification and Solidification
The vacuum environment is the key to purification. As the metal melts, the vacuum pulls out dissolved gases like hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. As the molten droplets fall, heavier non-metallic inclusions are also separated, resulting in a much cleaner liquid metal.
This purified metal collects and solidifies slowly and directionally from the bottom up in the water-cooled mold. This controlled solidification creates a new ingot with a highly uniform internal structure, free from the defects of the original electrode.
The Tangible Benefits of VAR Steel
The result of this meticulous process is a material with demonstrably superior characteristics compared to its conventional, air-melted counterparts.
Exceptional Cleanliness
VAR steel has significantly lower levels of dissolved gases and non-metallic inclusions. This material "cleanliness" is its most defining and important attribute.
Superior Mechanical Properties
Because it lacks the internal stress points found in conventional steel, VAR material exhibits dramatic improvements in fatigue strength, ductility, and fracture toughness. This means it can withstand more stress cycles and absorb more energy before fracturing.
Unmatched Consistency
The VAR process produces steel with highly predictable and repeatable properties from one batch to the next. This reliability is non-negotiable for applications where performance tolerances are razor-thin.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While VAR produces a superior material, its benefits come at a significant cost, which limits its application.
The High Cost
VAR is an additional, energy-intensive manufacturing step performed on an already-produced steel ingot. This secondary processing makes VAR steel substantially more expensive than standard alloys.
Slower Production and Scale
The process is slower and yields smaller ingots compared to primary steelmaking methods. It is not suitable for the mass production of structural steel but is reserved for smaller, higher-value components.
When to Specify VAR Steel
The choice to use VAR steel is driven entirely by the consequence of failure for the intended application.
- If your primary focus is maximum fatigue life and reliability: VAR is the standard for components under extreme cyclic loads, such as aircraft landing gear, engine shafts, and critical bearings.
- If your primary focus is absolute material purity: VAR is essential for applications like medical implants, where internal imperfections are unacceptable for both performance and biocompatibility.
- If your primary focus is general structural or industrial use: VAR is unnecessary and cost-prohibitive; conventional high-quality alloys are the more practical and economical choice.
Ultimately, specifying VAR steel is a decision to invest in the highest level of material integrity for applications where failure is simply not an option.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | VAR Steel | Conventional Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maximize purity & reliability | Cost-effective production |
| Key Process | Secondary remelting in a vacuum | Primary air melting |
| Impurity Level | Extremely low (gases & inclusions removed) | Higher (inherent to process) |
| Key Properties | Superior fatigue strength, ductility, toughness | Good general strength |
| Ideal For | Aerospace, medical implants, critical bearings | General structural, industrial parts |
| Cost | High | Lower |
Need Ultra-Reliable Steel for Your Critical Applications?
Specifying the right material is crucial for the safety and performance of your most demanding components. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-purity lab equipment and consumables needed to develop and test advanced materials like VAR steel.
Let us help you ensure material integrity. Whether you're in aerospace, medical technology, or advanced manufacturing, our expertise supports your quest for reliability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can meet your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is VAR in metallurgy? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Performance
- What is the benefit of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Structural Integrity
- What is the vacuum arc remelting process? Producing Ultra-Pure, High-Performance Metal Alloys
- How does vacuum arc remelting work? Achieve Ultra-Clean, High-Performance Metal Alloys
- What is the overview of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Ultra-Clean, High-Performance Alloys



















