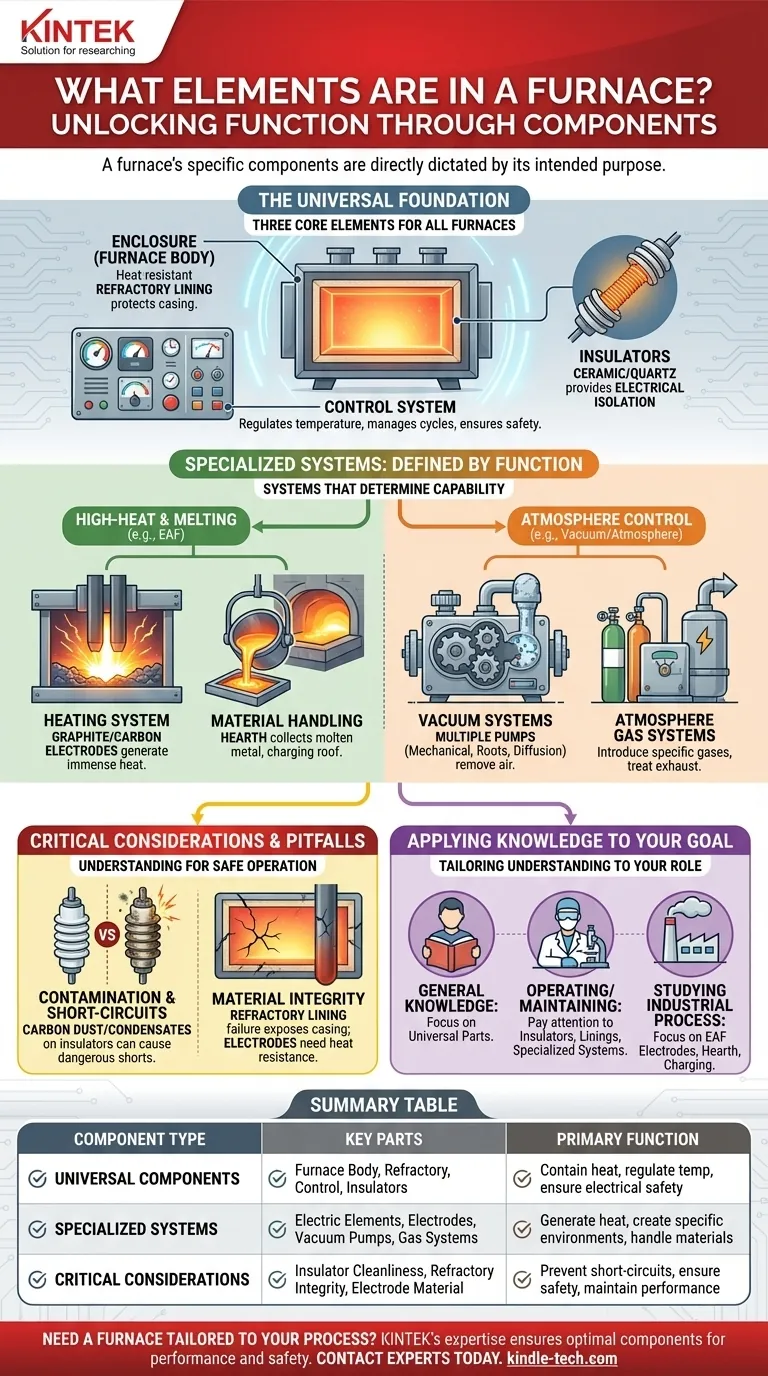
At its core, a furnace is comprised of three main elements: an enclosure to contain the heat, a system to generate that heat, and a control system to manage the process. However, the specific components vary dramatically based on the furnace's intended purpose, such as melting steel, creating a vacuum, or analyzing materials.
The essential takeaway is that a furnace is not a single entity but a category of tools. Its specific "elements" are directly dictated by its function, whether it's an industrial Electric Arc Furnace using massive electrodes or a laboratory vacuum furnace using a complex pump system.

The Universal Components of Most Furnaces
While specialized furnaces have unique parts, almost all are built around a common structural and operational foundation.
The Enclosure (Furnace Body)
The most fundamental component is the furnace body or casing. This is the physical structure that contains the intense heat.
To withstand extreme temperatures, this outer casing is typically lined with a refractory material, which is a heat-resistant substance that protects the metal structure.
The Control System
The control system is the brain of the furnace. It regulates temperature, manages cycles, and controls any specialized systems like gas or vacuum pumps. This ensures consistent and safe operation.
Insulators
Insulators, typically made of ceramic or quartz, are used to hold heating elements in place. Their primary job is to provide excellent electrical isolation, preventing the high-power heating system from short-circuiting to the furnace body.
Specialized Components Defined by Function
The real differentiation between furnaces comes from the specialized components required for specific tasks. These systems define what the furnace can actually do.
The Heating System
This is the heart of the furnace. In many high-temperature and atmosphere furnaces, electric heating elements are distributed evenly around the heating chamber to ensure uniform temperature.
In an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF), the heat is generated by massive graphite or carbon electrodes. A high-voltage current arcs between these electrodes and the metal charge, generating immense heat to melt it.
Atmosphere Control Systems
A vacuum furnace requires a complex system to remove air from the chamber. This is composed of multiple pumps, such as a mechanical pump, a roots pump, and a diffusion pump, working together to achieve a high vacuum level.
An atmosphere furnace, by contrast, will have systems for introducing specific gases and treating the exhaust gas.
Material Handling and Processing
An Electric Arc Furnace includes a hearth to collect molten metal, a removable roof for loading the charge, and a drain hole with a gutter to pour the final product.
An ashing furnace, used for analysis, often includes a weighing scale to measure materials before, during, and after the combustion process.
Common Pitfalls and Key Considerations
Understanding the function of these components is critical for safe and effective operation.
Contamination and Short-Circuits
The insulators holding heating elements are a common point of failure. Over time, carbon dust or metallic condensates can build up on them.
If not kept clean, this buildup can become conductive, bypassing the insulator and causing a dangerous short-circuit that can damage the equipment.
Material Integrity
The choice of materials is not arbitrary. Electrodes in an EAF are made of graphite or carbon because they can withstand extreme temperatures and conduct the massive electrical currents required.
Similarly, the refractory lining must be inspected and maintained, as its failure would expose the furnace's metal casing to destructive temperatures.
How This Applies to Your Goal
Your reason for asking about furnace elements will determine which components are most important to understand.
- If your primary focus is general knowledge: Concentrate on the three universal parts: the enclosure, the heating system, and the control system.
- If you are operating or maintaining a furnace: Pay close attention to the insulators, refractory linings, and any specialized systems like pumps or electrodes, as these are critical to safety and performance.
- If you are studying a specific industrial process like steelmaking: Focus on the specialized components of an Electric Arc Furnace, such as the graphite electrodes, hearth, and charging mechanism.
Understanding how a furnace's components are chosen for its specific task is the key to mastering its operation and purpose.
Summary Table:
| Component Type | Key Parts | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Universal Components | Furnace Body, Refractory Lining, Control System, Insulators | Contain heat, regulate temperature, ensure electrical safety |
| Specialized Systems | Electric Heating Elements, Graphite Electrodes (EAF), Vacuum Pumps, Atmosphere Gas Systems | Generate heat, create specific environments (vacuum/atmosphere), handle materials |
| Critical Considerations | Insulator Cleanliness, Refractory Integrity, Electrode Material | Prevent short-circuits, ensure safety, maintain performance |
Need a furnace tailored to your specific process? Whether you require precise temperature control for materials analysis, a robust system for melting, or a specialized vacuum or atmosphere environment, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment ensures you get the right components for optimal performance and safety. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and find the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why graphite is used in furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment & Energy Efficiency
- Does graphite have a melting point? Unlocking the Extreme Heat Resistance of Graphite
- What are the advantages of graphite furnace? Achieve High-Temperature Precision and Purity
- What temperature can graphite withstand? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential
- What are the applications of graphite material? Leveraging Extreme Heat and Precision for Industrial Processes



















