At its core, sintering is a thermal process that transforms a compacted powder into a dense, solid object without melting it. The process begins by heating the compacted "green body" to burn off any residual binders, followed by raising the temperature to a point where atoms begin to diffuse between particles. This atomic movement forms bonds, pulls the particles together, eliminates the voids between them, and causes the entire part to shrink and densify into a solid mass.
Sintering should not be viewed as simple melting and fusing. It is a complex, multi-stage process of atomic transport driven by surface energy, which systematically eliminates porosity to convert a fragile powder compact into a robust, engineered component.

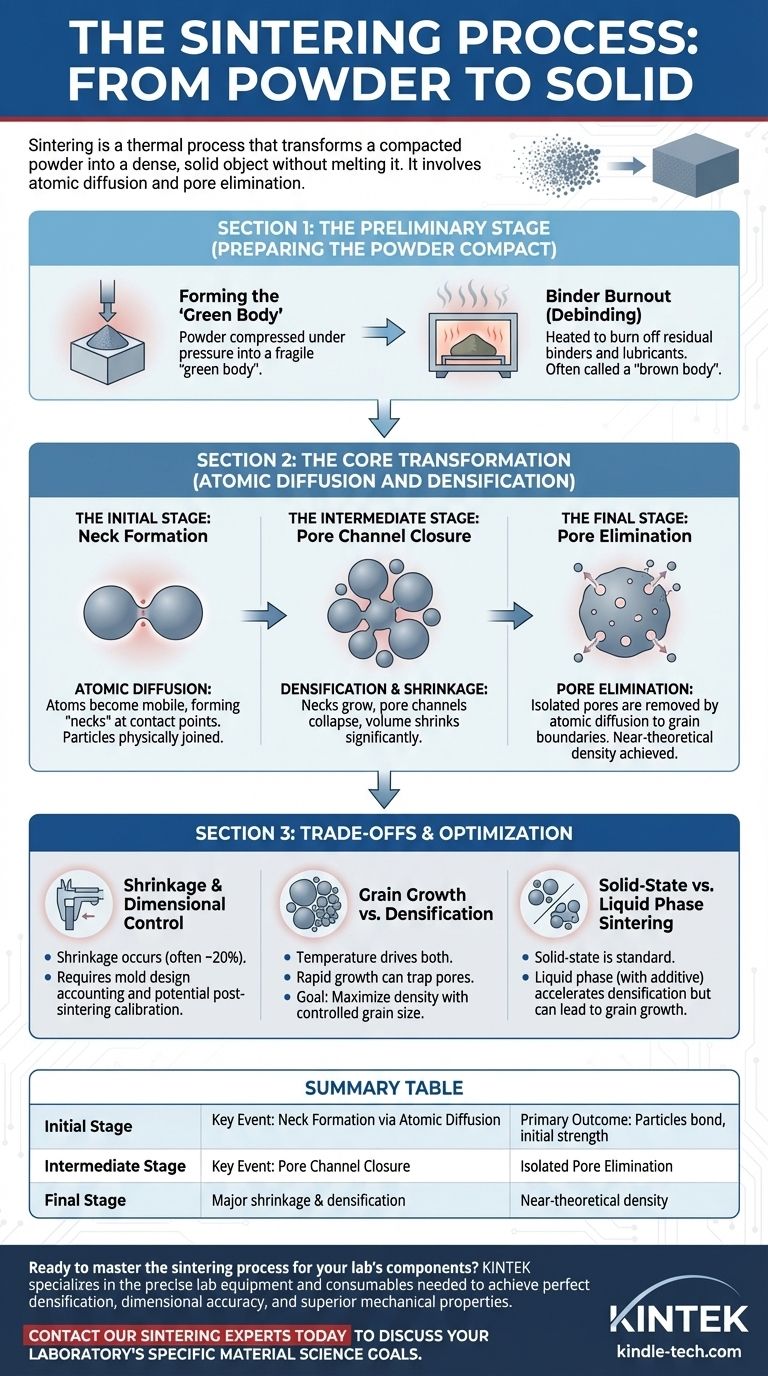
The Preliminary Stage: Preparing the Powder Compact
Before the main transformation can occur, the component must be properly prepared through compaction and cleaning. This initial phase sets the stage for successful densification.
Forming the "Green Body"
The process starts with a collection of fine metal or ceramic powder. This powder is compressed under high pressure in a die to form a "green body"—a fragile part that has the desired shape but possesses low mechanical strength and high porosity.
Binder Burnout (Debinding)
The green body is then heated slowly in a furnace with a controlled atmosphere. This initial heating, at relatively low temperatures, is designed to burn off the organic binders and lubricants used during compaction. The part after this stage is often called a "brown body."
The Core Transformation: Atomic Diffusion and Densification
This is the heart of the sintering process, where the loose powder structure is converted into a solid material. It occurs in overlapping stages driven by temperature, time, and the material's inherent desire to reduce its surface energy.
The Initial Stage: Neck Formation
As the temperature rises further (but stays below the material's melting point), a critical phenomenon begins. Atoms at the contact points between individual powder particles become mobile and start to diffuse across the boundary. This creates small bridges or "necks" between particles, a process known as diffusion bonding. The particles are now physically joined.
The Intermediate Stage: Pore Channel Closure
With continued time at temperature, the necks grow larger. This atomic movement pulls the centers of the particles closer together, causing a significant reduction in the volume of the pores. The network of interconnected pores collapses into a system of smaller, isolated, and more rounded voids. This is the stage where the majority of densification and shrinkage occurs.
The Final Stage: Pore Elimination
In the final stage, the material is already a mostly solid mass containing isolated, spherical pores. The primary mechanism now is the slow diffusion of atoms along grain boundaries to the surface of these internal pores. Driven by surface tension, this process redistributes mass to fill the remaining voids, further increasing density.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Consequences
Sintering is not a perfect process and involves critical trade-offs that must be managed to achieve the desired material properties.
Shrinkage and Dimensional Control
The elimination of porosity is a physical removal of empty space, which means the part will inevitably shrink. This shrinkage can be substantial, often around 20% in volume. This change must be accounted for in the initial design of the mold, and for high-precision parts, a post-sintering calibration or sizing step is often required.
Grain Growth vs. Densification
Temperature drives both densification (good) and grain growth (sometimes undesirable). If grains grow too large too quickly, they can sweep past and isolate pores within the grain itself, making them extremely difficult to remove. A key challenge in sintering is to maximize density while controlling the final grain size, as this has a major impact on mechanical properties like strength and toughness.
Solid-State vs. Liquid Phase Sintering
The process described above is solid-state sintering. An alternative is permanent liquid phase sintering, where an additive creates a small amount of liquid at the sintering temperature. This liquid phase can accelerate densification by flowing into pores, but it can also lead to more grain growth or part distortion if not carefully controlled.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Controlling the sintering process allows you to tailor the final properties of the component. Your primary objective will determine your focus.
- If your primary focus is maximum density: You must optimize for the final stage of sintering, using the right combination of high temperature, time, and atmospheric control to eliminate the last traces of porosity.
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy: You must start with highly consistent powder and uniform green body density, precisely predict shrinkage, and plan for post-sintering calibration or machining.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength: You must carefully balance the densification process against grain growth, often using lower temperatures for longer times to achieve a fine-grained, fully dense microstructure.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is about understanding and controlling the atomic-level changes that build a solid part from simple powder.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Stage | Key Event | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Stage | Neck Formation via Atomic Diffusion | Particles bond, part gains initial strength |
| Intermediate Stage | Pore Channel Closure | Major shrinkage and densification occurs |
| Final Stage | Isolated Pore Elimination | Part achieves near-theoretical density |
Ready to master the sintering process for your lab's components?
KINTEK specializes in the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to achieve perfect densification, dimensional accuracy, and superior mechanical properties in your sintered parts. Our expertise ensures you can control every stage—from binder burnout to final pore elimination.
Contact our sintering experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific material science goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the function of muffle furnace in food industry? Ensure Accurate Ash Determination for Quality Control
- How does a high-temperature muffle furnace work? Achieve Contaminant-Free, Uniform Heating
- What is the use of muffle furnace in chemistry laboratory? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Material Processing
- What is the difference between an oven and a muffle? Choose the Right Heating Tool for Your Lab
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a drying oven? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab



















