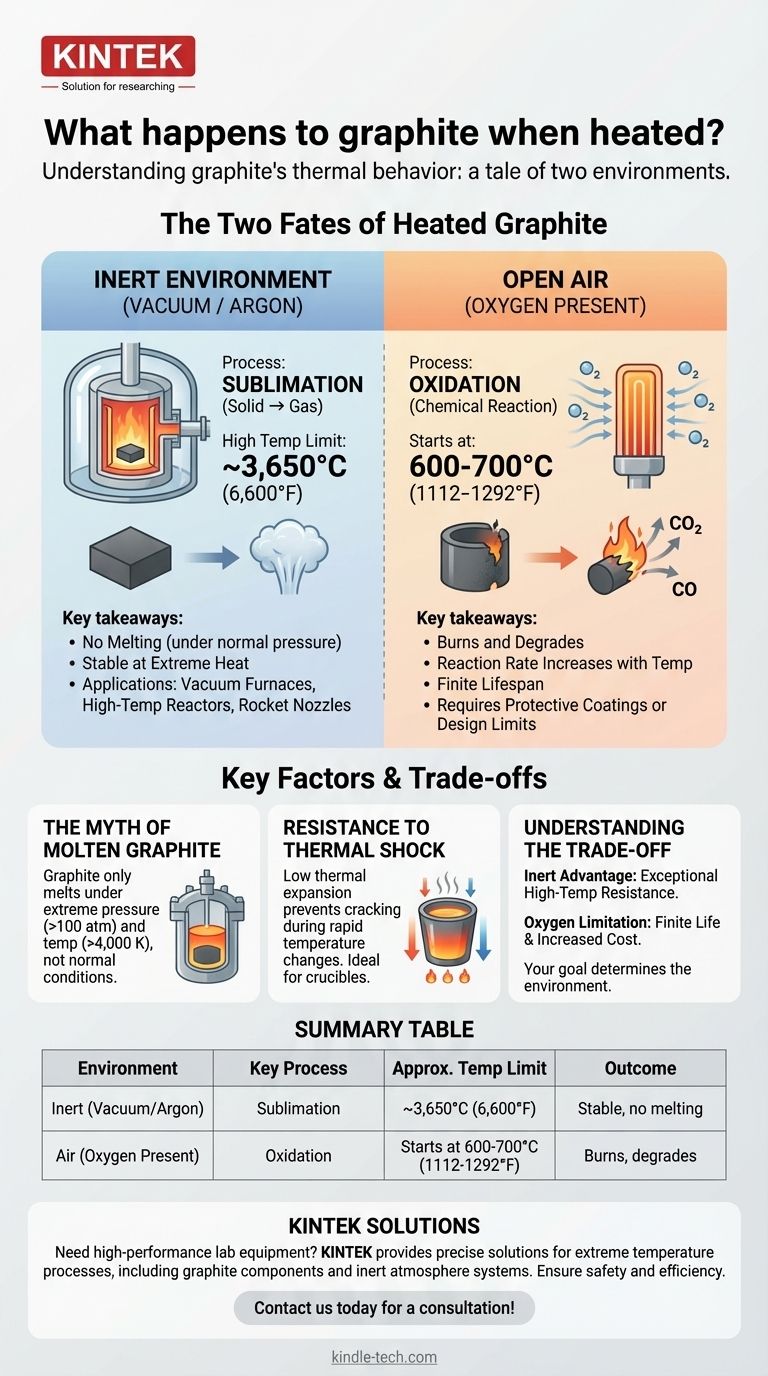
In short, graphite is one of the most heat-resistant materials known, but its behavior depends entirely on its environment. Under normal atmospheric pressure, graphite does not melt; it sublimates (turns directly from a solid to a gas) at an extremely high temperature of around 3,650°C (6,600°F). However, in the presence of oxygen, it will begin to burn or oxidize at a much lower temperature, typically starting around 600-700°C (1112-1292°F).
Understanding graphite's reaction to heat is a tale of two vastly different outcomes. In a vacuum or inert atmosphere, it remains stable to incredibly high temperatures. In the presence of air, its practical temperature limit is defined by oxidation, not its sublimation point.

The Two Fates of Heated Graphite
Graphite's unique atomic structure—strong carbon bonds within layers but weak bonds between them—governs its remarkable thermal properties. Depending on the atmosphere, one of two processes will dominate when it is heated.
Sublimation: The Path in an Inert Environment
Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from a solid to a gas, bypassing the liquid state entirely.
Graphite has one of the highest sublimation points of any element, occurring between 3,652–3,697 °C (6,608–6,687 °F). This is why it's a material of choice for applications that must endure extreme heat without melting.
This behavior is only possible in an oxygen-free environment, such as a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen). This is the principle behind its use in vacuum furnaces and high-temperature reactors.
Oxidation: The Reality in Open Air
In the presence of oxygen, graphite's performance is limited by a chemical reaction, not its physical state change.
Graphite begins to react with oxygen (oxidize) at temperatures starting around 600-700°C. This reaction forms carbon dioxide (CO₂) and carbon monoxide (CO) gas, effectively causing the graphite to burn away and degrade.
The rate of oxidation increases significantly with temperature. A graphite component heated in the open air to 1000°C will be consumed much faster than one held at 700°C.
Key Factors Influencing Thermal Behavior
Not all graphite is the same, and its environment dictates its limits. Understanding these factors is critical for any practical application.
The Myth of Molten Graphite
Under standard atmospheric pressure, you will never see liquid graphite.
However, graphite can be forced into a liquid state under extremely high pressures (over 100 atmospheres) and temperatures (above 4,000 K). This is a condition found in specialized industrial processes or scientific experiments, not in common applications.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
Graphite has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it does not expand or contract significantly when its temperature changes.
This property gives it excellent resistance to thermal shock, preventing it from cracking or fracturing when heated or cooled rapidly. This is a key reason it is used for crucibles that hold molten metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The primary trade-off with graphite is its exceptional inert-atmosphere performance versus its limited air-atmosphere performance.
The inert Advantage
In a vacuum or inert gas, graphite outperforms most metals and ceramics in terms of pure temperature resistance. It retains its strength at high temperatures, making it a reliable structural material for furnace linings, heating elements, and rocket nozzles.
The Oxygen Limitation
The requirement for an inert atmosphere adds complexity and cost to system design. In applications where graphite is exposed to air, its lifespan is finite and determined by the oxidation rate at the operating temperature. Protective coatings can be applied to slow this process, but they do not eliminate it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal determines which thermal property of graphite is most important.
- If your primary focus is reaching the absolute highest temperatures: You must use graphite in a vacuum or an inert gas environment to prevent oxidation and take advantage of its high sublimation point.
- If your primary focus is using graphite in open air: You must design around its oxidation limit, accepting that the material will slowly degrade at temperatures above ~600°C.
Ultimately, graphite's dual nature makes it both a uniquely capable high-temperature material and one that requires careful environmental control to unlock its full potential.
Summary Table:
| Environment | Key Process | Approximate Temperature Limit | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert (Vacuum/Argon) | Sublimation | ~3,650°C (6,600°F) | Stable, no melting |
| Air (Oxygen Present) | Oxidation | Starts at 600-700°C (1112-1292°F) | Burns, degrades |
Need high-performance lab equipment for extreme temperatures? Graphite's unique properties make it ideal for furnace linings, heating elements, and crucibles, but only when paired with the right environment. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables—including graphite components and the inert atmosphere systems needed to protect them—to ensure your high-temperature processes are safe, efficient, and reliable. Let our experts help you choose the right solution for your lab's needs. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the high temperature graphite material? The Ultimate Solution for Extreme Heat Applications
- What are the interferences of graphite furnace? Overcome Matrix & Spectral Issues for Accurate GFAAS
- What are the advantages of graphite? Unlock Superior Performance in High-Temperature Processes
- What is special about graphite? Unlocking Its Unique Properties for Extreme Applications
- What is the temperature of graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry? Mastering the Multi-Stage Heating Program
- Why is a graphite furnace more sensitive than a flame atomizer? Unlock the Physics of Trace-Level Analysis
- What is the principle of graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Temperatures with Direct Resistive Heating
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C



















