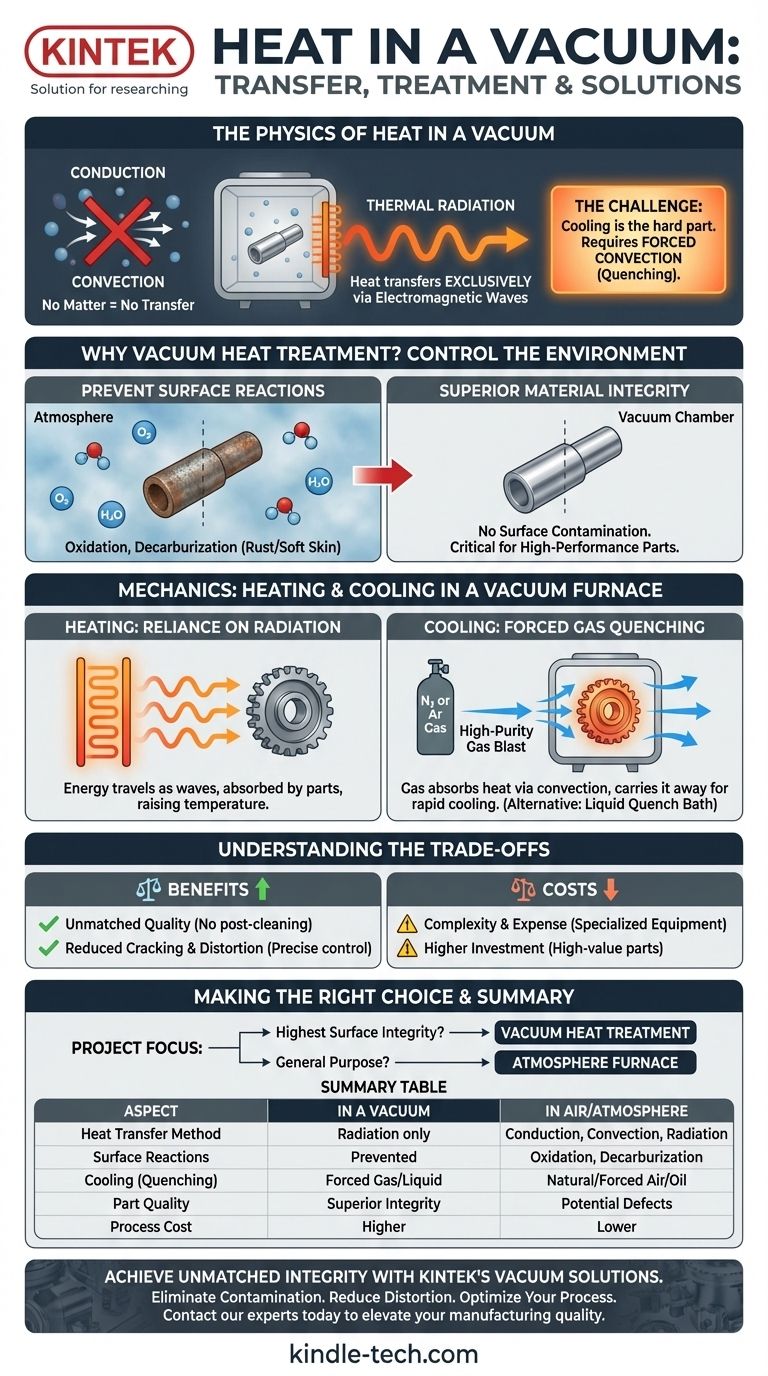
In a near-perfect vacuum, heat cannot transfer through conduction or convection because there is no matter to move the thermal energy. Instead, heat is transferred exclusively through thermal radiation, where an object emits energy as electromagnetic waves, similar to how the sun heats the Earth across the empty space.
The core challenge of working in a vacuum isn't heating an object, but rather cooling it effectively. Industrial processes overcome this by intentionally introducing a controlled, non-reactive gas to create forced convection for rapid cooling, known as quenching.

Why Use a Vacuum for Heat Treatment?
The primary reason for using a vacuum is not about managing heat, but about controlling the environment. It’s about what isn't in the chamber.
To Prevent Unwanted Surface Reactions
When a metal is heated, it becomes highly reactive with elements in the air.
Elements like oxygen, moisture, and carbon dioxide can bond with the metal's surface, causing oxidation (rusting), decarburization (a soft "skin"), or other undesirable effects. A vacuum removes these reactive gases.
The Result: Superior Material Integrity
By eliminating these reactions, vacuum heat treatment produces exceptionally clean parts with no surface contamination.
This process is critical for high-performance components, such as high-alloy tool steels, where precise surface hardness and integrity are non-negotiable.
The Mechanics of Heat Transfer in a Vacuum Furnace
Understanding how heat is both added and removed is key to understanding the entire process.
Heating: A Reliance on Radiation
Inside a vacuum furnace, objects are heated by heating elements. These elements get extremely hot and radiate thermal energy.
This energy travels as electromagnetic waves through the vacuum and is absorbed by the metal parts, causing their temperature to rise.
The Cooling Challenge: No Convection
Once the part is heated, it must often be cooled rapidly (quenched) to lock in the desired hardness. In open air, this is easy. In a vacuum, there is no air to carry heat away.
An object left alone in a vacuum can only cool by radiating its own heat away, which is a very slow process and insufficient for hardening most metals.
The Solution: Forced Convection via Gas Quenching
To solve this, modern vacuum furnaces use a powerful system for rapid cooling.
A high-purity, non-reactive gas like nitrogen or argon is blasted into the chamber at high speed. This gas absorbs heat from the hot metal through convection and carries it away, allowing for a controlled and rapid quench. The cooling effect can be enhanced by using pressures above normal atmosphere.
Alternative Method: Liquid Quenching
Some vacuum furnaces are designed to drop the heated parts into a sealed chamber containing oil or a water-based polymer.
This provides an even faster, more aggressive quench for specific alloys and applications, all while the initial heating remained in a pure vacuum environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Vacuum heat treating offers superior results, but it's a specialized process with clear trade-offs.
Benefit: Unmatched Quality
The process yields incredibly clean parts with no need for post-treatment cleaning. The surface finish and metallurgical properties are precisely controlled.
Benefit: Reduced Cracking and Distortion
Because heating and cooling are so tightly controlled, there is less thermal stress on the component. This significantly reduces the risk of parts cracking or warping during the hardening process.
Cost: Complexity and Expense
Vacuum furnaces and high-purity gases represent a significant investment. This makes the process more expensive than traditional atmosphere-based heat treating and is typically reserved for high-value or performance-critical parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Deciding whether to use vacuum heat treatment depends entirely on your project's requirements.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible surface integrity and performance: Vacuum heat treatment is the definitive choice for preventing any surface reactions on sensitive alloys.
- If your primary focus is hardening general-purpose components where minor surface oxidation is acceptable: Traditional atmosphere furnaces offer a more cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, vacuum processing provides an unparalleled level of environmental control, enabling the production of higher quality components.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | In a Vacuum | In Air/Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer Method | Radiation only | Conduction, Convection, Radiation |
| Surface Reactions | Prevented (no oxygen/moisture) | Oxidation, decarburization occur |
| Cooling (Quenching) | Forced gas convection or liquid quench | Natural or forced air/oil quench |
| Part Quality | Superior integrity, no contamination | Potential for surface defects |
| Process Cost | Higher (specialized equipment) | Lower (standard equipment) |
Achieve Unmatched Material Integrity with KINTEK's Vacuum Solutions
Are you developing high-performance components that demand flawless surface quality and precise metallurgical properties? The controlled environment of a vacuum furnace is essential for preventing oxidation and decarburization in sensitive alloys. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab and production equipment, including vacuum furnaces designed for superior heat treatment.
We provide the technology and expertise to help you:
- Eliminate Surface Contamination: Ensure your high-value parts are free from oxides and other defects.
- Reduce Cracking and Distortion: Benefit from precise thermal management that minimizes stress.
- Optimize Your Process: Whether you require high-pressure gas quenching or liquid quenching, we have a solution.
Don't let atmospheric reactions compromise your component's performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's vacuum heating and quenching systems can elevate your manufacturing quality and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions
- What is the vacuum heat treatment cycle? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Precision
- What are the advantages of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Precision and Cleanliness for Critical Components
- Why do you vacuum for heat treatment? Achieve Flawless, High-Performance Metal Components
- What is vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Control, Cleanliness, and Quality



















