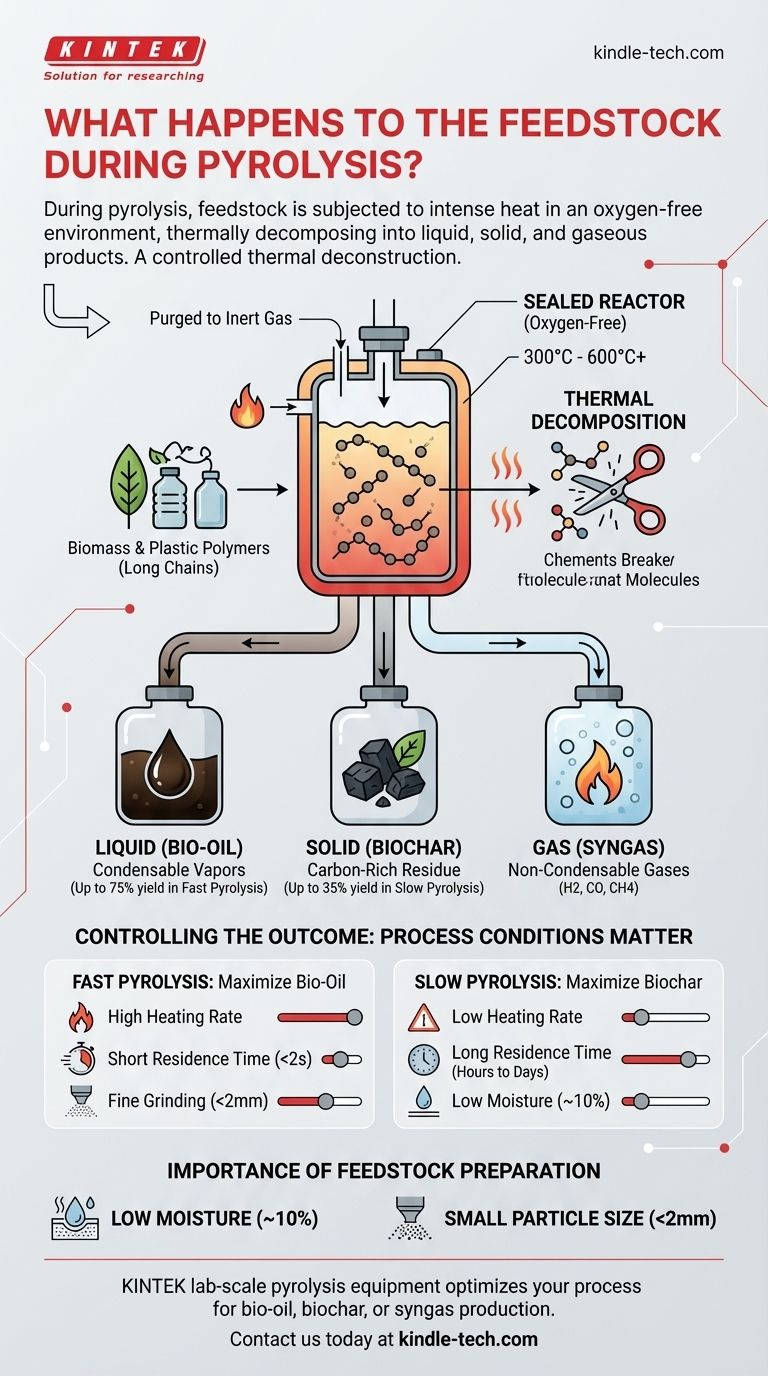
During pyrolysis, feedstock is subjected to intense heat in an oxygen-free environment. This process prevents the material from burning and instead causes its chemical structure to thermally decompose, breaking it down into a mixture of liquid, solid, and gaseous products.
Pyrolysis is not simply heating; it is a controlled thermal deconstruction. The core principle is that by precisely manipulating temperature and heating rate, you can dictate the final output, prioritizing the yield of valuable products like bio-oil, biochar, or syngas from the initial feedstock.

The Core Mechanism: Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
Creating the Right Environment
The defining characteristic of pyrolysis is the absence of oxygen. The feedstock is fed into a sealed reactor that has been purged with an inert gas.
This anoxic atmosphere is critical. Without oxygen, the material cannot combust (burn). Instead of releasing energy as heat and light, the chemical energy stored in the feedstock is preserved in the resulting products. Temperatures typically range from 300°C to over 600°C.
The Initial Breakdown of Polymers
Heat acts as a chemical scissor. Most organic feedstocks, like biomass or plastics, are made of large, complex polymers (e.g., cellulose, lignin, polyethylene).
The intense heat breaks the chemical bonds holding these long polymer chains together. This process, known as thermal decomposition or thermolysis, shatters them into smaller, more volatile molecules.
The Three Primary Products
As the polymers break down, a mix of compounds is formed. These are separated based on their physical state after cooling.
- Liquid (Bio-oil): A portion of the volatile compounds are condensable vapors. When cooled, they form a dark, viscous liquid known as bio-oil or pyrolysis oil, which can be a source for biofuels and chemicals.
- Solid (Biochar): The stable, carbon-rich solid material left behind is called biochar. It is a form of charcoal with applications in agriculture and carbon sequestration.
- Gas (Syngas): The non-condensable, permanent gases like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane are collected as syngas. This gas can be combusted to generate heat or electricity to power the pyrolysis process itself.
Controlling the Outcome: Process Conditions Matter
The ratio of these three products is not fixed. It is directly controlled by the process conditions, allowing you to tailor the output to a specific goal.
Fast Pyrolysis for Bio-Oil
To maximize the liquid bio-oil yield (up to 75% by weight), you use fast pyrolysis. This involves very high heating rates and a short residence time for the vapors in the reactor (typically less than 2 seconds). The goal is to rapidly break down the feedstock and remove the vapors before they can break down further into gas and char.
Slow Pyrolysis for Biochar
To maximize the solid biochar yield (around 35%), you use slow pyrolysis. This process uses lower heating rates and much longer residence times (hours to days). This slow "cooking" allows more carbon to rearrange into stable, aromatic charcoal structures.
The Importance of Feedstock Preparation
The efficiency and success of pyrolysis depend heavily on preparing the feedstock correctly before it enters the reactor.
Why Moisture Content is Critical
The feedstock must be relatively dry, ideally with a moisture content around 10%. Any water in the feedstock must be vaporized into steam, which consumes a significant amount of energy and lowers the overall thermal efficiency of the process. High-moisture materials require an energy-intensive pre-drying step.
Why Particle Size Matters
The feedstock must also be ground into small particles (e.g., under 2 mm). Smaller particles have a much higher surface-area-to-volume ratio. This allows heat to transfer into the material quickly and uniformly, which is absolutely essential for the precise control needed in fast pyrolysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Feedstock Variability
The exact composition of the feedstock has a massive impact on the final products. A woody biomass rich in cellulose will yield different results than a plastic waste stream or agricultural sludge. The process must be tuned for the specific material being used.
Product Quality and Upgrading
The raw products of pyrolysis are not always ready for immediate use. Bio-oil is often acidic, unstable, and corrosive, requiring significant and costly "upgrading" to be used as a drop-in fuel. The properties of biochar can also vary widely.
Energy Balance
Pyrolysis is an endothermic process, meaning it requires a constant input of energy to maintain the high temperatures. The energy required for drying the feedstock and running the reactor must be less than the energy value of the products for the process to be net-positive.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
Before choosing a pyrolysis pathway, you must be clear about your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuels: Pursue fast pyrolysis and invest in systems for fine grinding and extensive drying of your feedstock.
- If your primary focus is creating a soil amendment or sequestering carbon: Slow pyrolysis is the correct path, offering more flexibility on particle size but still demanding low moisture content.
- If your primary focus is generating on-site energy from waste gas: A fast pyrolysis or gasification-focused process will maximize the syngas yield, which can then fuel a generator.
Understanding these core principles allows you to transform diverse feedstocks into valuable resources with precision and purpose.
Summary Table:
| Process Condition | Primary Goal | Key Product | Key Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fast Pyrolysis | Maximize Liquid Yield | Bio-oil (up to 75%) | High heating rate, short vapor residence time, fine grinding (<2mm), low moisture (~10%) |
| Slow Pyrolysis | Maximize Solid Yield | Biochar (up to 35%) | Low heating rate, long residence time, low moisture (~10%) |
| Gas-Focused | Maximize Energy Gas | Syngas | High temperatures, optimized for non-condensable gases |
Ready to transform your biomass or waste stream into valuable resources?
At KINTEK, we specialize in lab-scale pyrolysis equipment that provides the precise control you need to optimize your process for bio-oil, biochar, or syngas production. Whether you're focused on renewable energy, carbon sequestration, or sustainable materials, our reactors are designed to help you achieve your specific goals with efficiency and reliability.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research and development. Let's turn your feedstock into opportunity together.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas



















