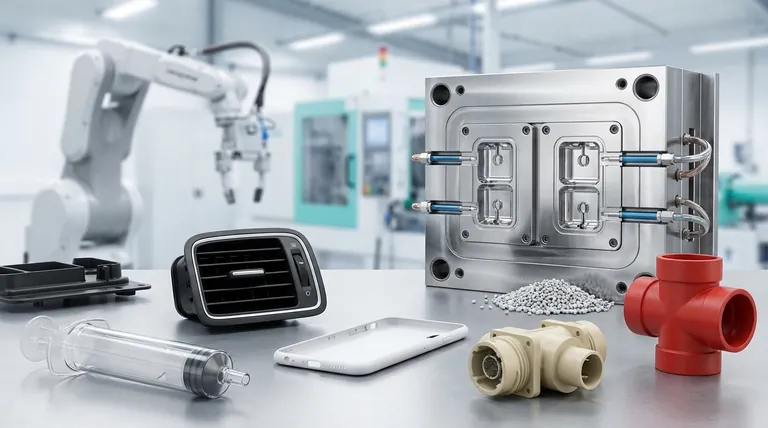
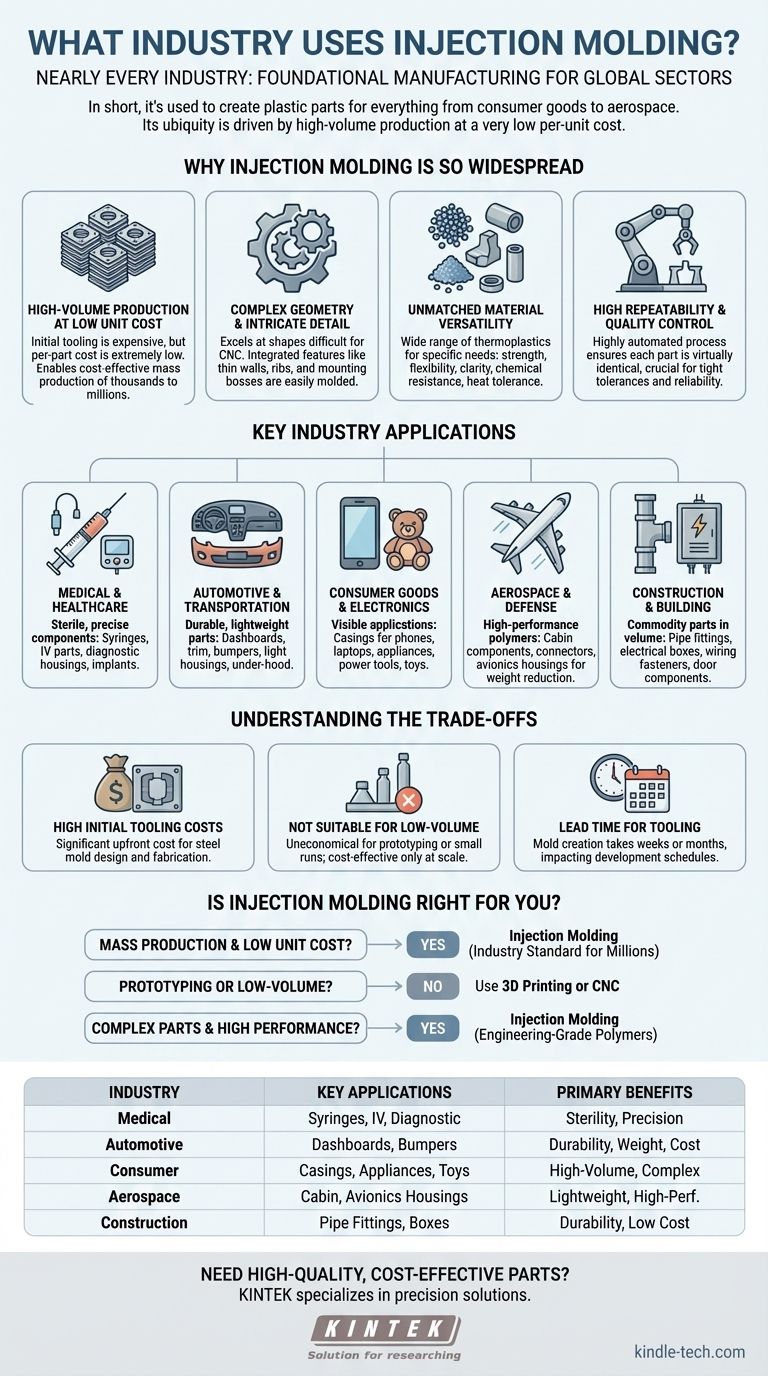
In short, nearly every industry. Injection molding is a foundational manufacturing process used to create plastic parts for sectors ranging from consumer goods and medical devices to aerospace and automotive. Its widespread adoption is due to its unmatched ability to produce complex, high-quality parts in enormous volumes at a very low per-unit cost.
The core reason for injection molding's ubiquity is not just its versatility, but its economic efficiency at scale. It is the definitive process for turning a validated design into millions of identical, cost-effective physical products.

Why Injection Molding Is So Widespread
The dominance of injection molding stems from a unique combination of benefits that solve critical manufacturing challenges across different industries. Understanding these principles reveals why it is often the default choice for producing parts in high volumes.
High-Volume Production at Low Unit Cost
The primary driver for injection molding is its economic model. While the initial investment in a steel mold (the "tool") is significant, the cost to produce each individual part is extremely low.
Once the mold is created, the automated process can produce thousands or millions of parts rapidly. This makes it the most cost-effective method for mass production.
Complex Geometry and Intricate Detail
Injection molding excels at producing parts with complex shapes and fine details that would be difficult or costly to achieve with other methods like CNC machining.
Features like thin walls, reinforcing ribs, and integrated mounting bosses can be designed directly into the mold. This allows for the creation of sophisticated, lightweight, and highly functional parts.
Unmatched Material Versatility
An enormous range of thermoplastic polymers can be used in injection molding, each with specific properties.
Engineers can select materials based on requirements for strength, flexibility, optical clarity, chemical resistance, or heat tolerance. This adaptability allows its use in everything from simple toy soldiers to high-performance aerospace components.
High Repeatability and Quality Control
The process is highly automated and precisely controlled. Once the parameters are set, each part produced is virtually identical to the last.
This exceptional consistency is critical for industries like medical and automotive, where tight tolerances and reliable performance are non-negotiable.
Key Industry Applications
While the list is nearly endless, certain industries rely heavily on injection molding for their core products.
Medical & Healthcare
The medical industry requires sterile, durable, and highly precise components. Injection molding is used to produce everything from single-use syringe bodies and IV components to complex housings for diagnostic equipment and biocompatible implants.
Automotive & Transportation
Weight reduction and durability are critical in the automotive sector. Injection molding is used for a vast array of parts, including dashboards, interior trim, bumpers, door handles, light housings, and under-the-hood components.
Consumer Goods & Electronics
This is perhaps the most visible application of injection molding. Casings for smartphones, laptops, and televisions, as well as parts for kitchen appliances, power tools, and children's toys, are almost universally injection-molded.
Aerospace & Defense
In aerospace, replacing heavier metal parts with high-performance polymers is crucial for fuel efficiency. Injection molding is used for interior cabin components, electrical connectors, and housings for sensitive avionics, where strength and low weight are paramount.
Construction & Building
For commodity parts needed in massive quantities, injection molding is ideal. This includes pipe fittings, electrical boxes, wiring fasteners, and components for windows and doors, where durability and low cost are key drivers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its benefits, injection molding is not the right choice for every situation. Objectively understanding its limitations is key to making a sound technical decision.
High Initial Tooling Costs
The primary barrier to entry is the cost of the mold. Designing and fabricating a high-quality steel tool can cost anywhere from a few thousand to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on its complexity and lifespan.
Not Suitable for Low-Volume Production
Because of the high upfront tooling cost, injection molding is uneconomical for prototyping or small production runs. The cost per part is only low when the initial investment is spread across thousands of units.
Lead Time for Tooling
Creating a production-ready mold takes time—typically several weeks or even months. This lead time must be factored into the product development schedule. For rapid prototyping, other methods like 3D printing are far more suitable.
Is Injection Molding Right for Your Application?
Choosing the correct manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's specific goals, volume, and budget.
- If your primary focus is mass production and low unit cost: Injection molding is the undisputed industry standard once you require thousands or millions of identical parts.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or low-volume runs: Use 3D printing or CNC machining to validate your design before committing to the significant investment of an injection mold.
- If your primary focus is complex parts with high-performance requirements: Injection molding supports a vast library of engineering-grade polymers, making it ideal for demanding applications in aerospace, medical, and automotive.
By understanding the relationship between volume, cost, and complexity, you can confidently determine where injection molding fits within your product's lifecycle.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Medical & Healthcare | Syringes, IV components, diagnostic equipment | Sterility, precision, biocompatibility |
| Automotive & Transportation | Dashboards, bumpers, interior trim | Durability, weight reduction, cost-efficiency |
| Consumer Goods & Electronics | Smartphone casings, appliance parts, toys | High-volume production, complex geometries |
| Aerospace & Defense | Cabin components, avionics housings | Lightweight, high-performance materials |
| Construction & Building | Pipe fittings, electrical boxes | Durability, low cost for high volumes |
Need high-quality, cost-effective parts for your industry? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, leveraging manufacturing expertise to deliver reliable solutions for laboratory needs. Whether you're in medical research, automotive testing, or materials development, our products are designed for accuracy and durability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific application with tailored equipment and consumables!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Lab Infrared Press Mold
- No Demolding Lab Infrared Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
People Also Ask
- What does calendering do for fabric? Transform Fabric's Look, Feel, and Performance
- What is the cost of blown film extrusion? From $20K to High-End Systems
- What is the meaning of calendering? Achieve Superior Surface Finish and Material Uniformity
- What is the process of extrusion blowing? A Guide to Efficient Hollow Plastic Part Production
- What is the difference between single layer film and multi layer film? A Guide to Material Selection
- What is the process of multilayer extrusion? Engineer High-Performance Plastic Films
- Why is a roller press machine required for CuMH solid-state membranes? Expert Insights on Flexible Electrolyte Forming
- What is the manufacturing process of rubber? From Raw Material to Durable End Product



















