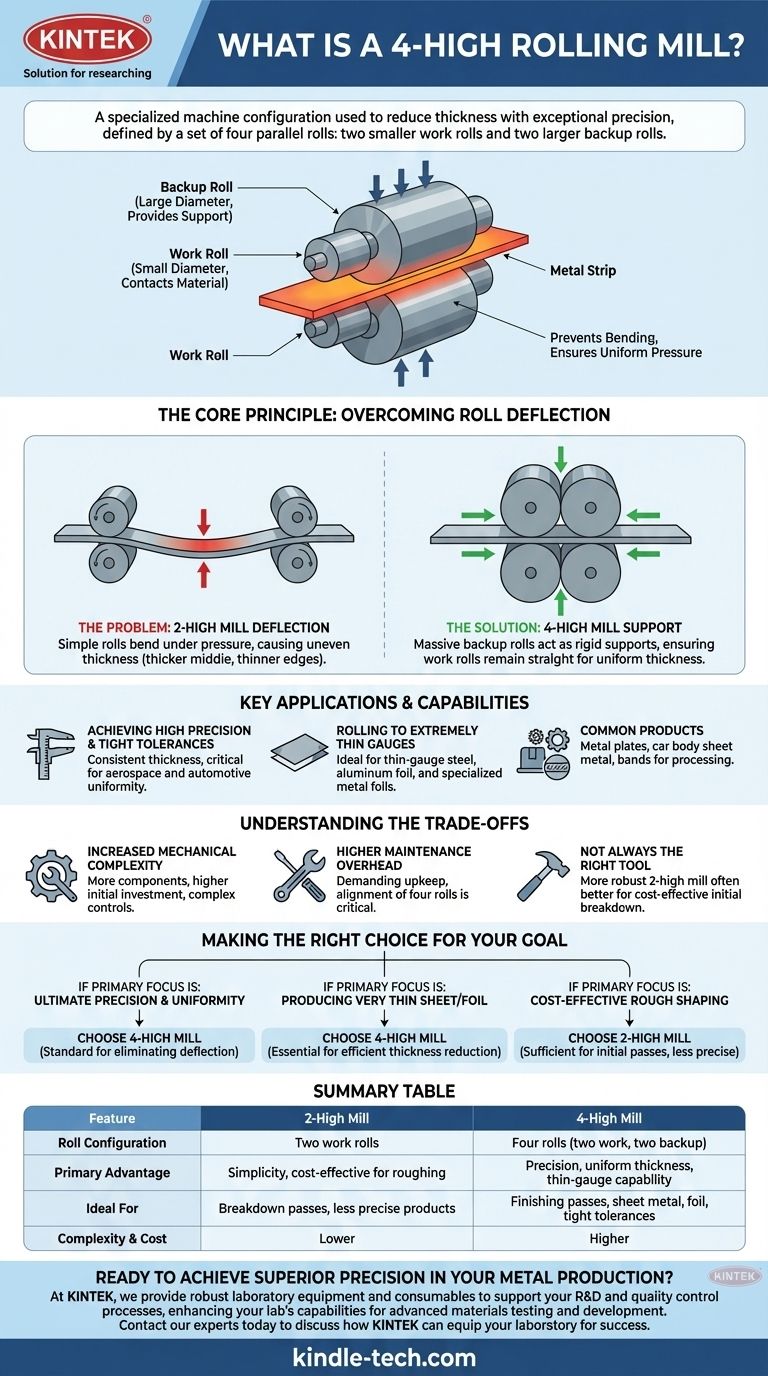
A 4-high rolling mill is a specialized machine configuration used to reduce the thickness of metals and other materials with exceptional precision. Its defining feature is a set of four parallel rolls: two smaller-diameter work rolls that directly contact the material, and two much larger backup rolls that support the work rolls, preventing them from bending under pressure.
The core purpose of the 4-high design is to overcome roll deflection. By using large backup rolls to support the smaller work rolls, the mill can apply immense force evenly, producing metal sheets and plates that are extremely thin and have a highly uniform thickness.
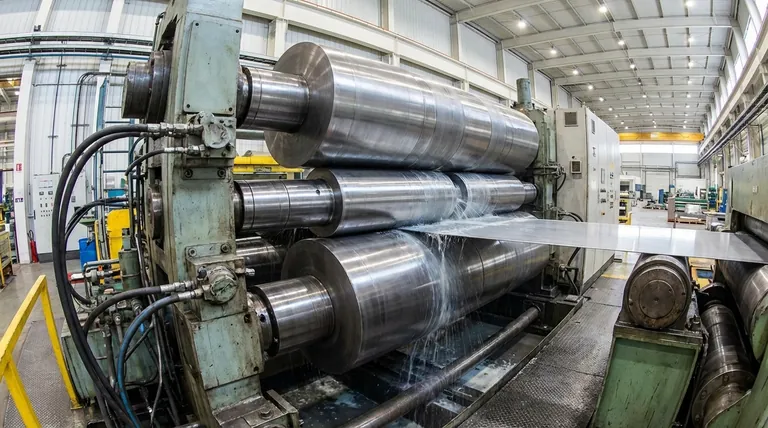

The Core Principle: Overcoming Roll Deflection
In any rolling operation, the immense pressure required to deform metal can cause the rolls themselves to bend or deflect in the middle. This is a critical engineering challenge that the 4-high mill is specifically designed to solve.
The Problem with Simpler Designs
In a basic 2-high mill, two rolls press directly against the material. Under high pressure, these rolls can sag slightly in the center, much like a ruler pressed between two hands. This deflection results in a final product that is thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges, failing to meet precise tolerance requirements.
The 4-High Solution
The 4-high configuration introduces two massive backup rolls positioned directly above and below the work rolls. These backup rolls act as rigid, unbending support structures. They ensure the slender work rolls remain perfectly straight along their entire length, transferring the rolling force uniformly across the width of the material.
Why Smaller Work Rolls are Better
The design allows for the use of smaller diameter work rolls. A smaller roll creates a smaller contact area with the metal, which concentrates the rolling force more efficiently. This reduces the power required to achieve a given thickness reduction and allows for finer control over the final product.
Key Applications and Capabilities
The unique design of the 4-high mill gives it capabilities that are essential for modern manufacturing. It is a cornerstone technology for producing high-quality flat-rolled products.
Achieving High Precision and Tight Tolerances
By eliminating roll deflection, the 4-high mill can produce sheets and plates with exceptionally consistent thickness from edge to edge. This ability to maintain tighter tolerances is critical for industries like aerospace and automotive, where material uniformity is paramount.
Rolling to Extremely Thin Gauges
The combination of immense, evenly distributed pressure and efficient small work rolls allows for the reduction of material to extremely small thicknesses. This makes the 4-high mill ideal for producing thin-gauge steel sheet, aluminum foil, and other specialized metal foils.
Common Products
This technology is used in the production of a wide range of high-quality intermediate and finished goods, including metal plates for construction, sheet metal for car bodies, and bands for subsequent processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the 4-high configuration is not the solution for every rolling application. Its advantages come with inherent complexities.
Increased Mechanical Complexity
A 4-high mill has more components—including four rolls, heavy-duty bearings, and sophisticated adjustment systems—than a simpler 2-high mill. This intricacy leads to a higher initial investment and more complex operational controls.
Higher Maintenance Overhead
With more moving parts operating under extreme stress, the maintenance requirements for a 4-high mill are more demanding. Proper alignment and upkeep of all four rolls are critical to performance.
Not Always the Right Tool
For initial "breakdown" passes on thick slabs or for products where high precision is not the primary concern, a more robust and less complex 2-high mill is often more cost-effective. The 4-high mill is fundamentally a tool for precision and finishing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a 4-high rolling process is directly tied to the quality requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is ultimate precision and uniform thickness: The 4-high mill is the standard, as its backup rolls eliminate the deflection that causes inconsistencies.
- If your primary focus is producing very thin sheet or foil: The supported, small-diameter work rolls of a 4-high mill are essential for achieving the required thickness reduction efficiently.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective rough shaping: A simpler 2-high mill is often sufficient for initial passes where tight tolerances are not yet a concern.
Ultimately, the 4-high rolling mill is a precision instrument engineered to solve the fundamental problem of roll bending, enabling the production of superior flat-rolled metal products.
Summary Table:
| Feature | 2-High Mill | 4-High Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Roll Configuration | Two work rolls | Four rolls (two work, two backup) |
| Primary Advantage | Simplicity, cost-effective for roughing | Precision, uniform thickness, thin-gauge capability |
| Ideal For | Breakdown passes, less precise products | Finishing passes, sheet metal, foil, tight tolerances |
| Complexity & Cost | Lower | Higher |
Ready to achieve superior precision in your metal production?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables to support your R&D and quality control processes. Whether you are developing new alloys or ensuring your materials meet the tightest tolerances, our solutions are designed to enhance your lab's capabilities.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can equip your laboratory for success in advanced materials testing and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Jar Mill with Agate Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Ten-Body Horizontal Jar Mill for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is a two-roll differential speed mill? Achieve Superior Polymer Mixing & Dispersion
- How does a vulcanizing machine work? Mastering the Art of Rubber Transformation
- What are the advantages of coextrusion? Achieve Multi-Material Efficiency and Superior Performance
- What is the process of calendering? A Guide to High-Volume Plastic Film Production
- Why is specific pressure applied during the cooling phase of UHMWPE processing? Ensuring Flatness and Structural Integrity
- What is the process of making rubber sheets? From Raw Rubber to Engineered Performance
- What fillers for rubber compounds? Choose the Right Filler for Performance vs. Cost
- What does a blown film machine do? Transform Plastic Pellets into Versatile Film



















