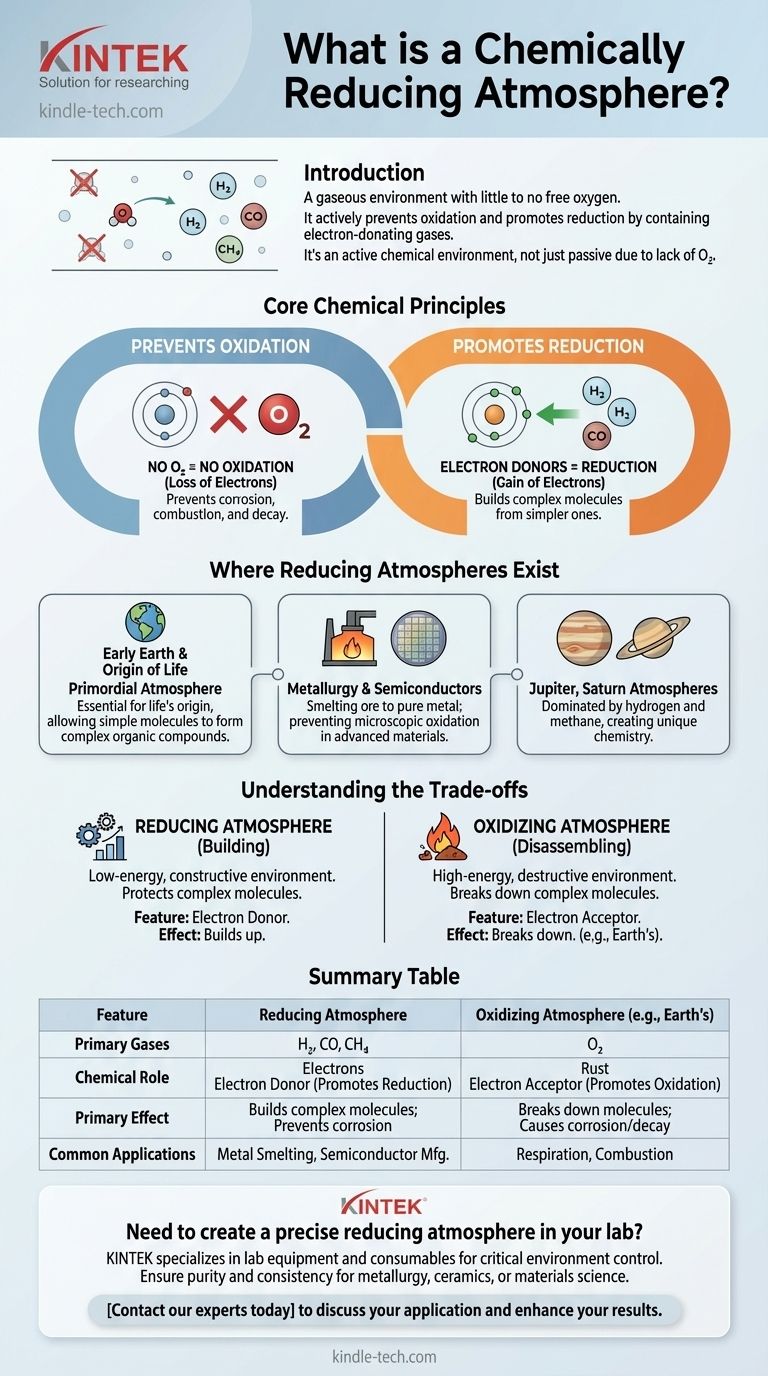
In simple terms, a chemically reducing atmosphere is a gaseous environment that contains little to no free oxygen. Because it lacks oxygen and often contains electron-donating gases like hydrogen or carbon monoxide, it actively prevents oxidation (like rusting) and instead promotes chemical reactions known as reduction.
The crucial insight is that a reducing atmosphere isn't just passive due to a lack of oxygen; it is an active chemical environment. The presence of reducing gases creates conditions that favor the construction of complex molecules rather than their breakdown.
The Core Chemical Principles
A reducing atmosphere is defined by the types of chemical reactions it allows. Its properties stem from two key functions that are two sides of the same coin.
It Prevents Oxidation
Oxidation is a chemical reaction where a substance loses electrons. While many elements can cause this, oxygen is the most famous oxidizing agent, readily stripping electrons from other materials.
A reducing atmosphere, by definition, has virtually no free oxygen. This removes the primary driver of oxidative breakdown, preventing processes like corrosion, combustion, and decay.
It Promotes Reduction
Reduction is the opposite of oxidation: a chemical reaction where a substance gains electrons. This process is fundamental to building more complex molecules from simpler ones.
Reducing atmospheres are rich in gases like hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), and methane (CH₄). These molecules are "electron donors"—they readily give away their electrons, causing other substances they interact with to become reduced.
Where Reducing Atmospheres Exist
These environments are not just a laboratory concept; they are found in critical contexts across science and industry.
Early Earth and the Origin of Life
Earth's primordial atmosphere was strongly reducing. Scientists believe this was essential for the origin of life, as it allowed simple inorganic molecules to form complex organic compounds without being immediately destroyed by oxygen.
Industrial and Material Processes
In metallurgy, a reducing atmosphere is used in a furnace to smelt ore. Carbon monoxide reacts with metal oxides (ore) to reduce them back to pure metal.
This process is also used in creating specific ceramic glazes and in the manufacturing of semiconductors, where preventing even microscopic oxidation is critical.
Giant Planets and Moons
The atmospheres of gas giants like Jupiter and Saturn are powerful reducing environments, dominated by hydrogen and methane. This is why their chemistry is so vastly different from that of Earth.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Reducing vs. Oxidizing
The difference between a reducing and an oxidizing atmosphere is one of the most fundamental dichotomies in chemistry and planetary science.
Oxidizing Atmospheres (Like Earth's Today)
Our current atmosphere, with nearly 21% oxygen, is highly oxidizing. It's an energy-rich environment that allows for efficient respiration, which powers complex, multicellular life.
However, this high reactivity comes at a cost. Oxygen is corrosive—it breaks things down. Iron rusts, organic matter decays, and fires burn. An oxidizing environment favors energy release through decomposition.
The Fundamental Dichotomy
You can think of the two environments as building versus disassembling.
A reducing atmosphere protects complex molecules and provides the chemical ingredients to build them up from simpler parts. It is a constructive, low-energy environment.
An oxidizing atmosphere provides abundant energy by breaking down complex molecules. It is a destructive, high-energy environment.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Understanding this distinction allows you to predict the chemical possibilities of a given environment.
- If your primary focus is astrobiology or early Earth history: A reducing atmosphere is considered a key prerequisite for abiogenesis—the natural process of life arising from non-living matter.
- If your primary focus is materials science or industrial chemistry: A reducing atmosphere is a powerful tool used to purify metals and prevent unwanted chemical reactions on material surfaces.
- If your primary focus is planetary science: The atmospheric composition of a planet—whether reducing or oxidizing—is the single most important factor determining its surface chemistry and potential for life as we know it.
Ultimately, knowing if an atmosphere is reducing or oxidizing tells you whether its fundamental chemical tendency is to build things up or break them down.

Summary Table:
| Feature | Reducing Atmosphere | Oxidizing Atmosphere (e.g., Earth's) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Gases | Hydrogen (H₂), Carbon Monoxide (CO), Methane (CH₄) | Oxygen (O₂) |
| Chemical Role | Electron Donor (Promotes Reduction) | Electron Acceptor (Promotes Oxidation) |
| Primary Effect | Builds complex molecules; Prevents corrosion/rust | Breaks down molecules; Causes corrosion/decay |
| Common Applications | Metal Smelting, Semiconductor Manufacturing, Ceramic Glazing | Respiration, Combustion |
Need to create a precise reducing atmosphere in your lab? KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables required to generate and control these critical environments for your research or production processes. Whether you're working in metallurgy, ceramics, or advanced materials science, our solutions ensure the purity and consistency your work demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application and enhance your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- What is nitrogen atmosphere for annealing? Achieve Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment
- What is the role of nitrogen in annealing process? Creating a Controlled, Protective Atmosphere
- How does a high-temperature furnace with atmosphere control optimize spinel coatings? Achieve Redox Sintering Precision



















