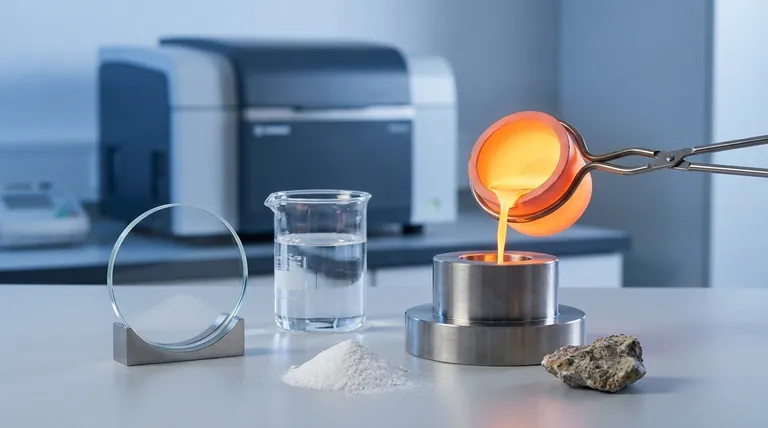
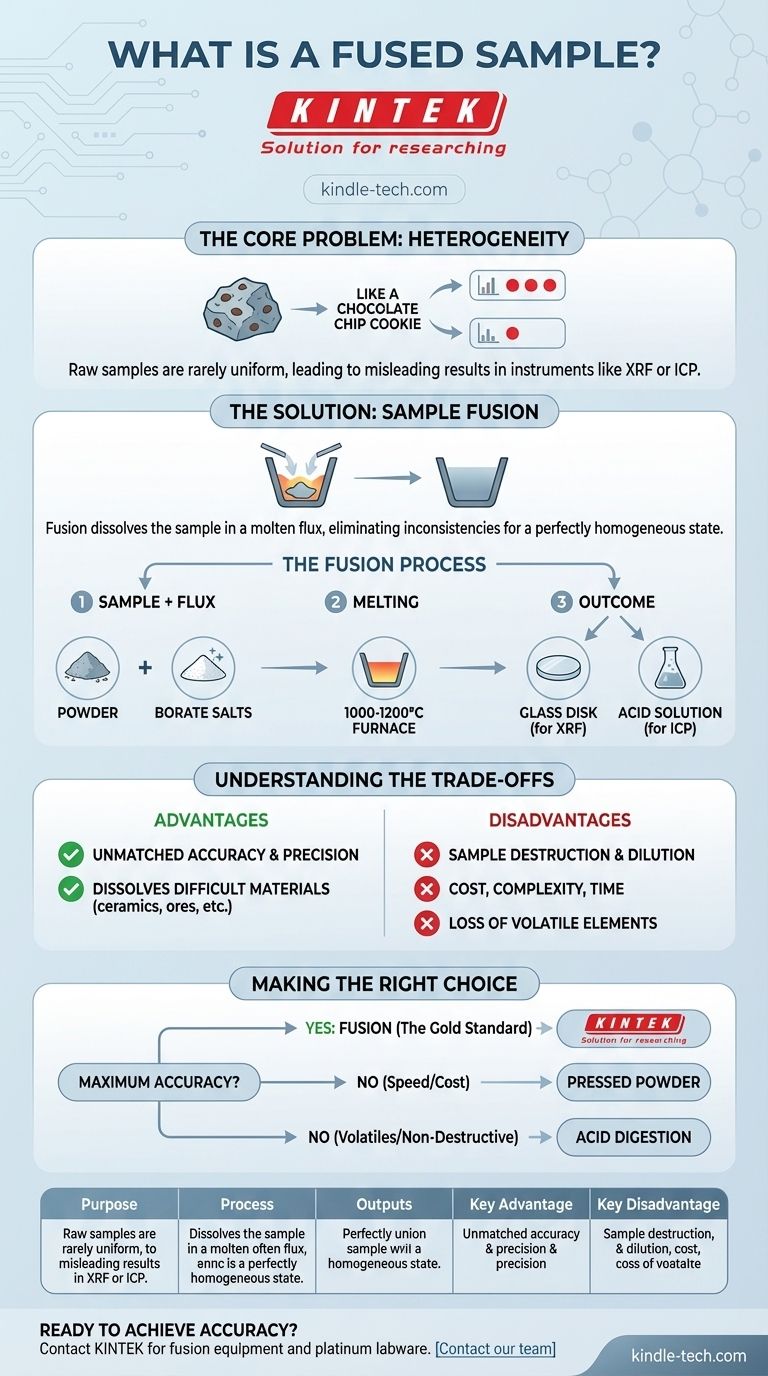
In analytical chemistry, a fused sample is a material prepared for analysis by dissolving it at high temperature into a molten solvent, known as a flux. This mixture is then cooled into a perfectly uniform solid glass disk or diluted with acid to form a liquid solution. The entire purpose of this process is to eliminate physical and chemical inconsistencies within the original, raw material.
The core problem in many analyses is that a raw sample is not uniform, leading to inaccurate and unreliable results. Sample fusion solves this by essentially "resetting" the material into a perfectly homogeneous state, ensuring that the portion being analyzed is a true and accurate representation of the whole.

The Core Problem: Why Fusion is Necessary
The Challenge of Sample Heterogeneity
Most raw materials, from mined ores and industrial cements to geological soils, are heterogeneous. This means their composition varies from one point to another.
Imagine a chocolate chip cookie. One bite might have three chocolate chips, while another has none. Analyzing a small piece of this "sample" would give you a misleading picture of the entire cookie's chocolate content.
How Heterogeneity Affects Analysis
Analytical instruments like X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) or Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) spectrometers analyze a very small portion of the presented sample.
If the sample is heterogeneous, factors like particle size, mineralogical structure, and surface finish can dramatically skew the results. This is known as the matrix effect, where the surrounding material interferes with the measurement of the elements you care about.
The Goal: A Perfectly Homogeneous Specimen
The goal of fusion is to destroy the original physical structure of the sample and create a new, perfectly homogeneous one.
By dissolving the sample completely into a molten flux, every molecule is evenly distributed. This ensures that whether the instrument analyzes the top, bottom, or middle of the prepared sample, the result will be identical and, therefore, highly accurate.
The Fusion Process: A Step-by-Step Overview
The Key Ingredients: Sample and Flux
The process begins by precisely weighing a small amount of the powdered sample and a much larger amount of a flux.
Common fluxes are borate salts, such as lithium tetraborate or lithium metaborate. These are chosen because they can dissolve a wide range of materials, especially metallic oxides, at high temperatures.
The "Melting Pot": Crucibles and Temperature
This mixture is placed into a crucible, typically made of a platinum-gold alloy to withstand the extreme conditions.
The crucible is heated in a specialized furnace to temperatures between 1000°C and 1200°C. The sample and flux melt and are agitated to ensure complete dissolution and mixing.
The Outcome: Glass Disks vs. Acid Solutions
Once the sample is fully dissolved, the molten liquid is poured into a mold to cool into a solid glass disk. This disk has a perfectly flat, clean surface ideal for XRF analysis.
Alternatively, the hot molten bead can be poured directly into a dilute acid solution. This creates a stable and perfectly homogeneous liquid sample ready for analysis by ICP-OES or ICP-MS.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Sample Fusion
Advantage: Unmatched Accuracy and Precision
For many materials, fusion is the gold standard for sample preparation. By eliminating the physical matrix effects, it provides the highest possible level of accuracy and repeatability in elemental analysis.
Advantage: Analysis of Difficult Materials
Fusion is one of the few methods capable of completely dissolving highly resistant or "refractory" materials. This includes ceramics, ores, ferroalloys, and geological samples that are impervious to acid digestion alone.
Disadvantage: Sample Destruction and Dilution
The process is completely destructive; the original sample cannot be recovered.
Furthermore, the sample is diluted by the flux (often at a 10:1 or 100:1 ratio). This lowers the concentration of the elements of interest, which can make it difficult to measure trace and ultra-trace elements near the instrument's detection limit.
Disadvantage: Cost, Complexity, and Time
Fusion requires expensive, specialized equipment, including automated fusion instruments and platinum crucibles. The process is also slower and more complex than simpler methods like pressing a powder pellet.
Disadvantage: Loss of Volatile Elements
The extremely high temperatures used in fusion will cause volatile elements like sodium (Na), sulfur (S), or halogens to be lost from the sample. If these elements are critical to your analysis, fusion is not a suitable method.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Choosing a sample preparation method requires balancing the need for accuracy against practical constraints like time, cost, and the specific elements being analyzed.
- If your primary focus is maximum accuracy and analyzing complex or refractory materials: Fusion is the definitive choice, providing results that are unmatched in precision and free from matrix effects.
- If your primary focus is speed, high throughput, and routine process control: A simpler method like pressed powder analysis is often sufficient and more cost-effective, though less accurate.
- If your primary focus is measuring volatile elements or preserving the sample: Fusion is not appropriate, and alternative methods like direct acid digestion must be considered.
Ultimately, understanding the trade-off between preparation effort and analytical certainty is the key to generating trustworthy and defensible data.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Creates a perfectly homogeneous sample from a heterogeneous raw material. |
| Process | Dissolves a powdered sample in a molten flux (e.g., lithium borate) at high temperatures (1000-1200°C). |
| Primary Outputs | Solid glass disk (for XRF) or acid solution (for ICP-OES/MS). |
| Key Advantage | Eliminates matrix effects, providing superior accuracy and precision. |
| Key Disadvantage | Destructive process; dilutes sample and can lose volatile elements. |
Ready to achieve the highest level of accuracy in your lab?
Choosing the right sample preparation method is critical for generating reliable data. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including high-performance fusion fluxers and durable platinum labware, to help you master this essential technique.
Our experts can guide you to the optimal solution for your specific materials and analytical goals, ensuring you get defensible results every time.
Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's needs for precision and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- XRF Boric Acid Lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for Laboratory Use
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
- Assemble Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
People Also Ask
- How do you prepare a sample for XRF analysis? Master the Key Methods for Accurate Results
- What is the size range of pellets? From 1mm to 25mm, Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application
- What equation do you use to calculate the heat required to melt a sample? Master the Heat of Fusion Formula
- What are the samples for XRF analysis? A Guide to Preparing Solids, Powders, and Liquids
- What is the difference between EDS and XRF? EDS for Microanalysis, XRF for Bulk Analysis



















