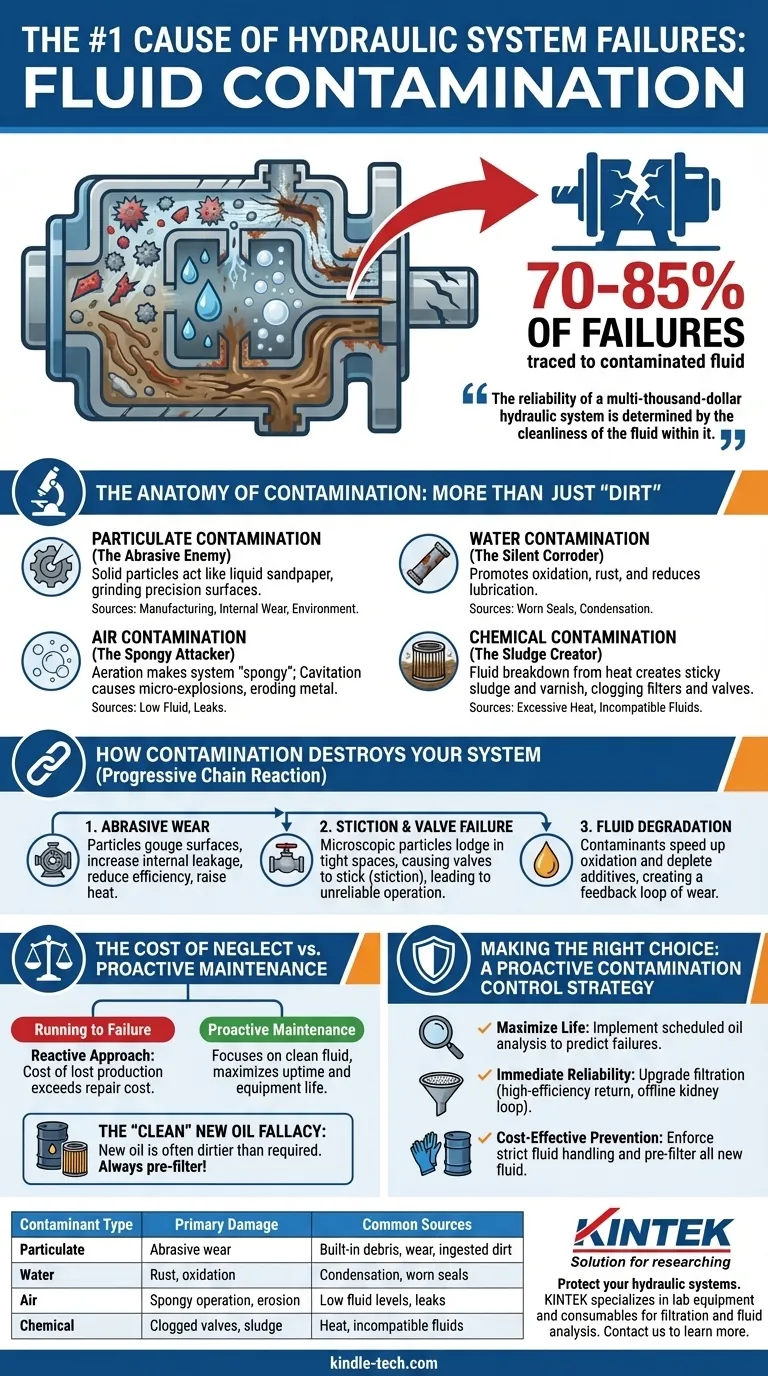
By far, the most significant cause of hydraulic system failures is fluid contamination. Industry studies consistently show that between 70% and 85% of all hydraulic component breakdowns can be traced directly back to contaminated fluid. This single issue is more destructive than high pressure, high temperature, or mechanical fatigue.
The reliability of a multi-thousand-dollar hydraulic system is determined by the cleanliness of the fluid within it. Focusing on preventing and removing contamination is the most effective strategy for extending component life and ensuring operational uptime.

The Anatomy of Contamination: More Than Just "Dirt"
When we talk about contamination, we are not just referring to visible dirt. The most damaging contaminants are often microscopic particles, along with water, air, and chemical impurities that degrade the system from the inside out.
Particulate Contamination: The Abrasive Enemy
Solid particles are the most common and destructive type of contaminant. They originate from built-in sources during manufacturing, are generated internally through component wear, or are ingested from the surrounding environment.
These particles act like a liquid sandpaper, grinding away at the tight-tolerance, precision-machined surfaces inside pumps, motors, and valves.
Water Contamination: The Silent Corroder
Water can enter a system through worn seals, reservoir breather caps, or condensation from temperature changes. It exists in three forms: dissolved, emulsified (giving the oil a milky appearance), and free water.
Even in small amounts, water promotes fluid oxidation, depletes critical additives, causes rust, and reduces the fluid's lubricating properties.
Air Contamination: The Spongy Attacker
Air can be entrained (aeration) or exist as vapor bubbles (cavitation). Aeration often results from low fluid levels or leaks on the pump's suction side, making the system feel "spongy" and unresponsive.
Cavitation is more destructive, occurring when pressure drops below the fluid's vapor pressure, creating bubbles that implode violently when re-pressurized. These micro-explosions erode metal surfaces and cause significant damage to pumps.
Chemical Contamination: The Sludge Creator
This occurs when the hydraulic fluid itself breaks down due to excessive heat (thermal degradation) or when incompatible fluids are mixed. This breakdown creates sludge and varnish.
These sticky deposits coat internal surfaces, clog small orifices in valves, and block filters, leading to sluggish performance and component starvation.
How Contamination Destroys Your System
The damage caused by contamination is not a single event but a progressive chain reaction of wear and tear that ultimately leads to catastrophic failure.
Abrasive Wear on Pumps and Motors
Particles caught between moving parts—like the pistons and barrel of a piston pump—gouge and score the metal surfaces. This scoring creates internal leakage paths.
As internal leakage increases, system efficiency drops, heat generation rises, and the pump must work harder to achieve the same output, accelerating its own destruction.
Stiction and Failure in Control Valves
Modern hydraulic systems rely on servo and proportional valves with clearances measured in microns. Particles smaller than the human eye can see can easily become lodged in these tight spaces.
This causes the valve spool to stick (a phenomenon called "stiction"), leading to erratic, unreliable, and unsafe machine operation.
Degradation of Hydraulic Fluid
Contaminants act as catalysts, accelerating the aging of the hydraulic oil. Water and metal particles speed up oxidation, depleting the additives that protect against wear, rust, and foaming.
Once the fluid degrades, it can no longer lubricate or protect components effectively, creating a feedback loop of increasing wear and particle generation.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Cost of Neglect
A proactive contamination control strategy requires investment, but it is insignificant compared to the cost of unplanned downtime and component replacement.
"Running to Failure" vs. Proactive Maintenance
A reactive approach—only changing filters when they are clogged or replacing components when they fail—is the most expensive way to manage a hydraulic system. The cost of lost production during unplanned downtime almost always exceeds the cost of the repair itself.
Proactive maintenance, centered on keeping the fluid clean, is a far more cost-effective strategy that maximizes uptime and equipment life.
The Fallacy of "Clean" New Oil
A common and costly mistake is assuming that new hydraulic oil from a drum or tote is clean enough for use. In reality, new oil is often dirtier than the allowable level for high-precision hydraulic systems.
All new fluid should be filtered before it is added to a machine—a process known as pre-filtering or "kidney looping"—to meet the cleanliness target set by the component manufacturer.
Making the Right Choice: A Proactive Contamination Control Strategy
Building a defense against contamination involves a multi-layered approach focused on exclusion (keeping it out) and removal (taking out what gets in).
- If your primary focus is maximizing equipment life: Implement a scheduled oil analysis program to track fluid health, wear metals, and contamination levels, allowing you to predict failures before they occur.
- If your primary focus is immediate reliability: Upgrade your system's filtration, focusing on high-efficiency return line filters and considering an offline (kidney loop) system for critical equipment.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective prevention: Enforce strict fluid handling and storage procedures, ensuring all new fluid is filtered before it enters a system and that all reservoirs are properly sealed.
Ultimately, treating your hydraulic fluid as a critical component—not just a consumable—is the key to a reliable and long-lasting system.
Summary Table:
| Contaminant Type | Primary Damage | Common Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Particulate (Solid Particles) | Abrasive wear on pumps, motors, and valves | Built-in debris, internal wear, ingested dirt |
| Water | Rust, oxidation, additive depletion | Condensation, worn seals, reservoir breathers |
| Air (Aeration/Cavitation) | Spongy operation, metal erosion | Low fluid levels, suction-side leaks |
| Chemical (Sludge/Varnish) | Clogged valves, blocked filters | Fluid breakdown from heat, incompatible fluids |
Protect your hydraulic systems from costly contamination failures. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including filtration systems and fluid analysis tools that help laboratories and industrial facilities maintain hydraulic fluid cleanliness. Our solutions support proactive maintenance strategies to extend equipment life and ensure operational uptime. Contact us today to learn how we can help you implement a reliable contamination control program tailored to your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What are the safety rules for a hydraulic press? Essential Protocols for Operator and Machine Safety
- Can you forge with hydraulic press? Yes, for Industrial-Grade Precision and Power
- How many tons can a hydraulic press produce? From 1 to 50,000+ Tons Explained
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- What is the difference between brake press and punch press? Choosing the Right Metal Fabrication Tool
- What is the function of a high-pressure hydraulic press? Optimize Silicide Bulk Material Preparation
- Why use KBr to make the pellet? Achieve Clear, Accurate IR Spectroscopy Results
- What types of hydraulic press systems are used for research? Discover Pellet, Hot, and Isostatic Solutions











