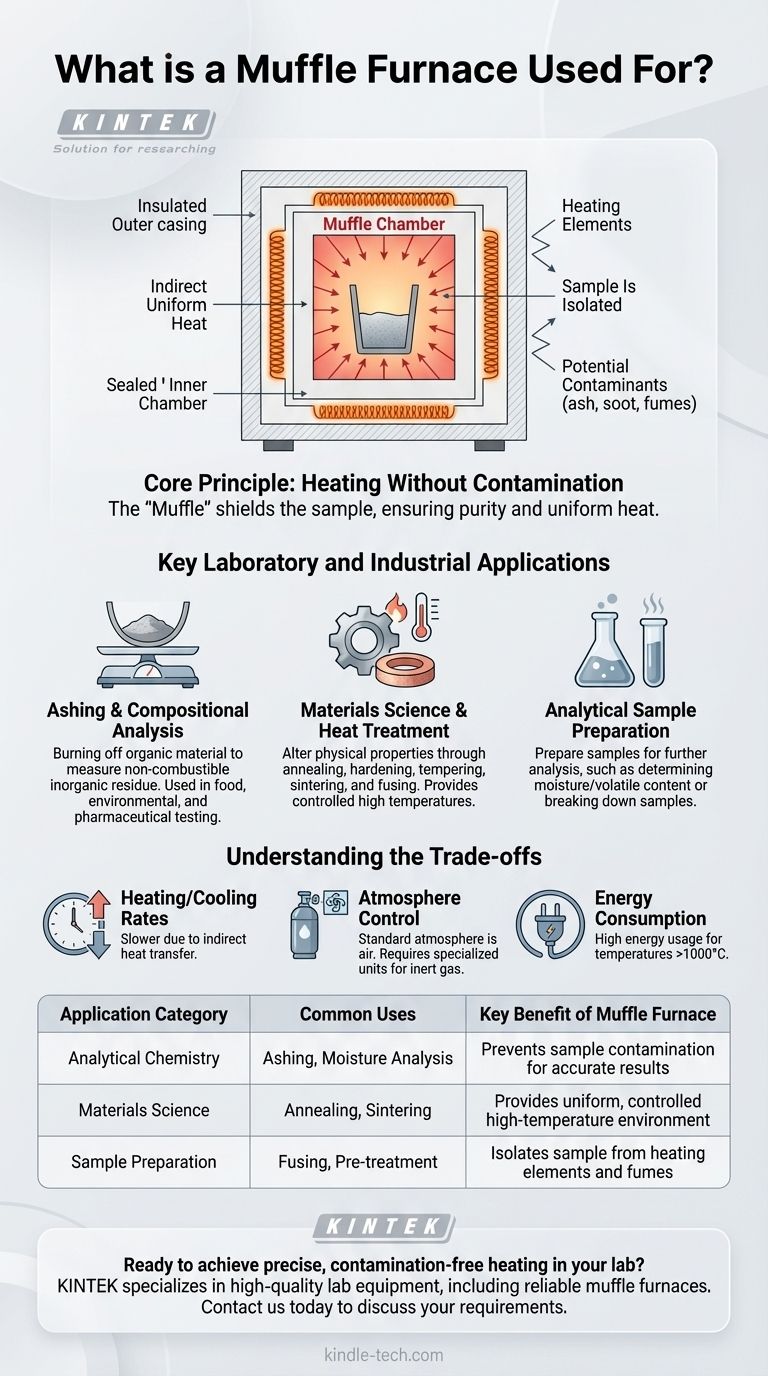
In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature laboratory oven that heats materials within a contained chamber. This design isolates the sample from direct contact with the heating elements and any potential contaminants, making it essential for processes like determining the ash content of a material, heat-treating metals, and firing ceramics.
The critical challenge in many high-temperature processes isn't just achieving the heat, but ensuring the sample remains pure and is heated uniformly. A muffle furnace solves this by using a protective inner chamber—the "muffle"—to shield the sample, enabling precise and uncontaminated thermal processing.

The Core Principle: Heating Without Contamination
A muffle furnace is defined by its core design feature, which separates its function from a standard oven.
The Role of the "Muffle" Chamber
Historically, furnaces were fuel-fired. The muffle was a sealed chamber that protected the material being heated from the byproducts of combustion, like ash, soot, and fumes.
This principle of isolation remains critical in modern electric furnaces. The muffle, now typically a high-temperature ceramic chamber, separates the workload from the electric heating elements.
The Benefit of Indirect Heat
By shielding the sample, the muffle provides two key advantages. First, it prevents contamination, which is crucial for analytical procedures. Second, it ensures uniform heating through radiation and convection within the chamber, rather than harsh direct radiation from the heating coils.
Key Laboratory and Industrial Applications
The unique design of the muffle furnace makes it the go-to instrument for several specific, high-temperature tasks.
Ashing and Compositional Analysis
This is one of the most common uses. Ashing is the process of burning off all organic material in a sample to precisely measure the weight of the non-combustible inorganic residue (ash).
This is a standard procedure in food science, environmental analysis, coal testing, and pharmaceutical quality control to determine mineral or filler content.
Materials Science and Heat Treatment
The furnace provides the controlled, high-temperature environment needed to alter the physical properties of materials.
This includes annealing, hardening, and tempering steel and other alloys. It is also used for sintering ceramics, fusing glass, and applying enamel coatings.
Analytical Sample Preparation
In analytical chemistry, a muffle furnace is used to prepare samples for further analysis.
This can involve determining a sample's moisture and volatile matter content by heating it to specific temperatures and measuring the weight loss. It is also used for melting point analysis and breaking down samples for elemental analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool with specific operational characteristics.
Heating and Cooling Rates
Because the heat is transferred indirectly to the sample, muffle furnaces can have slower heating and cooling cycles compared to other heating methods. This must be factored into process times.
Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace operates in a normal air atmosphere. If a process requires an inert or reactive gas environment (like nitrogen or argon), a specialized furnace with gas-purging capabilities is necessary.
Energy Consumption
Reaching temperatures often exceeding 1000°C (1800°F) requires a significant amount of energy. They are powerful but not always the most energy-efficient choice for lower-temperature applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating instrument depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is determining the inorganic (ash) content of a sample: The muffle furnace is the standard and essential tool for this procedure.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating metals or firing ceramics without surface contamination: The isolating design of the muffle furnace is critical for achieving a clean, uniform result.
- If your primary focus is simply drying glassware or removing moisture at low temperatures (below 300°C): A standard laboratory oven is a more practical and energy-efficient choice.
Ultimately, leveraging a muffle furnace correctly begins with understanding that its purpose is to provide pure, uniform, high-temperature heat.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Common Uses | Key Benefit of Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Chemistry | Ashing, Moisture/Volatile Content Analysis | Prevents sample contamination for accurate results |
| Materials Science | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering, Sintering | Provides uniform, controlled high-temperature environment |
| Sample Preparation | Fusing Glass, Preparing Samples for Elemental Analysis | Isolates sample from heating elements and fumes |
Ready to achieve precise, contamination-free heating in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, including muffle furnaces designed for reliability and accuracy in applications like ashing and heat treatment. Our experts can help you select the perfect furnace for your specific laboratory needs.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the use of muffle furnace in pharmaceuticals? Essential for Purity & Quality Control
- What is the meaning of debinding? Master the Critical Step to High-Performance Parts
- What is the tolerance of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Temperature Accuracy & Uniformity
- What are the uses of muffle furnaces? Achieve Precise, Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between oven incubator and muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lab Heating Tool



















