At its core, a retort furnace is a specialized type of heat-treating furnace distinguished by its internal sealed chamber, known as a retort. This design is not for general heating but for processes that require a highly controlled gas atmosphere. Its primary use is to modify the surface properties of materials, particularly metals, through processes like carburizing and nitriding, without allowing oxidation or other unwanted reactions.
The defining function of a retort furnace is its ability to isolate a workpiece inside a sealed container (the retort). This allows you to introduce specific reactive or inert gases, fundamentally changing the material's properties in a precise and repeatable way.
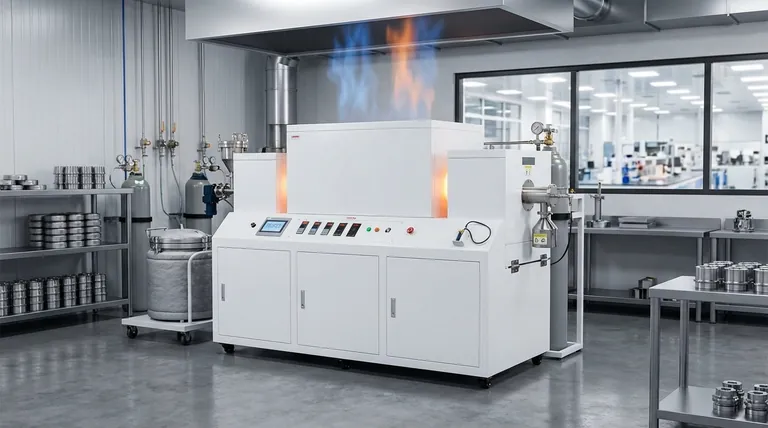

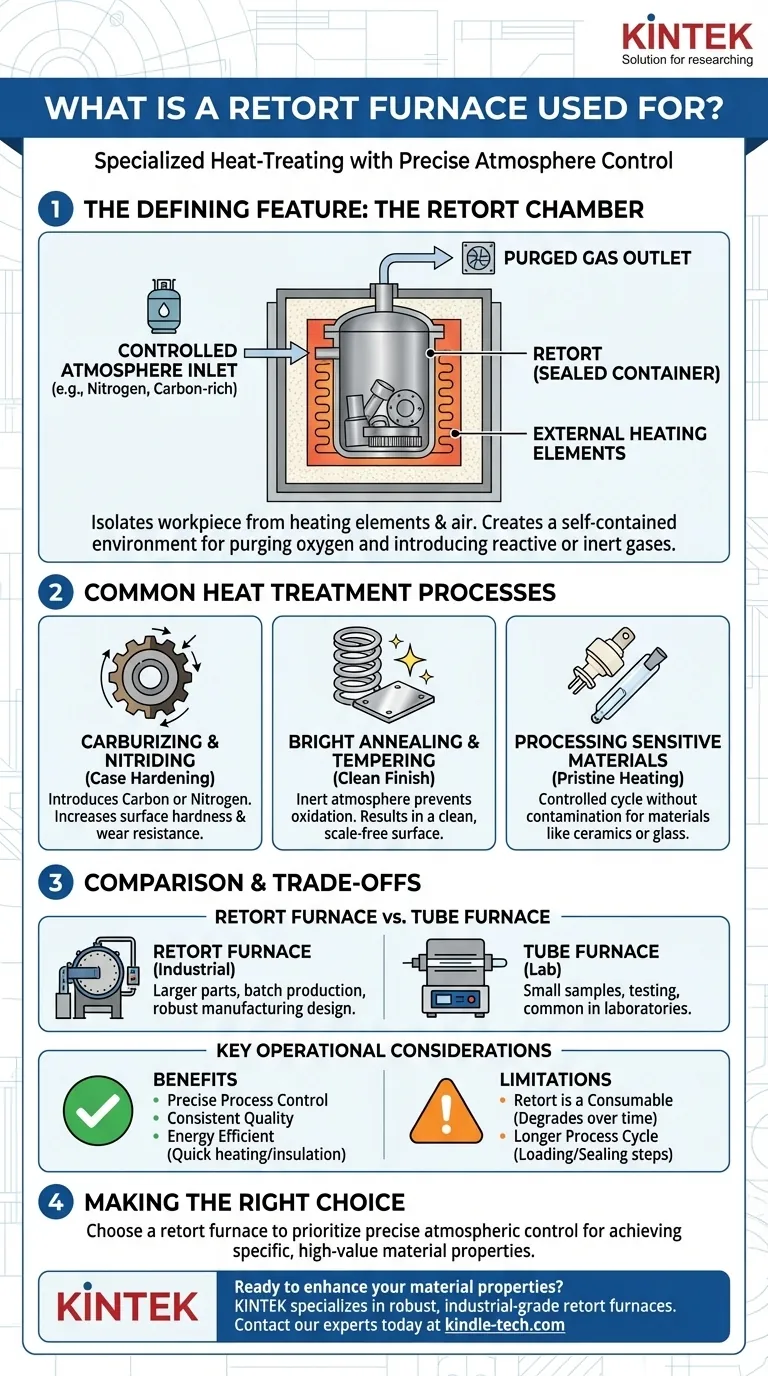
The Defining Feature: The Retort Chamber
A retort furnace's unique capabilities stem directly from the design of the retort itself. Understanding this component is key to understanding the furnace's purpose.
What is a Retort?
The retort is a cylindrical or box-shaped container, typically made of high-temperature metal alloys. The parts to be heat-treated are placed inside this container, which is then sealed.
The entire sealed retort is then placed inside the furnace and heated externally, either vertically or horizontally.
How It Enables Atmosphere Control
By isolating the workpiece from the furnace's heating elements (whether electric or gas-fired), the retort creates a self-contained environment.
This isolation allows operators to purge the oxygen from the chamber and introduce a specific gas atmosphere. This is critical for processes where interaction with the air would be detrimental, such as preventing oxidation, or for processes that rely on a chemical reaction with a specific gas.
Common Heat Treatment Processes
The ability to control the atmosphere makes retort furnaces essential for several key industrial applications.
Carburizing and Nitriding: These are case-hardening processes. A carbon-rich gas (for carburizing) or a nitrogen-rich gas (for nitriding) is introduced into the retort, causing carbon or nitrogen to diffuse into the surface of a steel part, making it significantly harder and more wear-resistant.
Annealing and Tempering: While many furnaces can perform annealing, using a retort furnace ensures the process happens in an inert atmosphere. This prevents the formation of scale or oxides on the material's surface, resulting in a clean, bright finish, as seen when annealing soft iron shot.
Processing Sensitive Materials: Materials like certain ceramics or glass can be treated in a retort furnace to ensure a pristine, controlled heating and cooling cycle without contamination from the ambient air or combustion byproducts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a retort furnace is not a universal solution. Its specialized nature comes with specific advantages and considerations compared to other furnace types.
Retort Furnace vs. Tube Furnace
A tube furnace is also used for controlled atmosphere processes but is typically smaller and more common in laboratory settings for testing or analyzing small samples.
A retort furnace is a more robust, industrial apparatus designed for treating larger parts or batch production. It is built for the rigors of manufacturing environments.
Key Operational Benefits
Compared to older or less advanced methods, modern retort furnaces provide significant advantages. They often feature quicker heating times and superior insulation, which leads to decreased fuel or electricity consumption.
This efficiency, combined with the precise process control, improves the consistency and quality of the treated parts.
Limitations to Consider
The retort itself is a consumable component. It is subject to extreme thermal stress and will eventually degrade, requiring replacement.
The process of loading, sealing, and purging the retort also adds steps to the production cycle compared to simply placing a part in an open-air furnace. This makes it less suitable for processes where atmosphere control is not a strict requirement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on the desired outcome for your material. The retort furnace excels at atmosphere-dependent surface modification.
- If your primary focus is case hardening metals (carburizing, nitriding): A retort furnace is the standard and most effective tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is bright annealing or tempering without oxidation: A retort furnace provides superior results by guaranteeing an inert environment.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab heating or analyzing small samples: A tube furnace is likely a more versatile and appropriate choice.
Ultimately, choosing a retort furnace is a decision to prioritize precise atmospheric control for achieving specific, high-value material properties.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Primary Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Sealed Retort Chamber | Isolates workpiece for precise atmosphere control | Carburizing, Nitriding (Case Hardening) |
| Inert/Reactive Gas Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation; enables chemical reactions | Bright Annealing, Tempering |
| Industrial-Scale Design | Batch processing of larger parts | Heat-treating metals, processing sensitive materials |
Ready to enhance your material properties with precise atmospheric control?
KINTEK specializes in robust, industrial-grade retort furnaces designed for demanding applications like carburizing, nitriding, and bright annealing. Our equipment ensures consistent, high-quality results by providing the exact gas environment your process requires.
Whether you are hardening metal components or annealing sensitive materials, our expertise in lab equipment can help you achieve superior surface properties and operational efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK retort furnace can meet your specific laboratory or production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies
- What are the main types of biomass conversion processes? Unlock the Best Pathway for Your Energy Needs
- How is a high-temperature calcination furnace utilized in BZY20 Sol-gel? Achieve Pure Cubic Perovskite Phases
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- At what temperature is conventional pyrolysis done? Unlock the Right Temperature for Your Desired Product



















