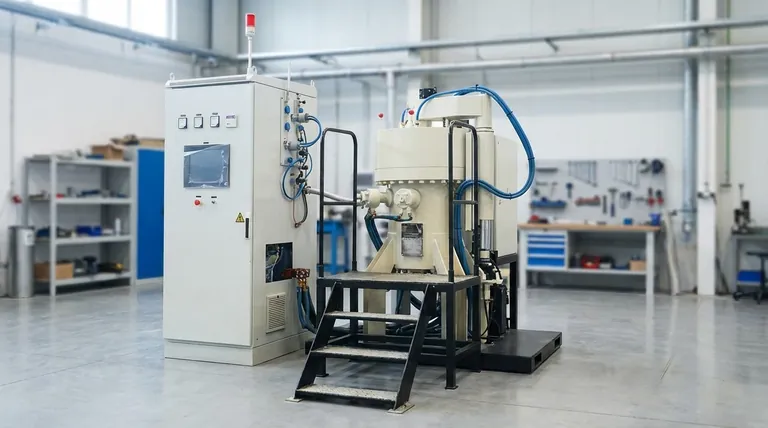
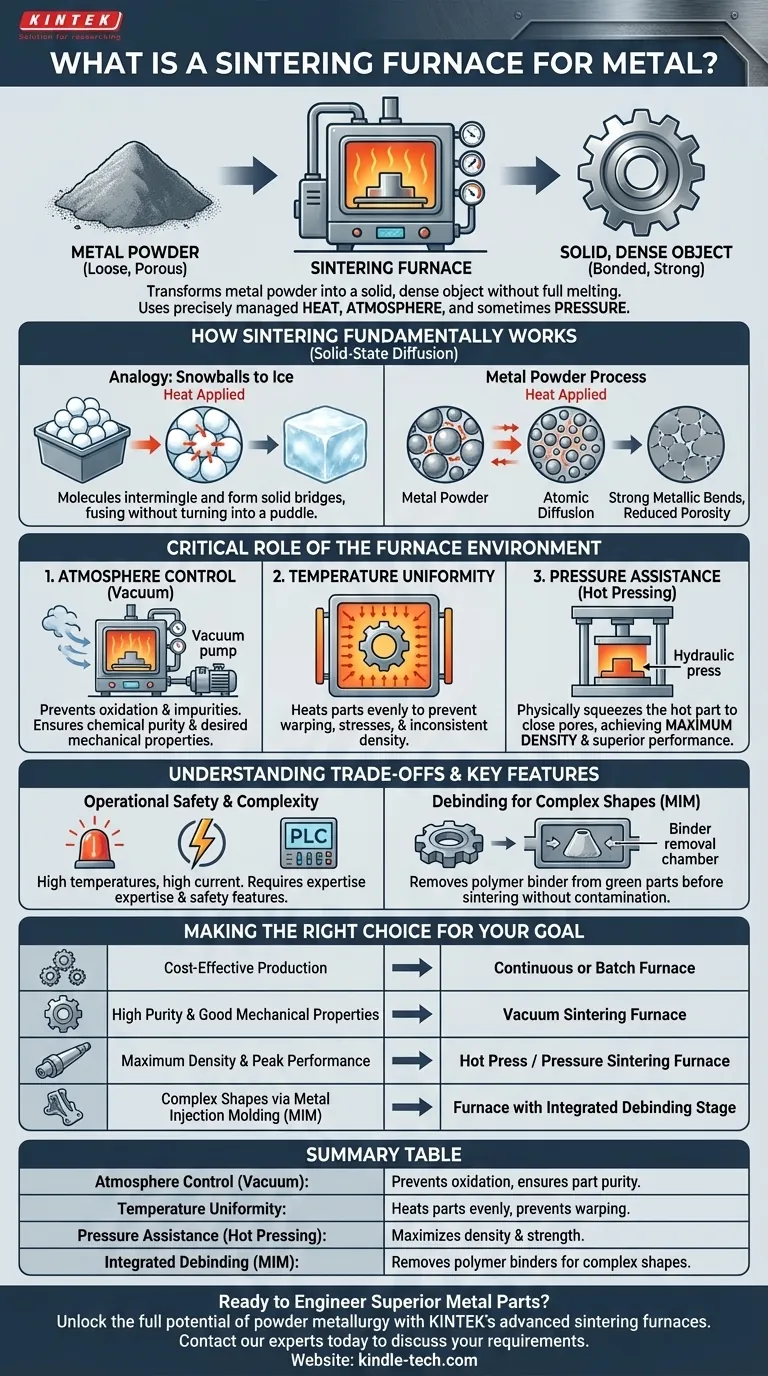
In essence, a metal sintering furnace is a highly controlled industrial oven that transforms metal powder into a solid, dense object without melting it completely. It uses precisely managed heat, atmosphere, and sometimes pressure to cause the individual powder particles to bond together at an atomic level, a process known as sintering. This technology is the cornerstone of powder metallurgy, enabling the creation of complex, near-net-shape metal parts.
A sintering furnace is not simply a hot box; it is a sophisticated system designed to manipulate a material's microstructure. Its primary function is to create a controlled environment where powdered metal can be fused into a strong, functional component, often with properties that are difficult to achieve through traditional casting or machining.

How Sintering Fundamentally Works
The process is more nuanced than simply heating a material. It relies on a principle called solid-state diffusion, which happens at temperatures below the metal's melting point.
The Principle of Atomic Diffusion
Imagine a bin of tightly packed snowballs on a cold day. If the temperature rises just slightly, the outer molecules of each snowball become more active. Where the snowballs touch, these molecules begin to intermingle and form solid ice bridges, fusing the individual balls into a single, solid mass without ever turning into a puddle of water.
Sintering works in a similar way. The furnace heats the compacted metal powder, giving the atoms enough energy to migrate across the boundaries of the individual particles, creating strong metallic bonds and turning the loose powder into a solid part.
The Goal: Density and Strength
As the particles bond, the gaps (or pores) between them shrink. The ultimate goal of sintering is to eliminate this porosity and achieve a part that is as dense and strong as possible. The furnace's features are all designed to optimize this process.
The Critical Role of the Furnace Environment
The quality of a sintered part is entirely dependent on the conditions inside the furnace. Modern furnaces offer precise control over three key variables: atmosphere, temperature, and pressure.
Controlling the Atmosphere: The Power of Vacuum
Most high-performance sintering is done in a vacuum. By removing air, the furnace prevents oxygen from reacting with the hot metal, which would cause oxidation (like rust) and other impurities.
A vacuum environment ensures the chemical purity of the final part, which is critical for achieving desired mechanical properties like strength and fatigue resistance.
The Impact of Temperature Uniformity
The furnace must heat the part evenly from all sides. If one area is hotter than another, it will sinter faster, leading to internal stresses, warping, or inconsistent density.
Advanced furnaces use specialized heating elements and insulation materials to guarantee excellent temperature uniformity throughout the hot zone, ensuring the part sinters predictably.
The Role of Pressure: Achieving Maximum Density
While some parts can be made with heat alone, applying external pressure during the heating cycle dramatically improves the final density. This is known as pressure-assisted sintering or hot pressing.
By physically squeezing the part while it is hot and malleable, this process closes remaining pores more effectively, resulting in superior mechanical performance. This is essential for components in demanding applications like aerospace or medical implants.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Features
Sintering furnaces are complex and powerful pieces of equipment, and their operation involves significant considerations.
Operational Safety is Paramount
These furnaces operate at extremely high temperatures for long periods and draw very high electrical current. Safety is a primary design feature, incorporating over-temperature alarms, automatic pressure protection, and interlocks to prevent accidents.
Complexity and Process Control
A modern furnace is an interdisciplinary system combining materials science, vacuum technology, high-pressure systems, and sophisticated PLC controls. They are not simple "plug-and-play" machines.
Achieving repeatable, high-quality results requires expertise in process development and a deep understanding of how the furnace parameters affect the final material properties.
Debinding for Complex Shapes
For manufacturing methods like Metal Injection Molding (MIM), the initial "green" part contains a polymer binder mixed with the metal powder. This binder must be removed before sintering.
Many furnaces incorporate a special, sealed "debinding muffle" to gently heat the part and remove this binder without contaminating the furnace's primary heating chamber.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right sintering process depends entirely on the requirements of the final component.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of standard parts: A continuous or batch furnace with basic atmospheric control may be sufficient.
- If your primary focus is high purity and good mechanical properties: A vacuum sintering furnace is the industry standard for producing clean, strong parts.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and peak performance for critical applications: A hot press or pressure sintering furnace is necessary to achieve near-theoretical density.
- If your primary focus is creating complex shapes via Metal Injection Molding (MIM): A furnace equipped with an integrated debinding stage is essential for a successful process.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering process unlocks the ability to engineer and manufacture next-generation metal components with unparalleled precision and performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Purpose & Benefit |
|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control (Vacuum) | Prevents oxidation, ensures part purity and superior mechanical properties. |
| Temperature Uniformity | Heats parts evenly to prevent warping and ensure consistent density. |
| Pressure Assistance (Hot Pressing) | Maximizes density and strength for critical applications. |
| Integrated Debinding (for MIM) | Removes polymer binders for complex shapes without contamination. |
Ready to Engineer Superior Metal Parts?
Unlock the full potential of powder metallurgy for your laboratory or production line. KINTEK specializes in advanced sintering furnaces and lab equipment, providing the precise control you need to achieve maximum part density, purity, and performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific metal sintering requirements and discover the right solution for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve high-density NTC ceramics with superior stability.
- What are the key functions of a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Produce High-Density UN Ceramic Pellets
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context



















