In short, a powder metallurgy (P/M) sintering furnace is a specialized, high-temperature oven that transforms a fragile, compacted metal powder shape into a solid, high-strength component. It accomplishes this through a precise heating process that bonds the powder particles together on a microscopic level without ever melting the material.
The critical function of a sintering furnace is not simply to heat metal, but to provide the controlled thermal energy necessary for atomic diffusion. This process essentially "welds" individual powder particles into a unified, dense structure, giving the final part its strength and integrity.

From Powder to Part: The Role of the Sintering Furnace
To understand the furnace's purpose, you must first understand its place in the powder metallurgy workflow. The process turns loose powder into a finished, functional component in two primary stages: compaction and sintering.
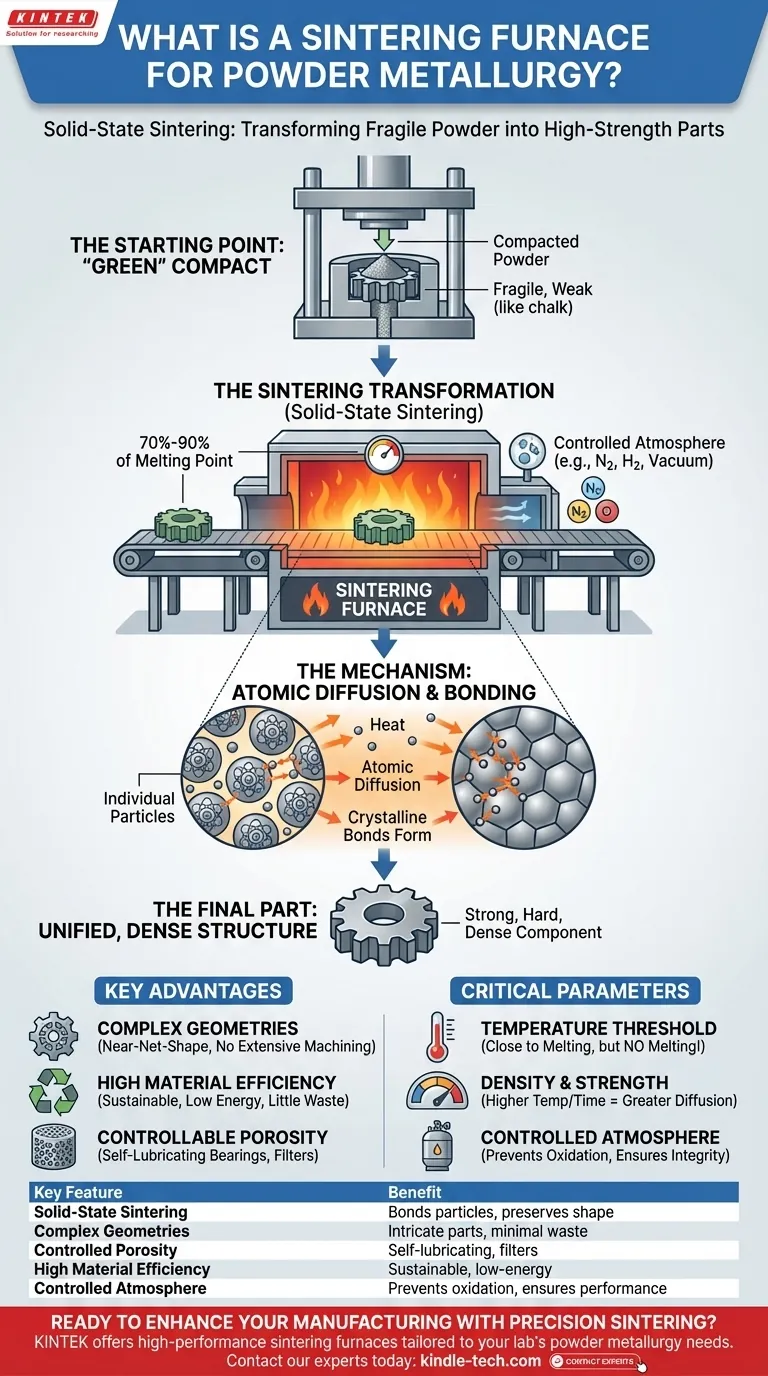
The Starting Point: The "Green" Compact
The journey begins by pressing metal powder into a rigid die or mold under immense pressure. The resulting part, known as a "green" compact, holds the desired shape but is mechanically weak and brittle, similar in fragility to a piece of chalk.
The Sintering Transformation
The green compact is then placed into the sintering furnace. The furnace heats the component to a temperature typically between 70% and 90% of the metal's melting point.
This process is known as solid-state sintering. The part is held at this elevated temperature for a specific duration, allowing a remarkable transformation to occur.
The Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion and Bonding
The heat from the furnace acts as a catalyst, giving the atoms within the individual powder particles enough energy to move. Atoms diffuse across the boundaries where particles touch one another.
This atomic migration creates strong, crystalline bonds between the particles. What was once a collection of individual grains becomes a single, solid piece of material with significant strength, hardness, and density.
Key Advantages Enabled by the Sintering Process
The sintering furnace is the key that unlocks the unique advantages of powder metallurgy as a manufacturing method. It finalizes the part, locking in the benefits created during the initial powder compaction stage.
Creating Complex Geometries
The initial pressing process can create highly complex internal and external shapes with extreme precision. The sintering process solidifies these intricate designs without the need for extensive post-process machining.
High Material Efficiency and Sustainability
Powder metallurgy is a near-net-shape process. Very little material is wasted, as the powder is formed directly into the final part's geometry. Because the metal is never melted, the process also consumes significantly less energy than casting or forging.
Controllable Porosity for Unique Properties
Unlike other metal-forming methods, sintering allows for precise control over the final part's porosity. This is a powerful feature, enabling the creation of self-lubricating bearings (which are impregnated with oil) and components designed for vibration dampening.
Understanding the Critical Parameters
Operating a sintering furnace effectively requires mastering a few key variables. Mismanaging these can compromise the quality and performance of the final component.
The Temperature Threshold
The single most important parameter is temperature. The goal is to get as close to the melting point as possible without actually reaching it. Accidental melting would cause the part to lose its shape and destroy its engineered properties.
The Impact on Density and Strength
Generally, higher sintering temperatures and longer times in the furnace lead to more atomic diffusion. This results in a denser, stronger final part as the voids between the original powder particles shrink.
The Necessity of a Controlled Atmosphere
Metal powders at high temperatures are extremely susceptible to oxidation, which would ruin the component. Sintering furnaces must maintain a tightly controlled atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen, hydrogen, or a vacuum) to prevent oxygen from reacting with the metal.
How Sintering Delivers on Specific Engineering Goals
Your decision to use a P/M process hinges on what you need to achieve. The sintering furnace is the final step that delivers on these goals.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production of complex parts: Sintering is ideal for creating repeatable, intricate shapes that require little to no final machining.
- If your primary focus is creating self-lubricating or filtering components: The process gives you direct control over the final part's porosity, a feature unmatched by most other metalworking methods.
- If your primary focus is material efficiency and sustainability: Sintering is a "green" technology that drastically reduces material waste and energy consumption compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing.
Ultimately, the sintering furnace is the critical link that converts the potential of metal powder into the performance of a finished product.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Solid-State Sintering | Bonds particles without melting, preserving shape and properties. |
| Complex Geometries | Enables production of intricate, near-net-shape parts with minimal waste. |
| Controlled Porosity | Allows creation of self-lubricating bearings and filters. |
| High Material Efficiency | A sustainable, low-energy alternative to casting or forging. |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation, ensuring part integrity and performance. |
Ready to enhance your manufacturing capabilities with precision sintering?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable sintering furnaces tailored to your laboratory's specific powder metallurgy needs. Our solutions deliver the precise temperature control and atmosphere management required for strong, consistent, and complex parts.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK sintering furnace can optimize your production process, reduce waste, and unlock new design possibilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs



















