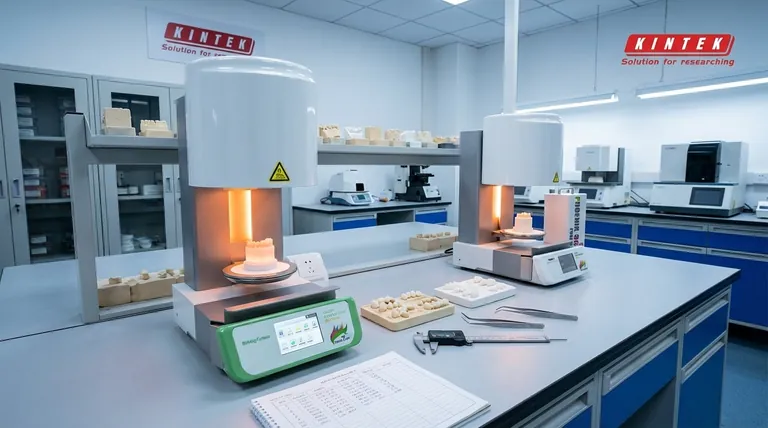
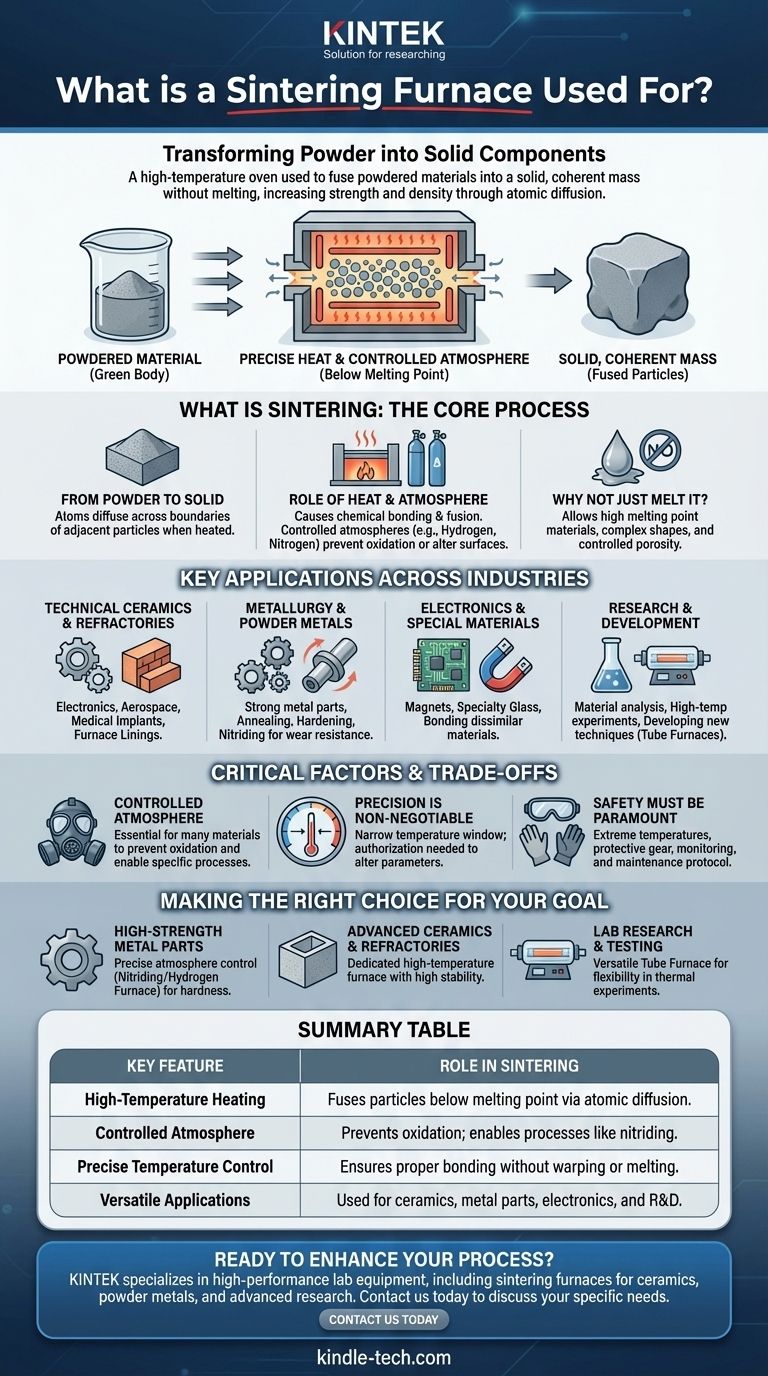
In essence, a sintering furnace is a high-temperature oven used to transform powdered material into a solid, coherent mass without melting it. This process, known as sintering, is fundamental for creating a vast range of products, from high-strength technical ceramics and metal parts to specialized electronic components. It achieves this by heating the material to a precise temperature that allows the individual particles to fuse together, dramatically increasing the object's strength and density.
The core function of a sintering furnace is not to melt material, but to apply precisely controlled heat and atmosphere to bond particles together. This technique is essential for manufacturing durable components from powders, especially those made from materials with extremely high melting points.

What is Sintering? A Look at the Core Process
To understand what a sintering furnace does, you must first understand the process of sintering itself. It's a method of thermal treatment that fundamentally changes a material's properties.
From Powder to Solid
Sintering begins with a compacted mass of powder, often referred to as a "green body." When this compact is heated inside the furnace to a point below its melting temperature, the atoms in the particles begin to diffuse across the boundaries of adjacent particles.
The Role of Heat and Atmosphere
This atomic diffusion causes the particles to chemically bond and fuse, forming a solid piece. The furnace provides not only the high heat required but often a specific, controlled atmosphere (like hydrogen or nitrogen) to prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation or to actively alter the material's surface, as in nitriding.
Why Not Just Melt It?
Sintering is preferred over melting for several reasons. It allows for the creation of parts from materials with exceptionally high melting points that are difficult or impossible to cast. It also enables the production of parts with controlled porosity and complex shapes that would be difficult to achieve otherwise.
Key Applications Across Industries
The precise control offered by sintering furnaces makes them indispensable tools in numerous high-tech and industrial fields.
Technical Ceramics and Refractories
These furnaces are used to produce advanced ceramics for electronics, aerospace, and medical implants. They also create refractories—materials highly resistant to heat—used to line other industrial furnaces and kilns.
Metallurgy and Powder Metals
In metallurgy, sintering is used to create strong, complex metal parts from powders. Specialized furnaces also perform critical heat treatments like annealing (softening metal), hardening, and nitriding, a process that diffuses nitrogen into a metal's surface to create an incredibly hard and wear-resistant case.
Electronics and Special Materials
Many electronic components, magnets, and specialty glass products rely on sintering to achieve their final properties. The process is critical for bonding dissimilar materials or creating composites with unique characteristics.
Research and Development
In scientific institutes and universities, smaller-scale tube furnaces are used for a wide range of thermal processes. They offer the versatility needed for high-temperature experiments, material analysis, and developing new sintering techniques.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
While powerful, operating a sintering furnace requires a deep understanding of the process and its risks. The success of the outcome is not just about heat, but about absolute precision.
The Need for a Controlled Atmosphere
For many materials, especially metals, heating in the presence of oxygen is catastrophic, leading to oxidation and ruining the final product. An atmosphere-controlled furnace (e.g., a hydrogen furnace) replaces the air with a specific gas to protect the material or actively participate in the chemical process.
Precision is Non-Negotiable
Sintering occurs within a specific temperature window. Too low, and the particles won't bond effectively; too high, and the part may warp or melt. The parameters set on the furnace are based on precise material science and should never be altered without authorization.
Safety Must Be Paramount
Operating equipment at extreme temperatures poses significant risks. Operators must use appropriate protective gear, continuously monitor the furnace for any abnormalities, and only perform maintenance when the equipment is fully disconnected and cooled.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The type of furnace required is dictated entirely by the material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is producing high-strength, wear-resistant metal parts: A furnace with precise atmosphere control, such as a nitriding or hydrogen furnace, is necessary to manage material chemistry and hardness.
- If your primary focus is creating advanced ceramics or refractory materials: A dedicated high-temperature furnace capable of reaching and holding extreme heat levels with high stability is essential.
- If your primary focus is laboratory research and material testing: A versatile tube furnace often provides the flexibility needed for a wide range of thermal experiments on a smaller scale.
Ultimately, a sintering furnace is a precision instrument designed to transform powdered materials into robust, functional components through the controlled application of heat.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Role in Sintering |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Heating | Fuses particles below melting point via atomic diffusion. |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation; enables processes like nitriding. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Ensures proper bonding without warping or melting. |
| Versatile Applications | Used for ceramics, metal parts, electronics, and R&D. |
Ready to enhance your material synthesis or production process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including sintering furnaces tailored for ceramics, powder metals, and advanced research. Our experts will help you select the right furnace to achieve superior strength, density, and material properties. Contact us today to discuss your specific sintering needs and discover the KINTEK advantage!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics



















