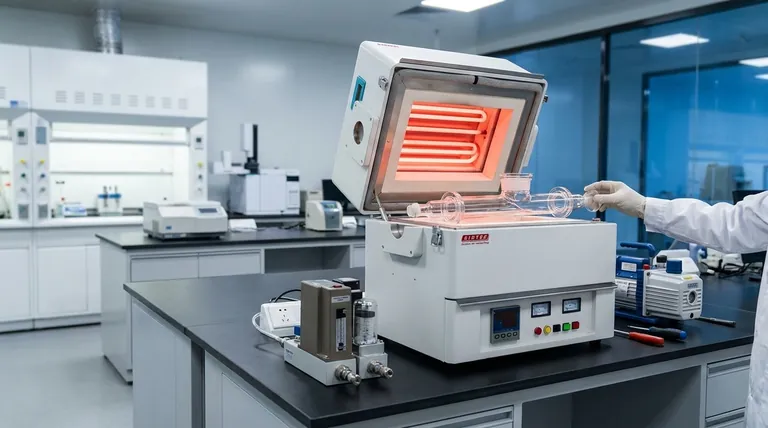
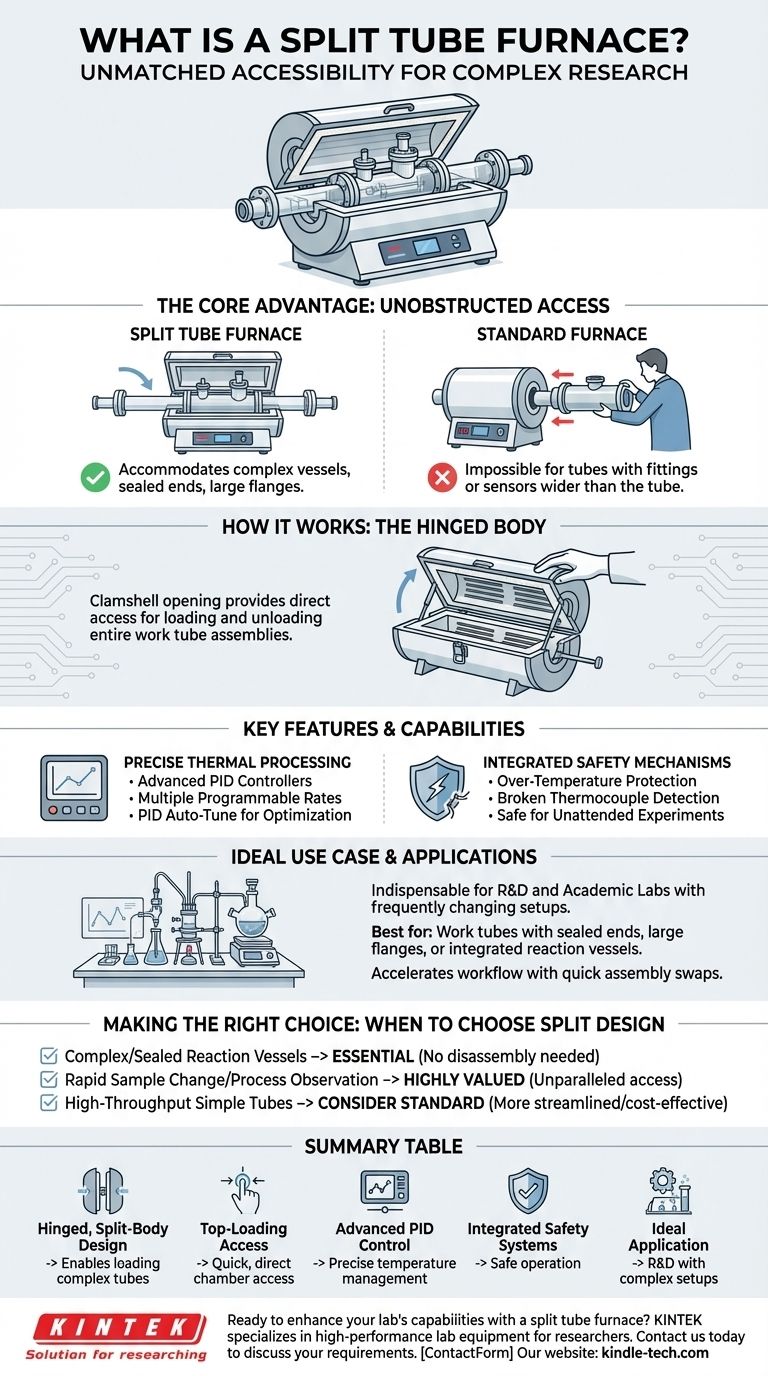
In essence, a split tube furnace is a high-temperature laboratory furnace whose body is built in two halves connected by a hinge. This design allows the heating chamber to be opened completely, providing direct and easy access for placing or removing the work tube and sample materials.
The critical advantage of a split tube furnace is not just convenience, but its unique ability to accommodate work tubes with pre-attached flanges, end-caps, or complex reaction vessels that are physically impossible to slide into a standard, non-split furnace.

The Core Design Principle: Unobstructed Access
The defining characteristic of a split tube furnace is its mechanical design, which directly addresses the limitations of conventional solid-body furnaces.
How It Works: The Hinged Body
A split tube furnace consists of a cylindrical heating chamber that is literally split lengthwise into two sections.
These halves are joined by a robust hinge on one side and a latch on the other. This allows the top half to be opened like a clamshell, often assisted by pneumatic struts for smooth and safe operation.
The Problem It Solves
Standard tube furnaces require the user to slide a work tube in from one end. This process becomes impossible if the tube has fittings, sensors, or flanges that are wider than the tube itself.
The split design completely eliminates this barrier. It allows the entire work tube apparatus to be placed directly into the heating chamber from the top, after which the furnace is closed around it.
Key Features and Capabilities
Beyond its unique physical access, a split tube furnace incorporates sophisticated control systems expected in modern laboratory equipment.
Precise Thermal Processing
These furnaces feature advanced PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers that provide extremely precise temperature management.
Users can program multiple heating rates, cooling rates, and dwell times into a single process. Features like PID Auto-Tune help the system learn and optimize its performance for a specific thermal load, ensuring accuracy and repeatability.
Integrated Safety Mechanisms
Given their common use in research for unattended or long-duration experiments, safety is paramount.
Standard features include over-temperature protection, which shuts down power if a set limit is exceeded, and broken thermocouple protection, which detects a sensor failure and prevents a dangerous thermal runaway event.
Understanding the Primary Use Case
While versatile, the split tube furnace is purpose-built for specific applications where its design offers a clear advantage.
When to Choose a Split Tube Furnace
This design is indispensable when your experimental setup involves work tubes with sealed ends, large flanges, or integrated reaction vessels.
It is also highly valued in R&D and academic labs where experimental setups are frequently changed. The ability to quickly swap out entire tube assemblies, rather than just samples, significantly accelerates workflow.
What to Consider
The primary benefit is access. If your process involves simple, uniform tubes that can be easily loaded from the end, the added mechanical complexity of a split design may not be necessary.
The hinged mechanism, while robust, introduces a seam in the insulation and heating element array. While high-quality models are engineered to minimize this, ensuring temperature uniformity across the seam is a key design consideration for manufacturers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace type depends entirely on your experimental workflow and the physical nature of your samples and apparatus.
- If your primary focus is working with complex or sealed reaction vessels: The split tube design is essential, as it allows you to place your entire apparatus without disassembly.
- If your primary focus is rapid sample changeover or process observation: The ability to quickly open the chamber provides unparalleled access compared to waiting for a standard furnace to cool.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput processing of simple, uniform tubes: A standard, non-split tube furnace may offer a more streamlined and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, choosing a split tube furnace is a decision to prioritize accessibility and experimental flexibility for complex setups.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Hinged, Split-Body Design | Enables loading of tubes with pre-attached flanges or complex vessels. |
| Top-Loading Access | Provides quick, direct access to the heating chamber without end-loading. |
| Advanced PID Control | Ensures precise temperature management and repeatable results. |
| Integrated Safety Systems | Includes over-temperature and broken thermocouple protection for safe operation. |
| Ideal Application | Essential for R&D labs frequently changing complex experimental setups. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a split tube furnace?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including split tube furnaces designed for researchers and technicians who need maximum accessibility and precision. Our furnaces are engineered to handle your most complex setups with ease, saving you time and simplifying your workflow.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your specific application requirements. Let our experts help you find the perfect solution to accelerate your research and achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a temperature-controlled tube furnace influence the performance of biochar adsorbents? Optimize Pore Structure
- What function does a high-temperature tube furnace serve in alkali fusion hydroxide recovery? Precision Thermal Control
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of SPAN? Optimize Your Li-S Battery Research Today
- How do vertical split tube furnaces and preheaters facilitate SCWO? Achieve Optimal Supercritical Water Oxidation
- Why is high-temperature hydrogen reduction in a tube furnace necessary before carbon nanofiber growth? Catalyst Activation Explained



















