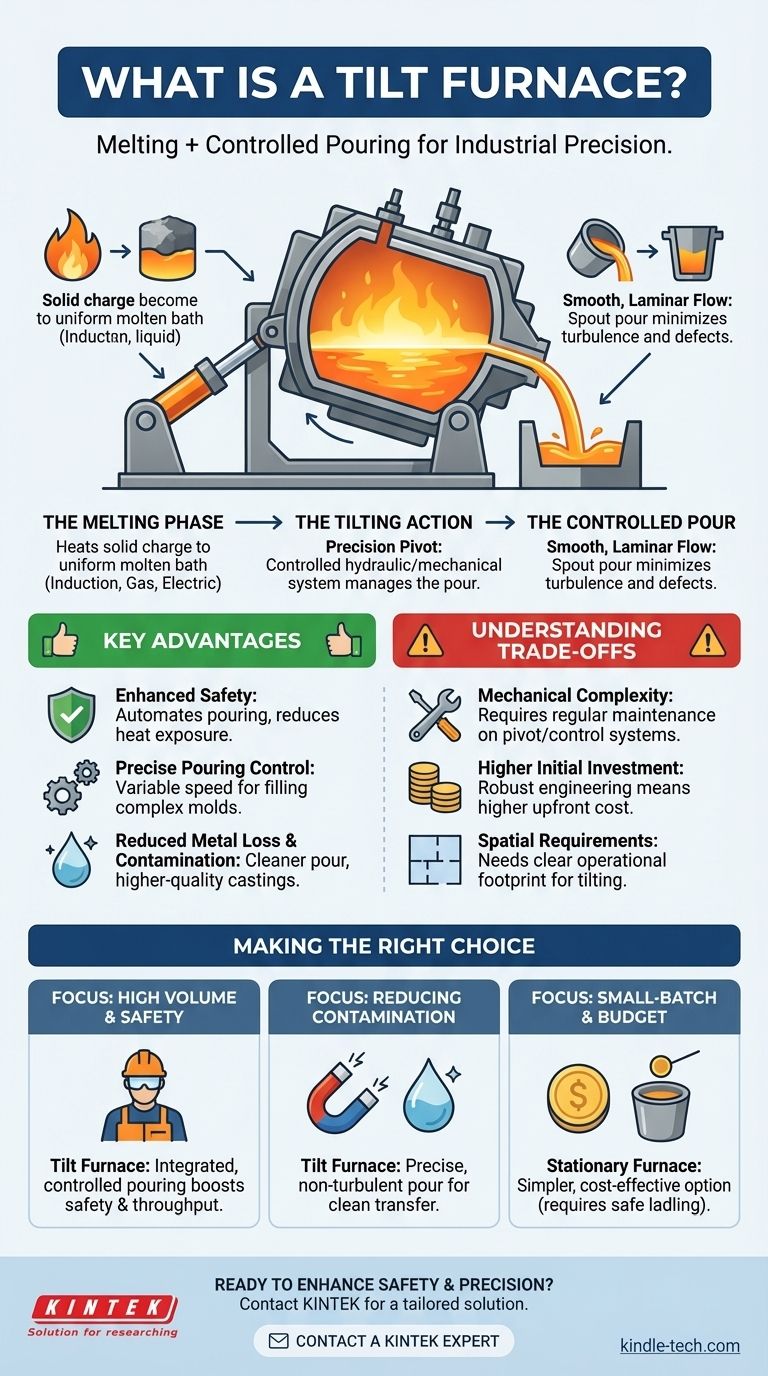
At its core, a tilt furnace is an industrial furnace designed for melting materials—most commonly metals—that can be physically tilted to pour out its molten contents. Unlike stationary furnaces that require tapping or ladling, the entire body of a tilt furnace pivots on an axis, using a hydraulic or mechanical system to precisely control the pouring process into a mold, ladle, or another vessel.
The defining characteristic of a tilt furnace is not just its ability to melt material, but its integrated function of providing a safe, controlled, and efficient method for pouring that molten material directly from the furnace vessel.
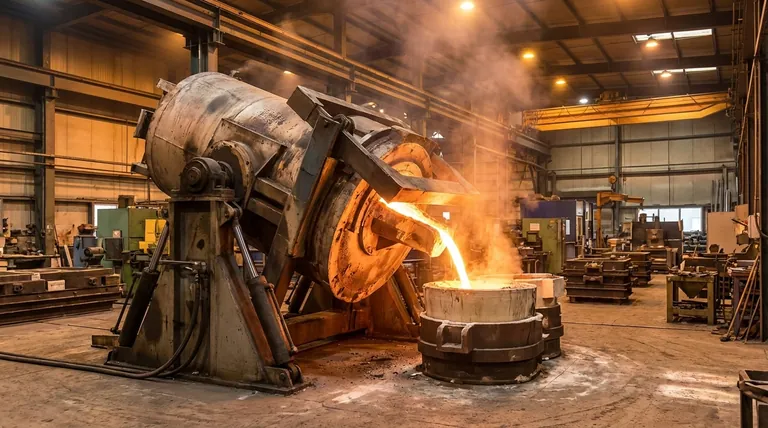

The Core Mechanism: How a Tilt Furnace Works
A tilt furnace integrates two critical industrial processes into a single piece of equipment: melting and transferring. Understanding its dual function is key to appreciating its value.
The Melting Phase
Like other furnaces, a tilt furnace first heats a solid charge until it becomes liquid. This is typically accomplished through induction heating, gas burners, or electrical resistance, depending on the furnace's specific design and application. The primary goal during this phase is to achieve a uniform temperature and homogenous molten bath.
The Tilting Action
Once the material is molten, the furnace's unique feature comes into play. A powerful hydraulic or mechanical system is activated to pivot the entire furnace crucible and its supporting structure. This action is precise and can be controlled with variable speed, allowing the operator to manage the pour with exceptional accuracy.
The Controlled Pour
The tilting motion allows the molten material to flow smoothly over a pour spout. This process is far more controlled than manual tapping, minimizing turbulence and slag inclusion. It is akin to carefully pouring liquid from a massive, high-temperature kettle, ensuring the molten metal is transferred safely and efficiently.
Key Advantages in Industrial Applications
The integrated design of a tilt furnace offers distinct advantages, particularly in foundry and casting operations where the quality and handling of molten metal are paramount.
Enhanced Safety
By automating the pouring process, tilt furnaces significantly reduce operator exposure to extreme heat and the risk of splashing molten metal. This eliminates one of the most hazardous tasks associated with traditional stationary furnaces.
Precise Pouring Control
The ability to start, stop, and vary the speed of the tilt gives operators unmatched control over the pouring rate. This precision is critical for filling complex molds and preventing defects in the final cast product.
Reduced Metal Loss and Contamination
The smooth, laminar flow from a tilt furnace minimizes oxidation and the mixing of slag into the molten metal stream. This results in a cleaner pour, higher-quality castings, and less wasted material that needs to be skimmed off or remelted.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, tilt furnaces are not the universal solution for every melting application. Their benefits come with specific considerations.
Mechanical Complexity
The tilting mechanism, whether hydraulic or electromechanical, adds a layer of complexity compared to a stationary furnace. This system requires regular maintenance on pivot points, cylinders, and control systems to ensure reliable and safe operation.
Higher Initial Investment
The robust engineering required for the tilting frame and actuation system means that tilt furnaces typically have a higher upfront capital cost than stationary furnaces of a similar capacity.
Spatial Requirements
The furnace requires a clear, defined operational footprint to accommodate the tilting motion. Facilities must be designed with adequate clearance around the furnace to prevent any interference or safety hazards during the pour.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the appropriate furnace depends entirely on the specific goals of your operation, balancing cost, safety, and production quality.
- If your primary focus is high-volume casting and operator safety: A tilt furnace is an excellent choice due to its integrated, controlled pouring which enhances both safety and throughput.
- If your primary focus is reducing metal contamination and improving casting quality: The precise, non-turbulent pour from a tilt furnace makes it a superior option for achieving clean metal transfer.
- If your primary focus is small-batch melting on a limited budget: A simpler, stationary crucible furnace may be a more cost-effective solution, provided you have safe procedures for tapping or ladling.
Ultimately, understanding that a tilt furnace solves the problem of both melting and transferring material is the key to leveraging its full operational potential.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Melts materials (e.g., metals) and tilts to pour molten contents. |
| Key Advantage | Integrated, controlled pouring enhances safety and reduces contamination. |
| Ideal For | Foundries and casting operations requiring precise, high-quality pours. |
| Consideration | Higher initial investment and mechanical complexity than stationary furnaces. |
Ready to enhance the safety and precision of your melting process?
A tilt furnace is a significant investment in both operator safety and final product quality. The experts at KINTEK can help you determine if a tilt furnace is the right solution for your specific laboratory or industrial application.
Contact us today to discuss your melting requirements, and let our team provide a tailored solution that maximizes your efficiency and safety. Get in touch with a KINTEK expert now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of rotary furnace? Maximize Uniformity & Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What reaction conditions do high-temperature tube furnaces provide for biochar reduction? Optimize Ore Processing
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What are the advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for MoVOx catalysts? Elevate Uniformity and Crystallinity



















