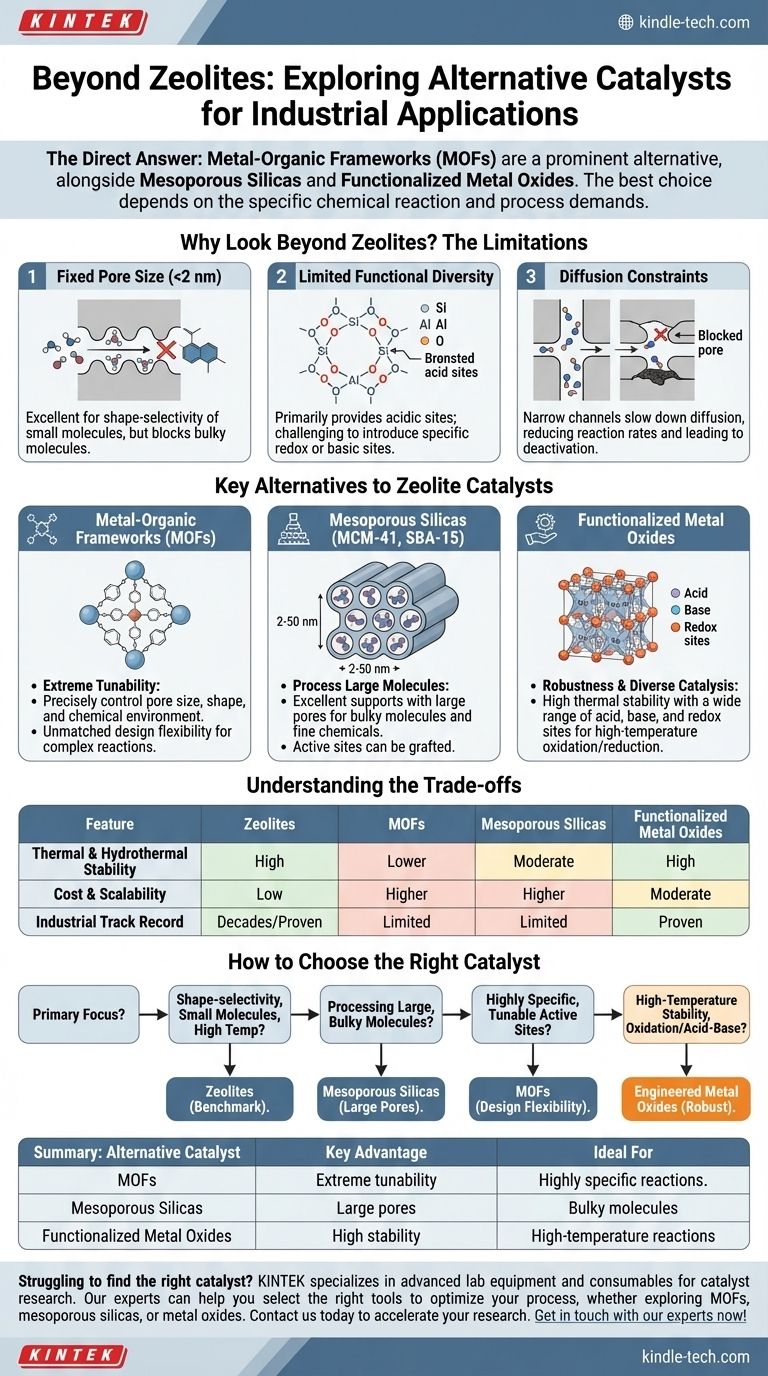
For a direct answer, the most prominent class of alternatives to zeolite catalysts are metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). However, other important classes include mesoporous silicas and functionalized metal oxides. The choice is not about finding a single replacement, but about understanding which material best suits the specific chemical reaction you are targeting.
The core challenge is matching the catalyst's properties—like pore size, stability, and active sites—to the demands of the chemical process. While zeolites are masters of shape-selective catalysis for small molecules, alternatives like MOFs and mesoporous silicas open the door to processing larger molecules and achieving highly tailored chemical functionality.

Why Look Beyond Zeolites?
Zeolites are crystalline aluminosilicates that have dominated industrial catalysis for decades, particularly in oil refining and petrochemistry. Their exceptional performance stems from their uniform micropores and strong acidic sites. However, certain inherent limitations drive the search for alternatives.
The Limitation of Fixed Pore Size
Zeolites have very small pores, typically less than 2 nanometers in diameter. This well-defined structure is a key strength, enabling shape-selectivity by only allowing molecules of a certain size to enter and react.
However, this becomes a major drawback when dealing with larger, "bulky" molecules found in fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and biomass conversion, as they simply cannot fit into the zeolite's active sites.
Limited Functional Diversity
The framework of a traditional zeolite is composed of silicon, aluminum, and oxygen. This primarily provides Brønsted acid sites, which are excellent for many reactions but limiting for others.
Achieving other types of catalytic activity, such as specific redox or basic sites, can be challenging and less efficient compared to materials designed for that purpose.
Diffusion Constraints
Even for molecules that can fit, the narrow channels of a zeolite can slow down the diffusion of reactants and products. This can reduce the overall reaction rate and sometimes lead to catalyst deactivation when pores get blocked by coke or other byproducts.
Key Alternatives to Zeolite Catalysts
No single material replaces zeolites across the board. Instead, different classes of materials offer distinct advantages for specific applications.
Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs)
MOFs are crystalline materials constructed from metal ions or clusters (nodes) connected by organic molecules (linkers). This "building block" approach gives them unprecedented design flexibility.
Their key advantage is extreme tunability. By changing the metal node and organic linker, scientists can precisely control pore size, shape, and chemical environment, creating active sites that are impossible to achieve in zeolites. Their exceptionally high surface areas are also a major benefit.
Mesoporous Silicas (e.g., MCM-41, SBA-15)
These are ordered materials made of amorphous silica, but they possess a highly regular array of much larger pores (mesopores), typically between 2 and 50 nanometers.
Their primary advantage is the ability to process very large molecules. While the silica itself is not highly catalytic, it serves as an excellent, stable support. Active sites can be introduced by grafting functional groups or dispersing metal nanoparticles within the large pores.
Functionalized Metal Oxides
Simple and mixed metal oxides like titania (TiO2), zirconia (ZrO2), and ceria (CeO2) are workhorses of industrial catalysis. Their properties can be engineered by controlling their synthesis to create high surface areas and specific crystalline structures.
Their strengths are their robustness and diverse catalytic properties. They offer excellent thermal stability and can provide a wide range of acid, base, and redox sites, making them ideal for high-temperature oxidation and reduction reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an alternative to a zeolite involves a critical evaluation of practical trade-offs, especially for industrial-scale applications.
Thermal and Hydrothermal Stability
This is the area where zeolites truly excel. They can withstand the harsh, high-temperature, and high-pressure steam environments common in processes like fluid catalytic cracking (FCC).
Many MOFs, by contrast, have lower thermal stability and can break down in the presence of water, especially at high temperatures. While highly stable MOFs exist, this remains a significant hurdle for their widespread industrial adoption.
Cost and Scalability
Zeolites are produced on a massive scale from relatively inexpensive raw materials. Their synthesis is a well-established, mature technology.
The synthesis of many advanced MOFs and mesoporous materials often involves more expensive organic templates or metal precursors and more complex procedures, making them significantly more costly to produce at scale.
Proven Industrial Track Record
Zeolites have a multi-decade history of reliable performance in some of the world's largest industrial processes. This long track record provides a level of confidence and operational knowledge that newer materials lack. Deploying a new catalyst in a billion-dollar facility requires overcoming a significant barrier of proven reliability.
How to Choose the Right Catalyst
Your final choice depends entirely on the specific requirements of your chemical reaction and process conditions.
- If your primary focus is shape-selectivity for small molecules at high temperatures: Zeolites remain the undisputed benchmark due to their rigid microporous structure and exceptional hydrothermal stability.
- If your primary focus is processing large, bulky molecules: Mesoporous silicas (like SBA-15) are the ideal platform, providing ample space for reactions that are impossible in zeolites.
- If your primary focus is creating highly specific, tunable active sites for complex reactions: Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) offer unmatched design flexibility for next-generation catalytic applications.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability for oxidation or acid-base catalysis: Engineered metal oxides provide a robust, reliable, and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, selecting the right catalyst begins not with the material itself, but with a clear understanding of your reaction's specific chemical and physical demands.
Summary Table:
| Alternative Catalyst | Key Advantage | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) | Extreme tunability of pore size & active sites | Highly specific, complex reactions |
| Mesoporous Silicas (MCM-41, SBA-15) | Large pores (2-50 nm) for bulky molecules | Processing large molecules, fine chemicals |
| Functionalized Metal Oxides | High thermal stability & robust performance | High-temperature oxidation/reduction reactions |
Struggling to find the right catalyst for your specific reaction? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for catalyst research and development. Whether you're exploring MOFs, mesoporous silicas, or metal oxides, our experts can help you select the right tools to optimize your process. Contact us today to discuss your catalytic challenges and discover how our solutions can accelerate your research. Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- What functions do laboratory centrifuges and high-shear homogenizers perform? Optimize Your Nano-Modified Composites
- What function do magnetic stirrers and high-shear homogenizers serve? Optimize Core-Shell PCM Synthesis
- What is the function of high-shear dispersion equipment in corona-resistant nanocomposites? Elevate Your Insulation
- What is the necessity of using an industrial-grade high-shear homogenizer for biomass washing? Ensure Process Efficiency
- Why are high-shear mixing or ultrasonic homogenizers necessary for MMT nanocomposites? Unlock True Nano-Reinforcement



















