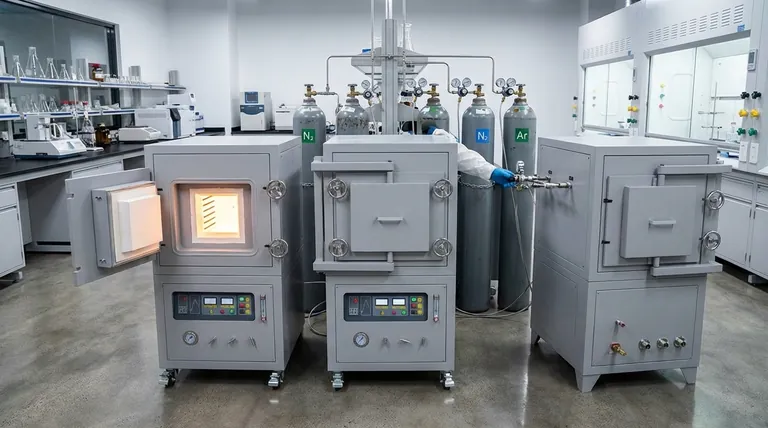
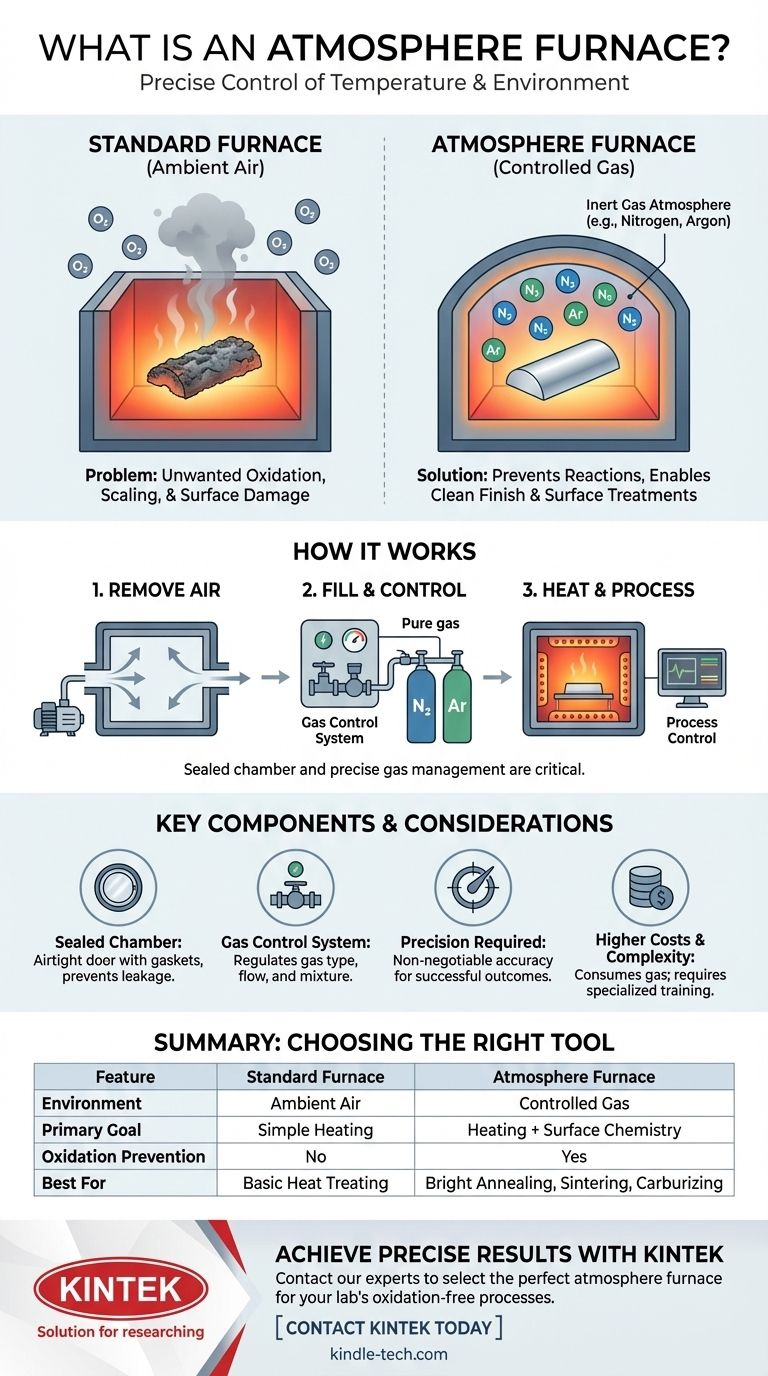
In simple terms, an atmosphere furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven that allows for complete control over the gaseous environment surrounding the material being heated. Unlike a standard furnace that operates in ambient air, this device uses a sealed chamber and a precisely managed gas supply to prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation or to intentionally cause specific surface reactions.
The critical distinction of an atmosphere furnace is not just its ability to heat, but its power to control the chemical environment. This transforms it from a simple oven into a precise tool for materials processing, enabling outcomes that are impossible in an open-air furnace.

How an Atmosphere Furnace Solves the Oxidation Problem
At its core, an atmosphere furnace is designed to overcome a fundamental challenge in materials science and manufacturing: the unwanted reaction of a material's surface with the air when heated.
The Challenge of Heating in Air
When most metals and many other materials are heated to high temperatures in the presence of oxygen, they oxidize. This can manifest as surface scaling, discoloration, or a change in the material's fundamental properties, which is often undesirable.
A standard furnace, which heats materials in normal air (roughly 21% oxygen), makes this oxidation unavoidable.
The Protective "Atmosphere"
An atmosphere furnace solves this by first removing the ambient air and then filling the sealed chamber with a specific, controlled gas or mixture of gases—the "atmosphere." This atmosphere displaces the reactive oxygen.
Most commonly, an inert gas like nitrogen or argon is used. These gases are chemically inactive and will not react with the material even at extreme temperatures, preserving its original surface finish. This is essential for processes like bright annealing or sintering.
Achieving a Controlled Environment
This level of control is made possible by a few key design features. The furnace chamber is fully sealed, often using high-temperature-resistant gaskets on the door. It includes an inlet for introducing the desired gases and an outlet for purging the initial air and venting process gases. This design ensures the internal atmosphere remains pure and at the correct pressure.
Key Components and Their Function
While structurally straightforward, the effectiveness of an atmosphere furnace relies on the precise coordination of its main systems.
The Sealed Chamber and Heating Elements
The foundation is a well-insulated chamber with electric heating elements capable of reaching the required process temperatures with high uniformity. The most critical feature is the airtight seal, which prevents oxygen from leaking in and contaminating the controlled atmosphere.
The Gas Control System
This is the brain of the operation. This system manages the type, flow rate, and mixture of gases entering the furnace. For processes requiring an inert environment, it ensures a steady flow of pure gas. For more advanced applications like carburizing, it precisely mixes reactive gases.
The Process Control and Safety Systems
A central controller monitors and regulates temperature, gas flow, and pressure throughout the heating cycle. An exhaust gas treatment system is also vital to safely handle and vent the process gases, which may be hot or chemically volatile.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, an atmosphere furnace introduces complexities not found in simpler thermal equipment.
Precision is Non-Negotiable
The success of a process depends entirely on the correct gas mixture and a leak-free chamber. Even a small oxygen leak or an incorrect gas ratio can ruin an entire batch of expensive materials. Constant monitoring and proper maintenance are critical.
Higher Operational Costs
Compared to a standard box furnace, an atmosphere furnace has higher ongoing costs. The primary driver is the consumption of process gases (like argon or nitrogen), which must be continuously supplied to maintain the environment.
Increased Complexity
While the furnace itself is simple, the associated gas delivery, safety, and control systems add a layer of operational complexity. Users require more specialized training to operate the equipment safely and effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right type of furnace depends entirely on the desired outcome of your thermal process, specifically how the material's surface must be treated.
- If your primary focus is simply heating materials without concern for surface oxidation: A conventional box or tube furnace is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation to achieve a clean, bright finish (e.g., bright annealing, sintering): An atmosphere furnace using an inert gas like nitrogen or argon is absolutely essential.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific surface chemistry (e.g., carburizing, nitriding): A reactive gas atmosphere furnace is the required tool, as it is designed to drive these chemical changes.
Ultimately, you choose an atmosphere furnace when the chemical environment is just as important as the temperature.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Furnace | Atmosphere Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Ambient Air | Controlled Gas (e.g., Nitrogen, Argon) |
| Primary Goal | Heating | Heating + Surface Chemistry Control |
| Oxidation Prevention | No | Yes |
| Best For | Processes where oxidation is acceptable | Bright annealing, sintering, carburizing |
| Complexity & Cost | Lower | Higher |
Ready to achieve precise, oxidation-free results in your lab?
An atmosphere furnace is essential for processes like bright annealing, sintering, and surface treatments where controlling the chemical environment is as critical as temperature. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables to meet these exact needs.
Let our experts help you select the perfect furnace for your application. We'll ensure you get the right solution for superior materials processing.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your requirements and discover the benefits of controlled atmosphere heating for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes



















