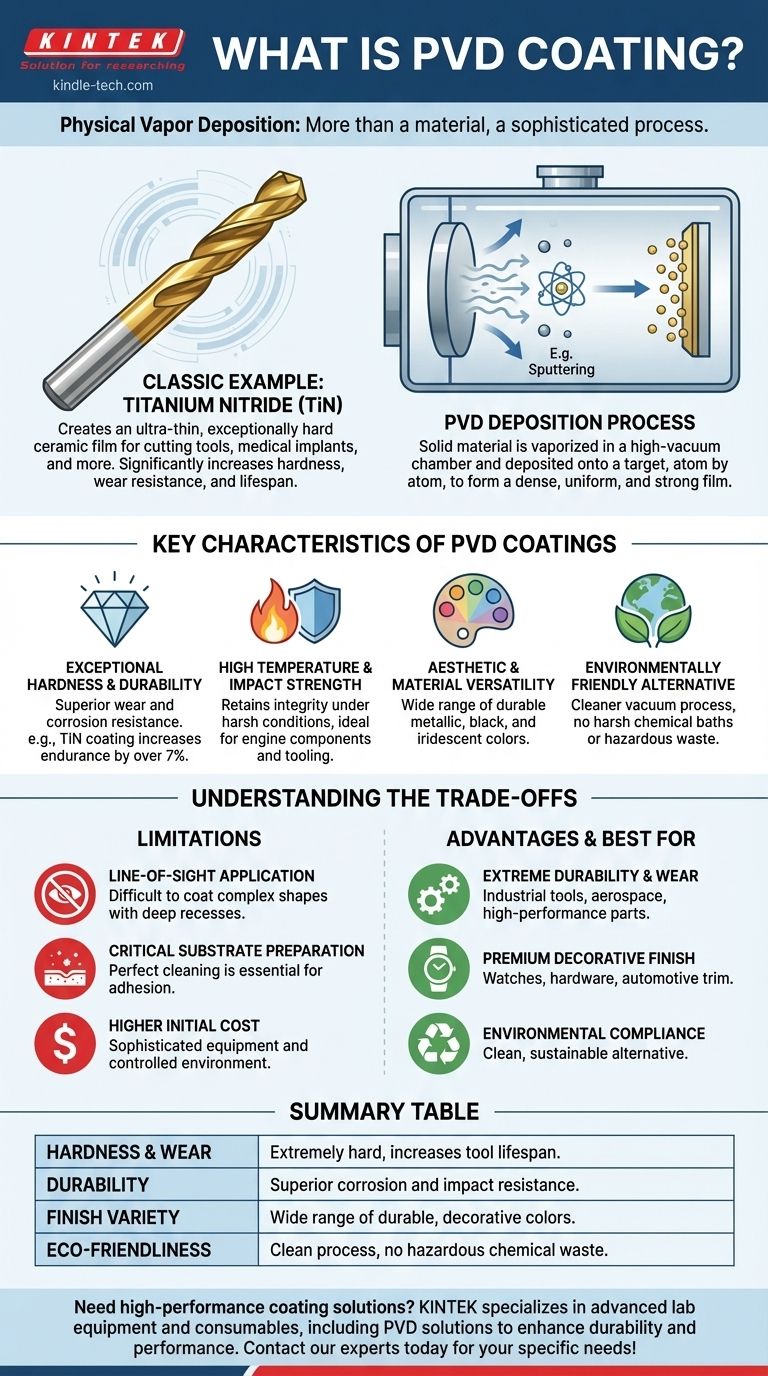
A classic example of a PVD coating is Titanium Nitride (TiN). This exceptionally hard ceramic material is applied as a thin film to surfaces like cutting tools, drill bits, and medical implants to dramatically increase their hardness, wear resistance, and lifespan.
The key insight is that "PVD" isn't a single material, but a sophisticated deposition process that creates an ultra-thin, high-performance film on a surface. This process is what gives materials like Titanium Nitride their superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to traditional coating methods.

What Defines a PVD Coating?
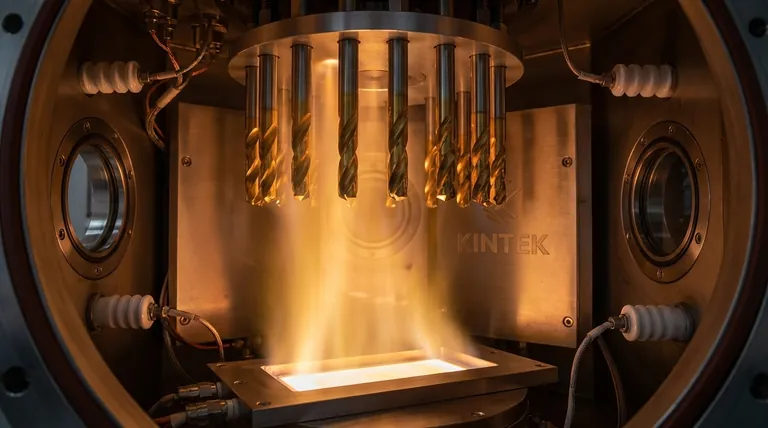
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is fundamentally different from painting or electroplating. Instead of applying a liquid or using a chemical bath, PVD transforms a solid coating material into a vapor within a vacuum, then deposits it onto a target object atom by atom.
The Vacuum Deposition Process
The process takes place in a high-vacuum chamber, which ensures the coating is extremely pure. The solid source material (like titanium) is vaporized through methods like heat or sputtering, and this vapor travels in a straight line to coat the substrate, forming a strong bond with its surface.
A Thin Film with Superior Properties
The result is a coating that is incredibly thin—often just a few microns—but is dense, uniform, and exceptionally well-adhered. This thin film is what provides the significant performance enhancements.
Key Characteristics of PVD Coatings
The PVD process delivers a unique combination of benefits that make it the preferred choice for demanding applications where performance and reliability are critical.
Exceptional Hardness and Durability
PVD coatings are significantly harder and more corrosion-resistant than coatings applied through processes like electroplating. For example, a TiN coating can increase the endurance of a titanium alloy part by over 7%.
High Temperature and Impact Strength
These coatings are inherently resistant to high temperatures and have good impact strength, maintaining their integrity even under harsh operating conditions. This makes them ideal for high-performance engine components and industrial tooling.
Aesthetic and Material Versatility
Nearly any inorganic material and some organic materials can be used for PVD coating. This allows for a massive range of colors and finishes—from metallic chromes and golds to blacks and iridescent colors—all while maintaining high durability.
An Environmentally Friendly Alternative
Because the process occurs in a vacuum and doesn't rely on harsh chemical baths, PVD is a much cleaner, more environmentally friendly process than traditional electroplating or painting. It produces no harmful chemical waste.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD is not the right solution for every situation. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Line-of-Sight Application
PVD is a "line-of-sight" process. The vaporized material travels in a straight line, which can make it difficult to uniformly coat complex shapes with deep recesses or internal channels.
Substrate Preparation is Critical
The exceptional adhesion of PVD coatings depends on a perfectly clean and prepared substrate. Any surface contamination can lead to imperfections or a failure of the coating to bond correctly.
Initial Cost Considerations
The equipment for PVD coating is sophisticated and requires a controlled vacuum environment. This can lead to a higher upfront cost compared to simpler processes like painting or some forms of electroplating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PVD depends entirely on the performance you require from the final product.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and wear resistance: PVD is the superior choice for industrial tools, aerospace components, and high-performance parts.
- If your primary focus is a premium, corrosion-resistant decorative finish: PVD provides a far more durable and long-lasting finish than traditional plating for items like watches, premium hardware, and automotive trim.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: PVD offers a clean, sustainable alternative to coating processes that rely on and produce hazardous chemicals.
Ultimately, PVD is a modern coating technology engineered for applications where performance and durability cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | PVD Coating Benefit |
|---|---|
| Hardness & Wear | Extremely hard, increases tool lifespan |
| Durability | Superior corrosion and impact resistance |
| Finish Variety | Wide range of durable, decorative colors |
| Eco-Friendliness | Clean process, no hazardous chemical waste |
Need a high-performance coating for your lab equipment or tools? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including PVD coating solutions that enhance durability and performance. Contact our experts today to find the perfect coating for your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Thermocouple Protection Tube
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance



















