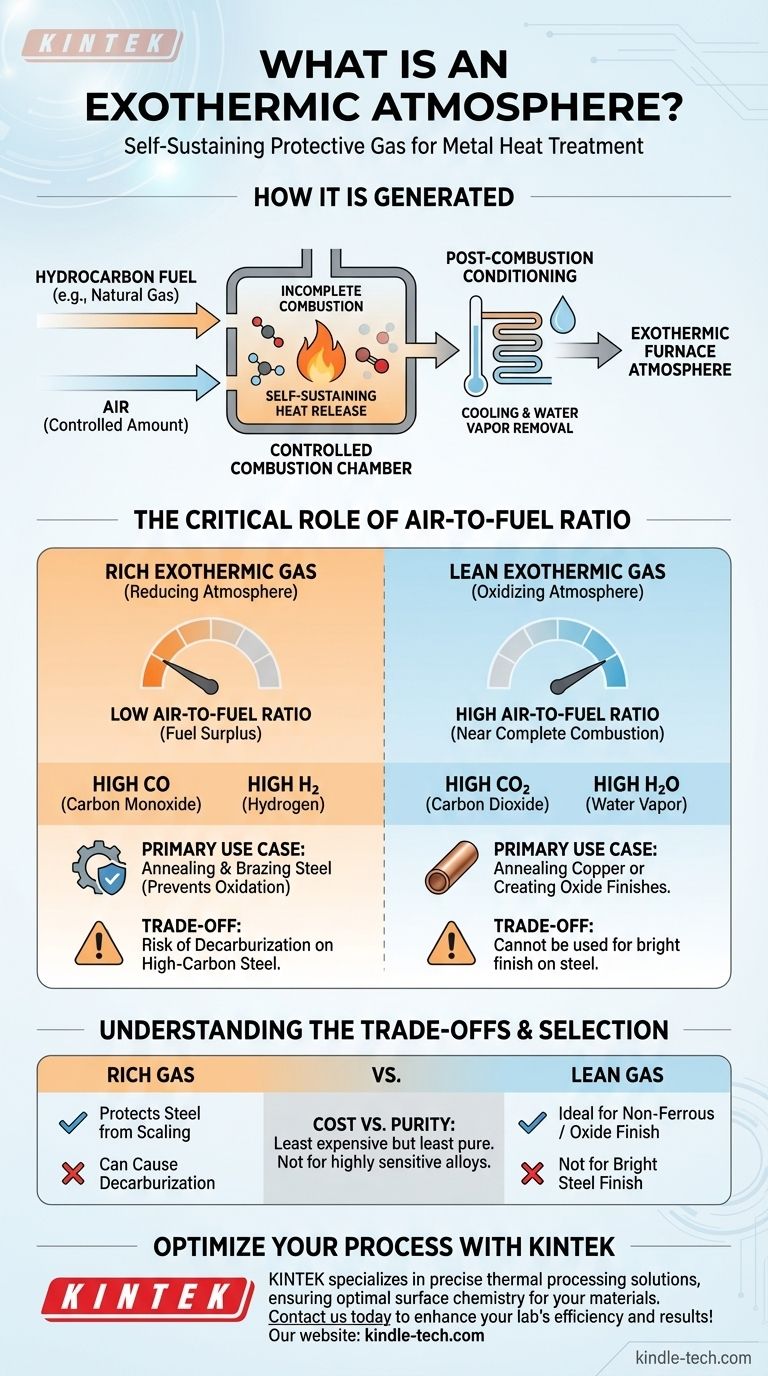
In metal heat treatment, an exothermic atmosphere is a protective gas generated on-site through a controlled combustion reaction. Unlike other furnace atmospheres that require external heating to form, this process is "exothermic"—meaning it releases its own heat, making it self-sustaining. It is primarily used to control the surface chemistry of metals during processes like annealing, brazing, and tempering, preventing or promoting oxidation as needed.
The crucial insight is that an exothermic atmosphere is not a single gas, but a tunable environment. By precisely controlling the air-to-fuel ratio during its creation, you can produce either a reducing atmosphere that protects steel from oxidation or an oxidizing one for treating non-ferrous metals.

How an Exothermic Atmosphere is Generated
The Core Principle: Controlled Combustion
An exothermic atmosphere is produced by burning a hydrocarbon fuel, such as natural gas or propane, with a specific, limited amount of air inside a reaction chamber.
The process is designed to achieve incomplete combustion, which yields a specific mixture of active and inert gases tailored for heat treatment.
The "Exothermic" Distinction
The key characteristic is that the combustion reaction releases a significant amount of heat. This thermal energy is sufficient to sustain the reaction without any external heat source.
This makes exothermic gas generators simpler and often more cost-effective to operate than endothermic generators, which require continuous energy input to drive their chemical reactions.
Post-Combustion Conditioning
After combustion, the hot gas mixture is typically passed through a heat exchanger to cool it down rapidly. This cooling process also causes excess water vapor—a byproduct of combustion—to condense and be removed, resulting in a more stable and useful furnace atmosphere.
The Critical Role of the Air-to-Fuel Ratio
The properties of the final atmosphere are dictated entirely by one variable: the ratio of air to fuel fed into the generator. This determines the balance between reducing agents (like carbon monoxide) and oxidizing agents (like carbon dioxide).
Rich Exothermic Gas (A Reducing Atmosphere)
To create a rich exothermic gas, the combustion reaction is run with a significant fuel surplus, or a low air-to-fuel ratio. This results in incomplete combustion.
The resulting atmosphere is high in carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H₂), which are powerful reducing agents. This type of atmosphere actively prevents surface oxidation and is used for treating steel.
Lean Exothermic Gas (An Oxidizing Atmosphere)
To create a lean exothermic gas, the reaction is run with only a slight fuel surplus, approaching complete combustion. This uses a high air-to-fuel ratio.
The output is low in CO and H₂ but rich in carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water vapor (H₂O). This creates a mildly oxidizing atmosphere suitable for processes like annealing copper or creating a controlled blue oxide finish on steel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Rich Gas: Protection at a Price
While a rich exothermic gas protects steel from scaling (heavy oxidation), its high CO₂ and water vapor content can still cause decarburization—the loss of carbon from the steel's surface. This can soften the surface, which is undesirable for high-carbon or tool steels.
Lean Gas: Limited Application
A lean gas is fundamentally oxidizing and cannot be used for applications where a clean, bright finish on steel is required. Its use is largely confined to non-ferrous metals like copper, which are less sensitive to oxidation, or when a decorative oxide layer is the intended outcome.
Cost vs. Purity
Exothermic atmospheres are generally the least expensive type of generated atmosphere. However, they are also the least "pure," containing reactive components. For highly sensitive alloys or critical applications requiring a perfectly inert environment, more expensive nitrogen-based or dissociated ammonia atmospheres are necessary.
Selecting the Right Atmosphere for Your Process
Choosing the correct atmosphere is a matter of matching the gas chemistry to the material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective annealing or brazing of low-carbon steels: A rich exothermic atmosphere is the standard choice to prevent heavy oxidation.
- If your primary focus is annealing copper or creating a controlled oxide finish: A lean exothermic atmosphere provides the necessary oxidizing potential safely and economically.
- If your primary focus is treating high-carbon or alloy steels sensitive to decarburization: You should consider a more controlled endothermic or pure nitrogen-based atmosphere instead.
Ultimately, controlling the combustion reaction is the key to engineering the precise surface environment your material requires.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Air-to-Fuel Ratio | Key Components | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rich (Reducing) | Low (Fuel Surplus) | High CO, H₂ | Annealing & brazing steel to prevent oxidation |
| Lean (Oxidizing) | High (Near Complete Combustion) | High CO₂, H₂O | Annealing copper or creating oxide finishes |
Optimize your metal heat treatment process with the right atmosphere. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for precise thermal processing. Our expertise ensures you achieve the desired surface chemistry for your materials, whether you're working with steel, copper, or other alloys. Contact us today to discuss how our systems can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety



















