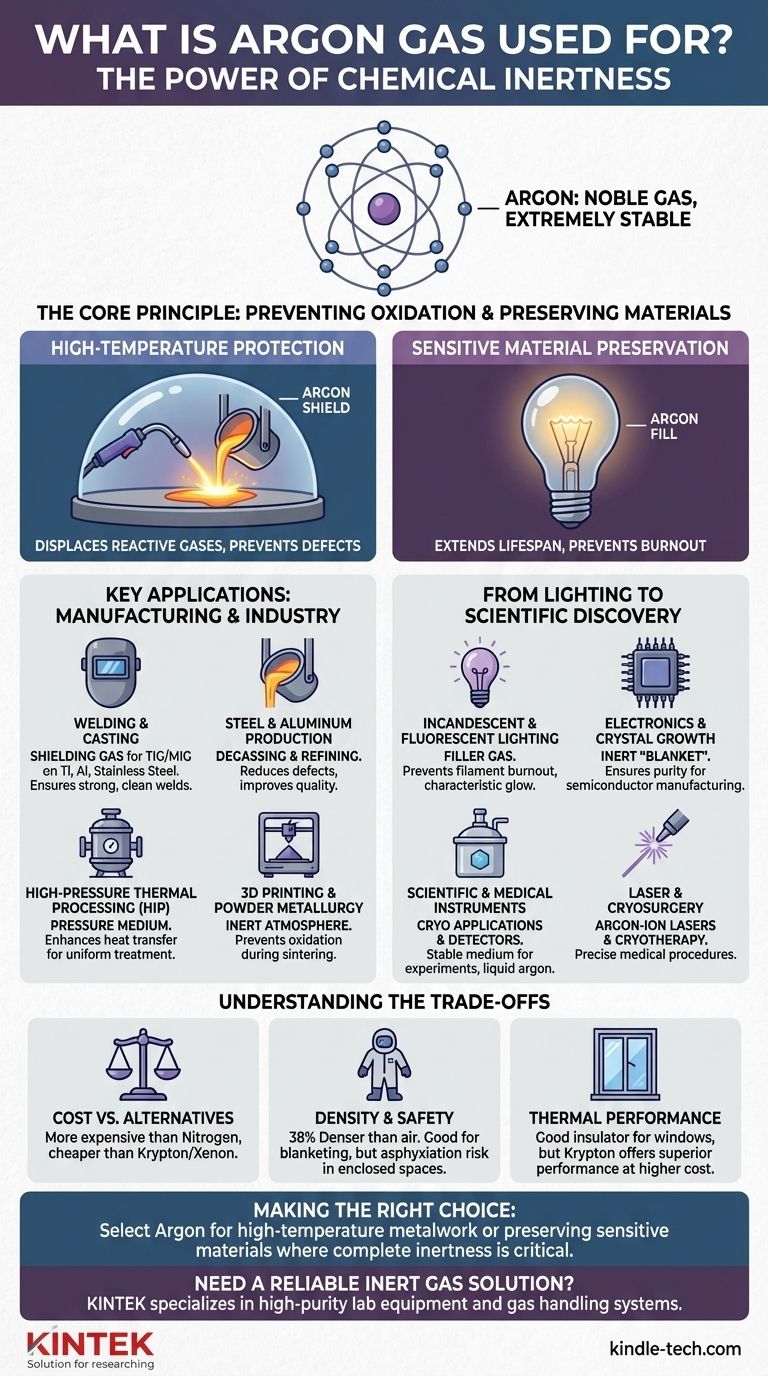
Argon is an indispensable industrial gas, prized for its chemical inertness. It is most commonly used as a protective shielding gas in high-temperature processes like welding and metal fabrication, as a non-reactive filler gas in light bulbs and insulated windows, and as a specialized medium in scientific research and medical procedures.
The fundamental value of argon lies in its inability to react with other elements. This chemical stability allows it to create a perfectly controlled, non-reactive atmosphere, preventing unwanted effects like oxidation that would otherwise compromise quality and safety in sensitive applications.

The Core Principle: Why Inertness Matters
Argon is a noble gas, meaning its outer electron shell is full. This structure makes it extremely stable and non-reactive under most conditions. This single property—its inertness—is the reason it is so widely used.
Preventing Oxidation in High-Temperature Processes
Many metals, when heated to molten temperatures for welding or casting, react aggressively with oxygen and nitrogen in the atmosphere. This reaction, called oxidation, creates defects, weakens the material, and ruins the final product.
By flooding the area with argon, we displace the reactive atmospheric gases. The argon forms a protective "shield" that doesn't interact with the molten metal, ensuring a clean, strong, and high-quality result.
Preserving Sensitive Materials
Even at room temperature, oxygen can degrade materials over time. Filaments in incandescent light bulbs would burn out almost instantly if exposed to oxygen.
Argon is used to fill the glass bulb, protecting the delicate filament from oxidation and dramatically extending its life. The same principle applies to preserving historical documents or protecting sensitive electronic components during manufacturing.
Key Applications in Manufacturing and Industry
The demand for controlled, non-reactive environments makes argon a workhorse in heavy industry and precision manufacturing.
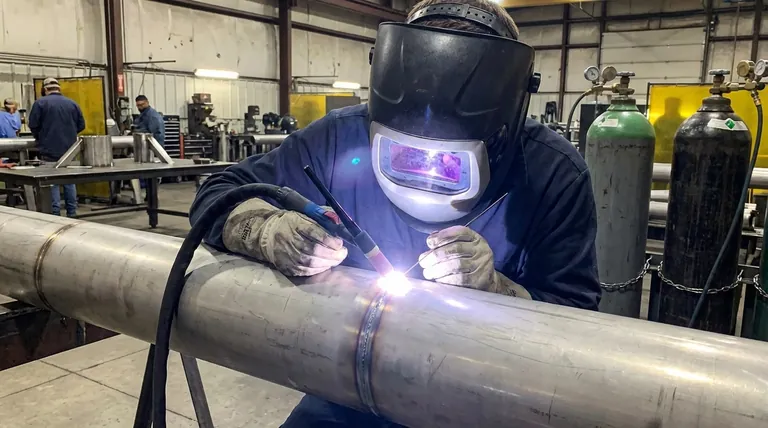
Shielding Gas in Welding and Casting
In arc welding processes like TIG and MIG, argon is the most common shielding gas. It protects the weld pool from contamination, allowing for precise and strong welds on reactive metals like titanium, aluminum, and stainless steel.
Steel and Aluminum Production
During steel manufacturing in an electric arc furnace, argon is often blown into the molten steel. This process helps reduce chromium losses and achieve the desired carbon content more efficiently.
In aluminum production, argon is used to degas the molten metal, removing dissolved hydrogen that can cause porosity and defects in the final cast product.
High-Pressure Thermal Processing (HIP)
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is a process that uses high temperature and pressure to densify materials and remove defects. Argon is used as the pressure medium because its thermal properties at extreme pressures are excellent for enhancing heat transfer and ensuring uniform treatment.
From Lighting to Scientific Discovery
Argon's unique properties extend beyond industrial metalwork into consumer products, electronics, and advanced scientific research.
In Incandescent and Fluorescent Lighting
As mentioned, argon prevents the filament in incandescent bulbs from burning out. It is also used in fluorescent tubes and "neon" signs; when an electric current passes through argon, it emits a characteristic pale purple-blue glow.
In Electronics and Crystal Growth
Manufacturing semiconductors and silicon crystals requires an exceptionally pure and non-reactive environment. Argon provides the perfect inert "blanket" for growing these crystals, preventing defects that would render the electronic components useless.
Scientific and Medical Instruments
Liquid argon is used in highly sensitive scientific experiments, such as neutrino detectors and dark matter searches, due to its cryogenic properties and stability.
In medicine, argon-ion lasers are used for delicate procedures like eye surgery, while cryosurgery can use liquid argon to freeze and destroy diseased tissue.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, argon is not always the default choice. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Cost vs. Other Gases
Argon is more abundant and therefore less expensive than other noble gases like krypton or xenon. However, it is more expensive than nitrogen, which is also relatively inert. For applications that can tolerate the minimal reactivity of nitrogen, it is often the more cost-effective choice.
Density and Safety Risks
Argon is about 38% denser than air. This is an advantage in welding, as it effectively blankets the work area and displaces lighter atmospheric gases.
However, this same property creates a significant asphyxiation hazard in enclosed or poorly ventilated spaces. Because it is odorless and colorless, an argon leak can displace breathable oxygen from the bottom up, leading to serious risk for personnel.
Thermal Performance
Argon is a good thermal insulator and is commonly used to fill the gap in double-paned insulated glass windows. While effective, other noble gases like krypton offer superior insulation performance, but at a significantly higher cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right gas depends entirely on the technical requirements and budget of your application.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature metal fabrication (welding, casting): Argon is the industry standard for creating a stable, non-reactive shield that ensures high-quality results with reactive metals.
- If your primary focus is preserving a sensitive material (light bulb filaments, electronics): Argon's complete inertness prevents degradation from oxidation, significantly extending the material's lifespan and ensuring product integrity.
- If your primary focus is a cost-sensitive inerting application: You should evaluate if nitrogen, a less expensive alternative, can meet your needs, as it is sufficient for many processes that don't involve highly reactive materials at extreme temperatures.
Ultimately, argon serves as a powerful and versatile tool for precisely controlling the chemical environment of a process.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Use of Argon | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Welding & Metal Fabrication | Shielding gas for TIG/MIG welding | Prevents oxidation, ensures clean, strong welds |
| Steel & Aluminum Production | Degassing and refining molten metals | Reduces defects, improves material quality |
| Lighting | Filler gas in incandescent and fluorescent bulbs | Extends filament life, prevents burnout |
| Electronics & Crystal Growth | Inert atmosphere for semiconductor manufacturing | Ensures purity, prevents defects in components |
| Scientific Research | Medium for detectors and cryogenic applications | Provides stability for sensitive experiments |
Need a Reliable Inert Gas Solution for Your Lab or Production Process?
Argon's inert properties are essential for achieving precision and purity in high-temperature applications and sensitive environments. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including gas handling systems, to meet the exacting demands of laboratories and industrial clients.
Whether you are working on advanced material synthesis, metal fabrication, or require a stable atmosphere for critical research, KINTEK has the expertise and products to support your goals.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your process quality and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature for ceramics? Find the Right Material for Your High-Temp Application
- What is the difference between PPF and coating? Armor vs. Slick Shell for Your Car
- What is ceramic insulation used for? Master High-Temperature Solutions for Industrial Efficiency
- What are the applications of zirconia ceramics? Unlock High-Performance Solutions for Extreme Environments
- Can ceramic withstand high temperatures? Discover the Superior Materials for Extreme Heat












