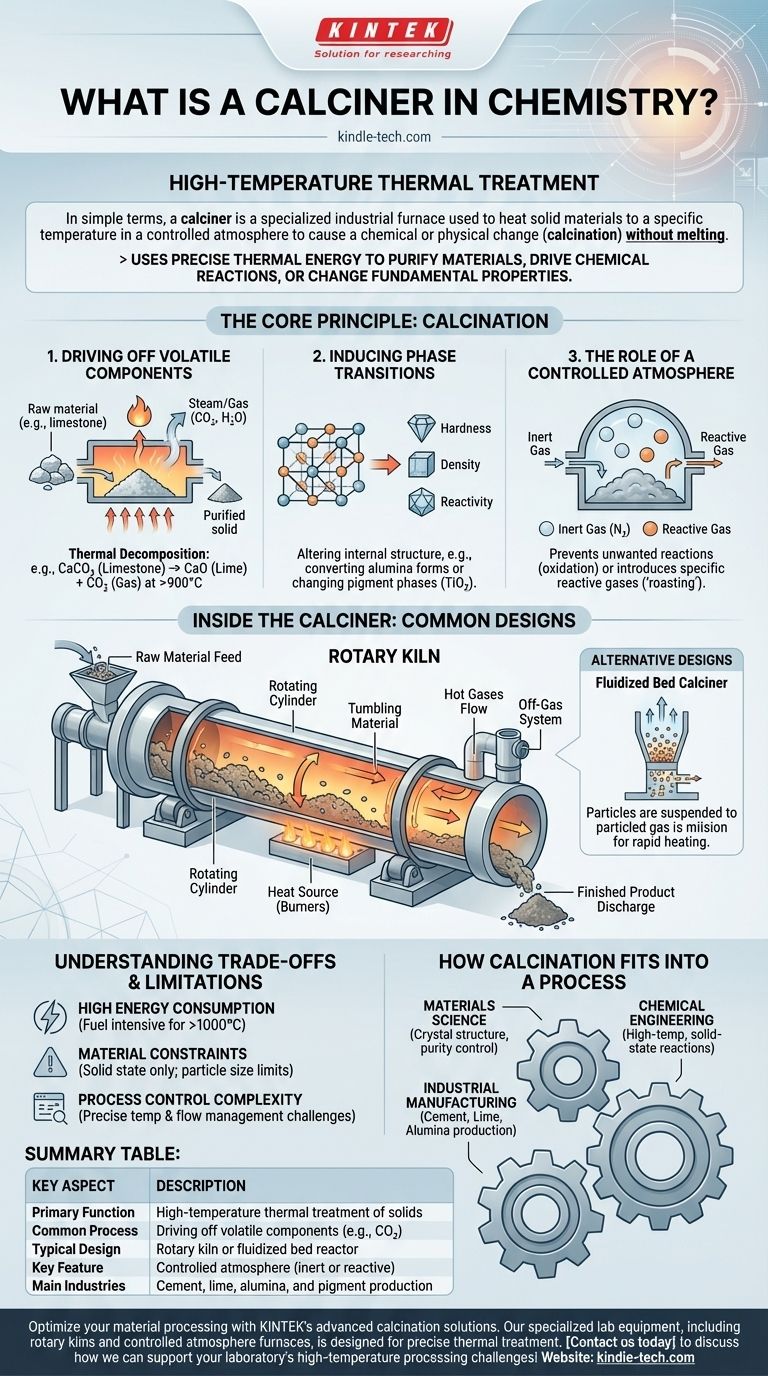
In simple terms, a calciner is a type of industrial furnace used for high-temperature thermal treatment. Its primary purpose is to heat solid materials to a specific temperature in a controlled atmosphere to cause a chemical or physical change, a process known as calcination. This is done without melting the material.
A calciner is not just an oven; it is a specialized reactor that uses precise thermal energy to purify materials, drive chemical reactions, or change a solid's fundamental properties by removing volatile components like water and carbon dioxide.
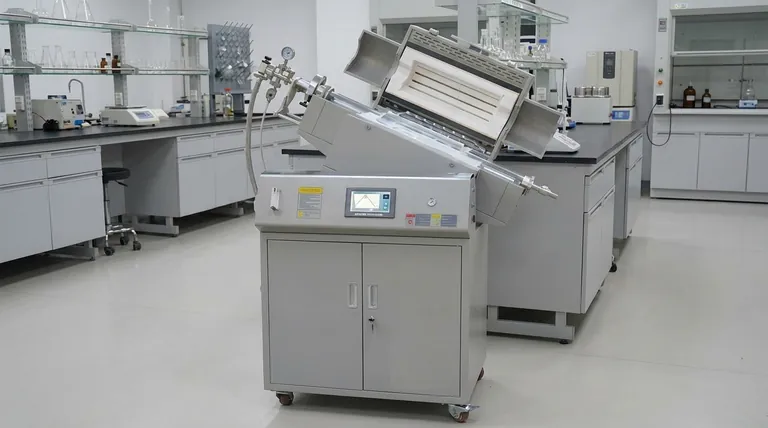

The Core Principle: What is Calcination?
The equipment—the calciner—exists to perform the process of calcination. Understanding this process is key to understanding the equipment's function and design.
Driving Off Volatile Components
The most common use of calcination is thermal decomposition. This involves heating a compound to break it down into simpler, more stable substances.
A classic example is the production of lime (calcium oxide) from limestone (calcium carbonate). The calciner heats the limestone above 900°C (1650°F), driving off carbon dioxide gas and leaving behind the solid lime.
Inducing Phase Transitions
Heat can also be used to change the internal crystalline structure of a material, altering its physical properties like hardness, density, and reactivity.
For instance, calcination is used to convert different forms of alumina or to create specific crystalline phases in pigments like titanium dioxide, which affects its opacity and brightness.
The Role of a Controlled Atmosphere
A critical feature of calcination is the control over the atmosphere inside the furnace. This prevents unwanted reactions, primarily oxidation.
In many processes, an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen) is used. In others, a specific reactive gas might be introduced to achieve a desired chemical change, a process sometimes called "roasting."
Inside the Calciner: How It Works
While designs vary, most industrial calciners share a common set of principles and components designed for continuous, high-volume processing.
The Rotary Kiln: A Common Design
The most recognizable type of calciner is the rotary kiln. This is a large, rotating steel cylinder lined with heat-resistant brick, mounted at a slight angle.
Raw material is fed into the upper end. As the kiln slowly rotates, the material tumbles and slides down towards the lower end, where it is discharged. This tumbling action ensures excellent mixing and uniform exposure to the hot gases flowing through the kiln.
Other Key Components
A complete calciner system includes a heat source (typically powerful gas or coal burners), a material handling system for feeding raw materials and collecting the finished product, and an off-gas system to safely handle and treat the gases released during the process.
Alternative Designs
For finer materials or processes requiring even better heat transfer, other designs are used. A fluidized bed calciner suspends the solid particles in an upward-flowing stream of hot gas, creating a fluid-like behavior that allows for rapid and uniform heating.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, calcination is an energy-intensive and complex process with specific constraints that are important to recognize.
High Energy Consumption
Bringing thousands of tons of material to temperatures often exceeding 1000°C requires an immense amount of fuel. Energy cost is a primary operational expense and a significant factor in the environmental footprint of industries like cement manufacturing.
Material Constraints
The process is only suitable for materials that remain solid at the target temperature. Materials with low melting points cannot be calcined. Furthermore, the physical form of the material (particle size, density) can dictate which type of calciner is appropriate.
Process Control Complexity
Maintaining a precise temperature profile along the length of a 100-meter-long rotary kiln while controlling gas flow and residence time is a major engineering challenge. Slight deviations can lead to an incomplete reaction or undesirable byproducts.
How Calcination Fits into a Process
Calcination is rarely a final step. It is a critical intermediate process that transforms low-value raw materials into a refined, reactive, or purified solid ready for the next stage of production.
- If your primary focus is materials science: Calcination is a key thermal processing tool for controlling a material's crystal structure, surface area, and purity.
- If your primary focus is chemical engineering: A calciner is a unit operation designed for high-temperature, solid-state reactions and phase changes in a controlled environment.
- If your primary focus is industrial manufacturing: Calcination is the core process for producing foundational commodities like cement, lime, and alumina from natural minerals.
Ultimately, understanding the calciner means grasping a fundamental process for transforming raw materials into the engineered products that build our world.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | High-temperature thermal treatment (calcination) of solids |
| Common Process | Driving off volatile components (e.g., CO₂ from limestone) |
| Typical Design | Rotary kiln or fluidized bed reactor |
| Key Feature | Controlled atmosphere (inert or reactive gases) |
| Main Industries | Cement, lime, alumina, and pigment production |
Optimize your material processing with KINTEK's advanced calcination solutions. Our specialized lab equipment, including rotary kilns and controlled atmosphere furnaces, is designed for precise thermal treatment, helping you achieve superior material purity, phase transitions, and decomposition efficiency. Whether you're in research or industrial production, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures reliable performance for your calcination needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's high-temperature processing challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- What is the primary function of an industrial rotary tube furnace? Master Tungsten Powder Hydrogen Reduction
- What are the advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for MoVOx catalysts? Elevate Uniformity and Crystallinity
- What is modified chemical vapour deposition method? The Inside-Out Process for Ultra-Pure Optical Fibers



















