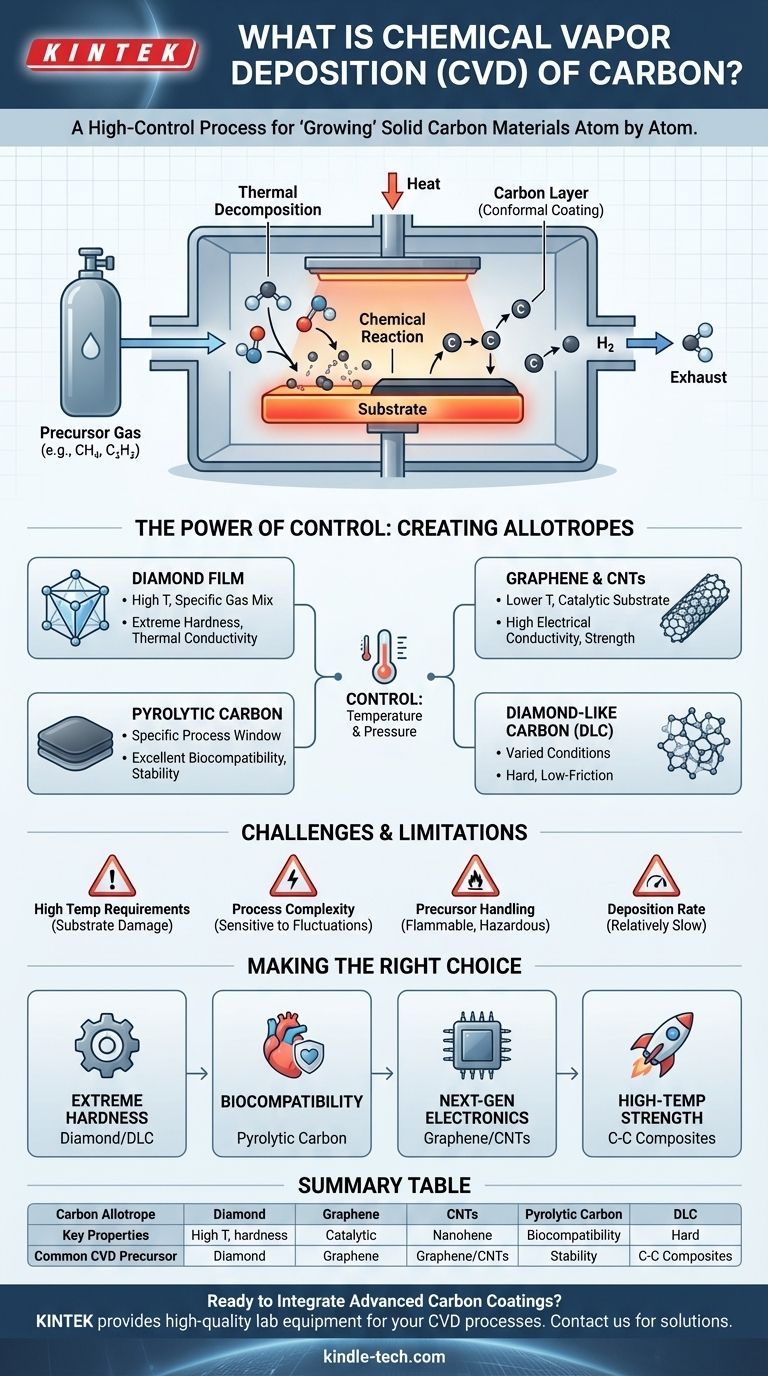
In essence, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of carbon is a high-control manufacturing process for "growing" solid carbon materials onto a surface. It works by introducing a carbon-containing gas (a hydrocarbon precursor) into a reaction chamber where a heated object, or substrate, is placed. The heat triggers a chemical reaction, breaking down the gas molecules and depositing a pure, solid layer of carbon atoms directly onto the substrate's surface.
The core challenge in materials science is not just creating a substance, but precisely controlling its atomic structure. Carbon CVD solves this by providing a method to build different forms of carbon—from ultra-hard diamond films to single-atom-thick graphene—by carefully tuning gas, temperature, and pressure.

How CVD of Carbon Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Chemical vapor deposition is a bottom-up process, building materials atom by atom. Understanding its fundamental steps is key to appreciating its power.
The Chamber and Substrate
The entire process occurs within a sealed chamber, which is typically held under a vacuum to eliminate contaminants. Inside, the substrate—the component to be coated—is heated to a specific, high temperature.
Introducing the Carbon Source
A volatile precursor gas that contains carbon is injected into the chamber. Common precursors for carbon deposition include hydrocarbons like methane (CH₄) or acetylene (C₂H₂).
The Chemical Reaction at the Surface
When the hot precursor gas molecules come into contact with the heated substrate, they gain enough energy to break their chemical bonds in a process called thermal decomposition.
For example, methane breaks down into solid carbon (C), which bonds to the surface, and hydrogen gas (H₂), which is a waste byproduct that gets pumped out of the chamber.
Building the Carbon Layer
This deposition process builds up a solid carbon film, one atomic layer at a time. A key advantage of CVD is its conformal nature; the gas surrounds the entire substrate, so the coating grows evenly on all exposed surfaces, including complex shapes and internal bores. This is a major distinction from line-of-sight methods like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
The Power of Control: Creating Different Carbon Allotropes
The true value of carbon CVD lies in its tunability. By precisely adjusting the process parameters, you can dictate the exact atomic structure, or allotrope, of the deposited carbon.
The Role of Temperature and Pressure
The combination of substrate temperature, chamber pressure, and gas composition determines the final material. Different conditions favor the formation of different carbon-carbon bonds, leading to materials with vastly different properties.
Creating Synthetic Diamond Films
To create the strong sp³ bonds characteristic of diamond, the process requires very high temperatures and specific gas mixtures. The resulting films are exceptionally hard, thermally conductive, and wear-resistant.
Growing Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes
Lower temperatures and the use of a catalytic substrate (like copper foil for graphene) can favor the formation of sp² bonds. This enables the growth of single-layer graphene sheets or rolled-up sheets known as carbon nanotubes (CNTs), foundational materials for next-generation electronics and composites.
Producing Pyrolytic Carbon and DLC
Other process windows can produce pyrolytic carbon, an extremely stable and biocompatible material used for medical implants like heart valves. Alternatively, Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) can be formed—an amorphous material that combines sp² and sp³ bonds to create a super-hard, low-friction coating.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, carbon CVD is not a universal solution. Acknowledging its challenges is crucial for proper application.
High Temperature Requirements
Traditional thermal CVD often requires temperatures that can damage or deform the substrate material. This has led to the development of variants like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), which uses an electric field to energize the gas, allowing deposition at much lower temperatures.
Process Complexity and Sensitivity
The final material quality is highly sensitive to small fluctuations in temperature, pressure, and gas purity. Achieving consistent, high-quality results requires sophisticated process control and a very clean environment.
Precursor and Byproduct Handling
The hydrocarbon gases used as precursors are often flammable, and the chemical reactions can produce hazardous byproducts. This necessitates robust safety protocols and exhaust management systems.
Deposition Rate
CVD can be a relatively slow process, especially when growing thick or highly crystalline films. For applications requiring rapid, thick coatings, other methods might be more cost-effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The versatility of carbon CVD allows you to tailor the output to your specific application. Your primary objective dictates the type of carbon you need to produce.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: You are likely seeking a synthetic diamond or Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coating for tools, bearings, or mechanical seals.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility for medical implants: Pyrolytic carbon is the industry standard due to its excellent stability and resistance to blood clotting.
- If your primary focus is next-generation electronics or composites: You are exploring the growth of graphene or carbon nanotubes on specific substrates to leverage their unique electrical and mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature strength: Carbon-carbon composites, where a carbon fiber matrix is densified with CVD-infiltrated carbon, are the target for applications like brakes and rocket nozzles.
By mastering the parameters of this process, you can transform simple gases into some of the most advanced materials known to science.
Summary Table:
| Carbon Allotrope | Key Properties | Common CVD Precursor |
|---|---|---|
| Diamond Film | Extreme hardness, high thermal conductivity | Methane (CH₄) with hydrogen |
| Graphene | Single-atom thick, high electrical conductivity | Methane (CH₄) on catalytic metal |
| Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) | High strength, unique electrical properties | Hydrocarbons like acetylene (C₂H₂) |
| Pyrolytic Carbon | Excellent biocompatibility, stability | Hydrocarbons like propane |
| Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) | Hard, low-friction, amorphous | Various hydrocarbon gases |
Ready to integrate advanced carbon coatings into your R&D or production? The precise control offered by CVD is key to developing next-generation materials. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables necessary for successful carbon CVD processes. Whether you are developing medical implants with pyrolytic carbon, creating durable tools with DLC coatings, or pioneering electronics with graphene, our expertise supports your innovation. Contact our team today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and help you achieve superior material performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















