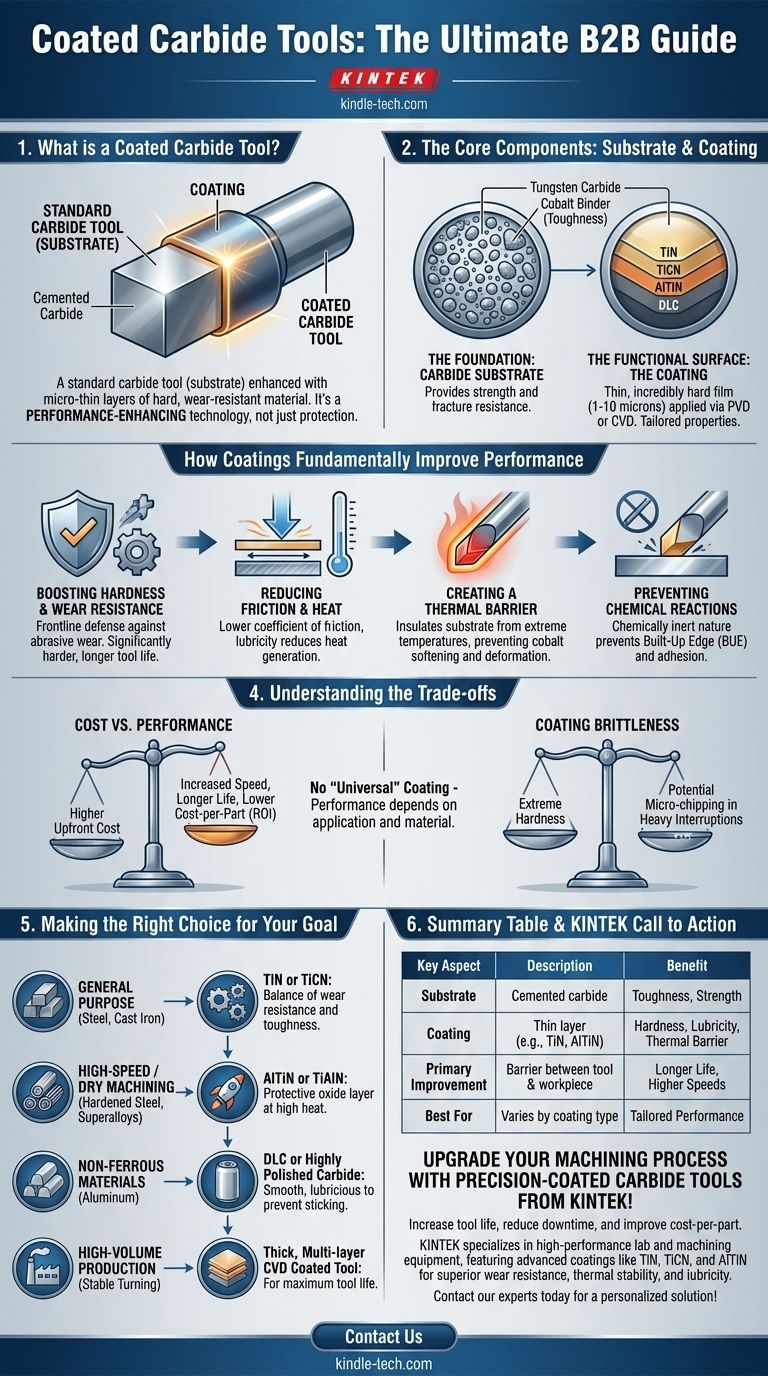
In essence, a coated carbide tool is a standard carbide cutting tool (the substrate) that has been enhanced with one or more micro-thin layers of a very hard, wear-resistant material. This coating acts as a barrier between the tool and the workpiece, fundamentally improving its performance and lifespan far beyond what the uncoated carbide could achieve alone.
The critical takeaway is that coatings are not just a protective layer; they are a performance-enhancing technology. They allow carbide tools to cut faster, run hotter, and last significantly longer by creating a functional surface with superior hardness, lubricity, and thermal stability.

The Core Components: Substrate and Coating
To understand a coated tool, you must understand its two distinct parts: the tough inner core and the hard outer shell. Each plays a critical role.
The Foundation: The Carbide Substrate
The body of the tool is made from cemented carbide. This is a composite material created by sintering powdered tungsten carbide (which provides hardness) with a metallic cobalt binder (which provides toughness).
This substrate is responsible for the tool's underlying strength and its ability to resist fracturing under the immense forces of cutting.
The Functional Surface: The Coating
Applied via processes like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the coating is an extremely thin (typically 1-10 microns) but incredibly hard film.
Common coating materials include Titanium Nitride (TiN), Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN), and Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN). Each has unique properties tailored for specific applications.
How Coatings Fundamentally Improve Performance
The addition of a coating transforms the tool's capabilities by directly addressing the primary failure modes in machining.
Boosting Hardness and Wear Resistance
The most obvious benefit is hardness. Coatings are significantly harder than the carbide substrate itself, providing a frontline defense against the abrasive wear caused by hard particles in the workpiece material. This directly translates to longer tool life.
Reducing Friction and Heat
Coatings have a lower coefficient of friction than raw carbide. This lubricity reduces the resistance as the chip flows over the tool face, which in turn generates less heat. Less heat is always a primary goal in machining.
Creating a Thermal Barrier
The coating acts as an insulator, protecting the carbide substrate from the extreme temperatures generated at the cutting edge. This thermal stability is crucial because if the carbide gets too hot, its cobalt binder will soften, leading to rapid deformation and catastrophic tool failure.
Preventing Chemical Reactions
At high cutting temperatures, there is a strong tendency for the workpiece material to weld itself to the tool's cutting edge. This phenomenon, known as Built-Up Edge (BUE), ruins surface finish and can lead to edge chipping. The chemically inert nature of most coatings prevents this adhesion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly beneficial, coated tools are not without their complexities and compromises. Acknowledging these is key to making an informed choice.
Cost vs. Performance
Coated tools have a higher upfront cost than their uncoated counterparts. The justification lies in the return on investment: increased cutting speeds, longer tool life, and fewer tool changes result in higher productivity and a lower overall cost-per-part.
Coating Brittleness and Chipping
The extreme hardness of a coating can also make it more brittle. In applications with heavy interruptions (like milling across a keyway) or where machine rigidity is poor, the coating can be prone to micro-chipping at the sharp cutting edge.
The Myth of the "Universal" Coating
There is no single coating that is best for every application. A coating like AlTiN excels in the high-heat environment of machining hardened steel, but its performance may be inferior to a smoother, more lubricious coating when machining a "gummy" material like aluminum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct tool requires matching the coating's properties to the material you are cutting and your production goals.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose machining of steels and cast iron: A workhorse coating like TiN or TiCN provides an excellent and cost-effective balance of wear resistance and toughness.
- If your primary focus is high-speed or dry machining of hardened steels and superalloys: An aluminum-based coating like AlTiN or TiAlN is necessary, as it forms a protective aluminum oxide layer at high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is machining non-ferrous materials like aluminum: A very smooth, lubricious coating like DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) or an uncoated, highly polished carbide tool is ideal to prevent material from sticking.
- If your primary focus is maximum tool life in stable, high-volume production: A thick, multi-layer CVD-coated tool is often the best choice, particularly for turning operations.
Ultimately, selecting the right coating transforms a cutting tool from a simple consumable into a precisely engineered solution for your specific manufacturing challenge.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate | Cemented carbide (tungsten carbide + cobalt binder) | Provides toughness and strength |
| Coating | Thin layer (1-10 microns) of materials like TiN, TiCN, AlTiN | Adds hardness, lubricity, and thermal barrier |
| Primary Improvement | Acts as barrier between tool and workpiece | Increases tool life and allows higher cutting speeds |
| Best For | Varies by coating type (e.g., AlTiN for hardened steel, DLC for aluminum) | Tailored performance for specific materials and conditions |
Upgrade your machining process with precision-coated carbide tools from KINTEK!
Are you looking to increase tool life, reduce downtime, and improve your cost-per-part? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab and machining equipment, including coated carbide tools designed for your specific material and application needs. Our tools feature advanced coatings like TiN, TiCN, and AlTiN to deliver superior wear resistance, thermal stability, and lubricity.
Let us help you select the perfect tool coating for your operations—whether you're machining steel, aluminum, or superalloys. Contact our experts today for a personalized solution that maximizes your productivity and ROI!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Measuring Cylinder 10/50/100ml
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Stirring Bar Recovery Rod
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- How does ion sputtering work? Precision Thin Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- What are the advantages of CVD process? Achieve Superior, Conformal Coatings for Complex Parts
- What is deposition in semiconductor fabrication? Building Chips Layer by Layer with CVD & PVD
- What are the advantages of thin film resistors? Precision, Stability & Low Noise for Sensitive Circuits
- What is the method of sputtering? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What temperature is CVD coating? Find the Right CVD Process for Your Material
- What is the advantage of LPCVD over APCVD? Achieve Superior Film Uniformity and Conformality
- Is sputtering expensive? The True Cost of High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition














