Vapor deposition is a high-precision manufacturing process used to apply an extremely thin film of material onto a surface, known as a substrate. It works by first converting a source material into a gaseous vapor within a vacuum chamber. This vapor is then transported and allowed to condense or react on the substrate's surface, building the desired film one atomic layer at a time.
The central principle of vapor deposition is controlled phase transition—turning a material into a gas and then precisely depositing it back into a solid state. This method is the bedrock for creating the high-purity, high-performance films essential for modern electronics, optics, and advanced materials.

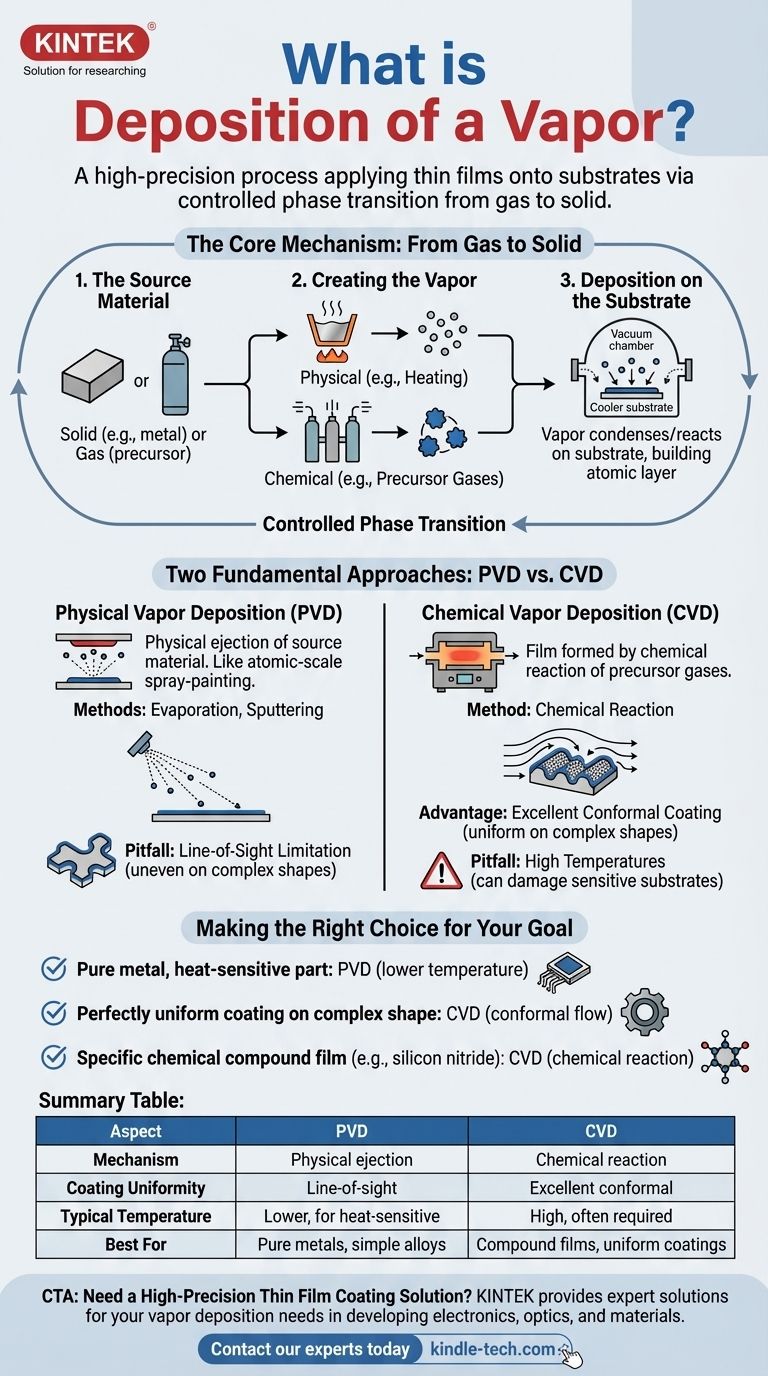
The Core Mechanism: From Gas to Solid
To grasp vapor deposition, it's best to break it down into its three fundamental stages. Each step is meticulously controlled to achieve specific film properties like thickness, purity, and structure.
The Source Material
The process begins with the material you intend to deposit. This "source" or "precursor" can be a solid (like a metal) or a gas, depending on the specific technique being used.
Creating the Vapor
The source material must be converted into a gas. This is accomplished in one of two primary ways: physically or chemically.
A physical process, like heating a metal until it evaporates, creates a vapor of the material itself. A chemical process uses reactive precursor gases that will later form the desired solid on the substrate.
Deposition on the Substrate
Inside the vacuum chamber, the vaporized material travels and makes contact with the cooler substrate. It then condenses, transitioning directly from a gas to a solid state, and begins to form a thin, uniform film on the surface.
Two Fundamental Approaches: PVD vs. CVD
While the goal is the same, vapor deposition is broadly divided into two distinct families of techniques: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
In PVD, the source material is physically ejected into the vapor phase. Think of it as an atomic-scale spray-painting process.
The material is vaporized through methods like evaporation (heating) or sputtering (bombarding the source with high-energy ions). The vapor then travels in a straight line to coat the substrate.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
In CVD, the film is not made from the source material itself but is the product of a chemical reaction.
Specialized precursor gases are introduced into the chamber. When they interact with the heated substrate, they decompose and react, forming a solid film of a completely new material (e.g., silicon nitride) on the surface.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
Choosing a deposition method requires understanding its inherent limitations. The "best" technique is entirely dependent on the application's specific requirements.
The PVD Line-of-Sight Limitation
Because the vapor in PVD travels in a straight line, it can struggle to evenly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes. Areas not in the direct "line of sight" of the source may receive little to no coating.
The CVD Temperature Challenge
CVD processes often require very high substrate temperatures to drive the necessary chemical reactions. This heat can easily damage sensitive substrates, such as plastics or certain electronic components.
The Universal Vacuum Requirement
Nearly all vapor deposition processes must occur in a vacuum. This prevents the vapor from reacting with air and ensures the film's purity. However, creating and maintaining this vacuum requires complex, expensive equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between PVD and CVD hinges on the material you need, the shape of your substrate, and its tolerance for heat.
- If your primary focus is depositing a pure metal or simple alloy onto a heat-sensitive part: PVD is often the superior choice due to its lower operating temperatures.
- If your primary focus is creating a perfectly uniform (conformal) coating over a complex shape: CVD is typically preferred because the precursor gases can flow and react on all surfaces.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific chemical compound film, like silicon dioxide or titanium nitride: CVD is the necessary method, as the film is built through a chemical reaction.
Ultimately, mastering vapor deposition means seeing it as a foundational tool for atomic-scale engineering and material design.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Physical ejection of source material (e.g., evaporation, sputtering) | Chemical reaction of precursor gases on the substrate surface |
| Coating Uniformity | Line-of-sight; can struggle with complex 3D shapes | Excellent conformal coating on complex shapes |
| Typical Temperature | Lower temperatures, suitable for heat-sensitive substrates | High temperatures often required, can damage sensitive materials |
| Best For | Pure metals, simple alloys | Compound films (e.g., silicon nitride), uniform coatings |
Need a High-Precision Thin Film Coating Solution for Your Lab?
Whether you are developing next-generation electronics, advanced optics, or specialized materials, choosing the right deposition method is critical. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert solutions for your vapor deposition needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PVD or CVD systems can help you achieve superior film quality, purity, and performance for your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- How does a precision furnace affect 316LN phase transformation? Control Sigma Phase & Prevent Micro-Cracks
- Why is a vacuum oven used for drying polymer-ceramic membranes? Optimize Performance at Low Temperatures
- Why is a high vacuum brazing furnace necessary for nickel-based alloys? Achieve Oxidation-Free, High-Strength Joints
- How does annealing equipment affect the functional characteristics of Ti-22Nb alloys? Optimize Superelasticity Now
- What conditions does a vacuum sintering furnace provide for the diffusion bonding of titanium? Achieve Isotropic Purity
- What materials are used in an electric arc furnace? A Guide to Scrap, Electrodes & Refractories
- What is the range of pyrolysis? Master Temperature Control for Optimal Bio-Product Yields
- How does annealing change the properties of a metal? Restore Workability and Improve Performance



















