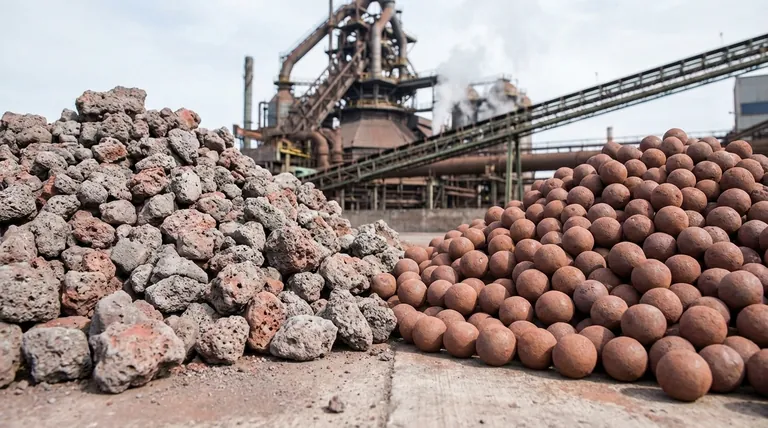
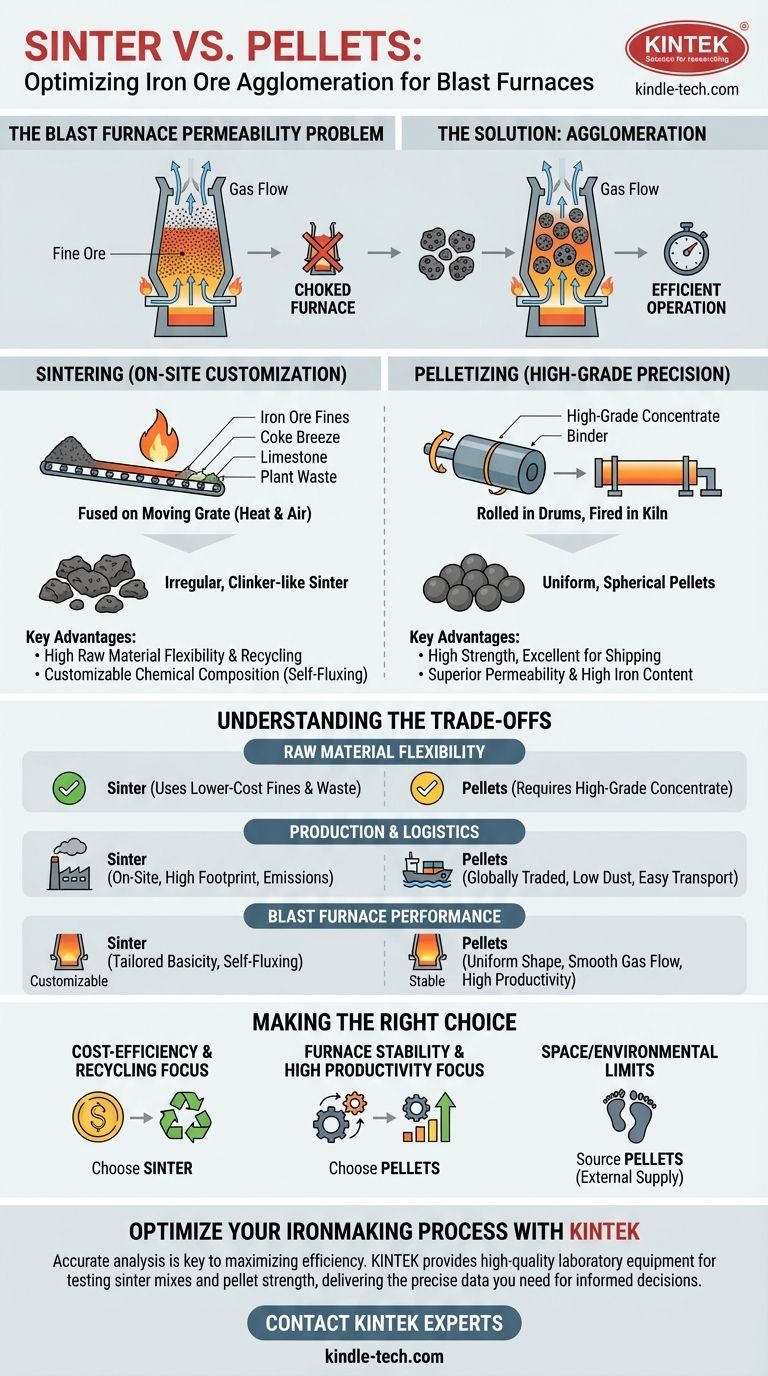
The fundamental difference lies in how and where they are made. Sinter is a fused, clinker-like material produced at the steel plant by heating fine iron ore with other materials on a moving grate. Pellets, in contrast, are small, hardened, spherical balls of high-grade ore concentrate made at the mine site and then shipped.
While both sinter and pellets are forms of agglomerated iron ore designed for the blast furnace, the choice between them is a strategic decision balancing raw material flexibility, transportation logistics, and desired furnace performance.

Why Agglomeration is Necessary
A blast furnace operates like a giant chemical reactor that requires hot gases to flow upwards through a stack of raw materials.
The Blast Furnace Permeability Problem
Raw iron ore is often extracted as fine dust or sand-like particles.
If you were to charge these fines directly into a blast furnace, they would pack together tightly, blocking the flow of reducing gases. This would choke the furnace, halting the ironmaking process.
The Solution: Creating Lumps
Both sintering and pelletizing are agglomeration processes. They solve this problem by taking fine ore particles and binding them into larger, stronger, and more porous lumps.
This ensures good permeability in the blast furnace, allowing hot gases to move freely and react efficiently with the iron ore.
The Sintering Process: On-Site Customization
Sintering is the most widely used agglomeration process, tightly integrated with the operations of a steel plant.
How Sinter is Made
A mixture of iron ore fines, coke breeze (a fuel), limestone (a flux), and recycled plant waste (like dust and mill scale) is spread on a moving grate called a sinter strand.
The surface of this bed is ignited, and air is pulled down through it. The burning coke breeze generates intense heat that fuses, but does not melt, the particles into a single porous, clinker-like cake. This cake is then broken into smaller, irregular lumps.
Key Characteristics of Sinter
Sinter is irregular in shape and size. Its key advantage is that its chemical composition, particularly its basicity (the ratio of basic to acidic components), can be precisely controlled by adding fluxes like limestone during production.
This "self-fluxing" sinter improves blast furnace efficiency by promoting better slag formation and reducing the amount of raw coke needed.
The Pelletizing Process: High-Grade Precision
Pelletizing is a more refined process typically performed at the mining location, focused on upgrading the quality of the iron ore concentrate.
How Pellets are Made
High-grade iron ore is ground into an extremely fine powder, mixed with a binder (like bentonite clay), and rolled into small, uniform spheres in large rotating drums.
These "green balls" are then fired at very high temperatures (around 1300°C) in a kiln. This process hardens the pellets, giving them excellent mechanical strength for handling and transport.
Key Characteristics of Pellets
Pellets are uniform, spherical, and have a high iron content. Their consistent size and shape provide a highly predictable and permeable burden in the blast furnace, leading to very stable and efficient operation.
Their high strength also means they produce very little dust during shipping and handling, a significant logistical advantage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither process is universally superior; the right choice depends on economics, logistics, and operational strategy.
Raw Material Flexibility
Sinter is the clear winner here. Its primary economic advantage is the ability to use a wide variety of lower-cost, lower-grade iron ore fines. Crucially, it is also an effective way to recycle iron-bearing waste products generated within the steel plant.
Pellets require higher-grade iron ore concentrates to be effective. The process is less tolerant of impurities.
Production and Logistics
Sinter plants are built on-site at the steel mill. This requires a significant capital investment and a large physical footprint. They are also a major source of on-site emissions (dust, SOx, NOx) that require extensive environmental controls.
Pellets are produced at the mine and are a globally traded commodity. Their strength and uniform shape make them ideal for long-distance shipping by sea or rail with minimal degradation. This allows steel plants to source high-quality ore from anywhere in the world without investing in their own agglomeration facility.
Blast Furnace Performance
Pellets generally provide superior permeability due to their uniform, spherical shape. This leads to smoother gas flow, lower fuel consumption, and higher productivity.
Sinter, while less uniform, can be custom-tailored for a specific furnace's needs. The inclusion of fluxes to create self-fluxing sinter provides significant metallurgical advantages that can improve the efficiency of the smelting process itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
The decision to use sinter, pellets, or a mixture of both is a core element of a steel plant's operational philosophy.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency and recycling: Sinter is often the preferred choice, as it allows the use of cheaper iron ore fines and in-plant waste materials.
- If your primary focus is furnace stability and high productivity: Pellets are ideal due to their uniform size, high iron content, and excellent mechanical strength, which ensure predictable and efficient furnace operation.
- If your operation lacks space or faces strict on-site environmental limits: Sourcing high-quality pellets from external suppliers is a more viable strategy than building and operating a sinter plant.
Ultimately, understanding the distinct properties of sinter and pellets is the key to optimizing the entire ironmaking value chain from the mine to the blast furnace.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Sinter | Pellets |
|---|---|---|
| Production Site | Steel Plant | Mine Site |
| Shape & Uniformity | Irregular, clinker-like | Uniform, spherical balls |
| Raw Material Flexibility | High (can use fines & plant waste) | Lower (requires high-grade concentrate) |
| Key Advantage | On-site customization, recycling | High strength, excellent for shipping |
| Blast Furnace Role | Customizable basicity, self-fluxing | Superior permeability, stable operation |
Optimize Your Ironmaking Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right agglomerate—sinter or pellets—is crucial for maximizing your blast furnace's efficiency and profitability. The decision impacts everything from raw material costs and logistics to furnace stability and environmental compliance.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables to help you analyze and optimize your agglomeration processes. Whether you are developing sinter mixes or testing pellet strength, our reliable tools deliver the precise data you need to make informed decisions.
Ready to enhance your operation? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can support your specific laboratory and production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- kbr pellet press 2t
People Also Ask
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness
- What is vacuum sintering? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Performance for Advanced Materials
- Why is sintering easier in the presence of a liquid phase? Unlock Faster, Lower-Temperature Densification
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding



















