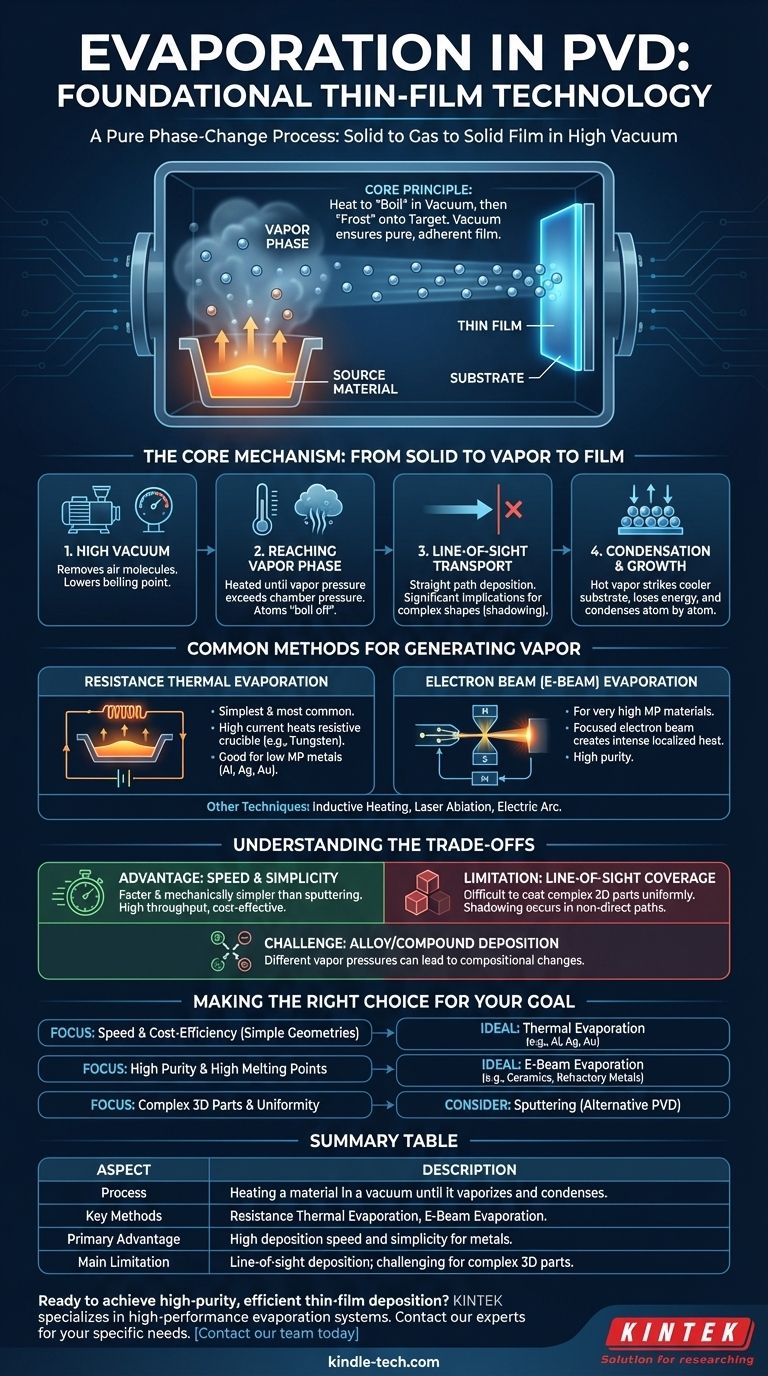
In the world of thin-film technology, evaporation is one of the foundational methods of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). It is a process where a source material is heated in a high vacuum chamber until it vaporizes into a gas. This vapor then travels and condenses onto a cooler surface, known as the substrate, forming a solid, ultra-thin film. It is a pure phase-change process: solid to gas, and back to solid.
The core principle of evaporation PVD is straightforward: use heat to "boil" a material in a vacuum and then "frost" it onto a target. The vacuum is the critical element, as it allows the vaporized atoms to travel directly to the substrate without colliding with air molecules, ensuring a pure and adherent film.
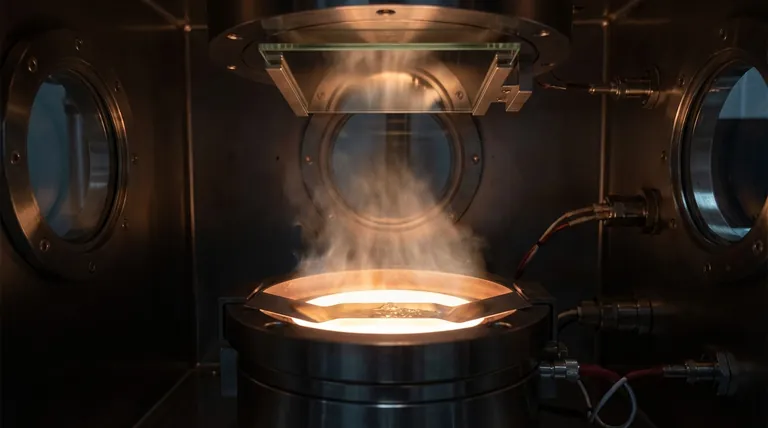

The Core Mechanism: From Solid to Vapor to Film
To truly understand evaporation, it's essential to break down the process into its fundamental stages. Each step is precisely controlled to determine the final properties of the thin film.
The Role of High Vacuum
The entire process occurs under high vacuum for two critical reasons. First, removing air molecules prevents the vaporized source material from reacting with contaminants like oxygen or nitrogen. Second, the vacuum lowers the boiling point of the material, allowing it to vaporize at a lower temperature.
Reaching the Vapor Phase
The source material is heated until its vapor pressure exceeds the pressure of the vacuum chamber. This causes atoms to "boil off" or sublimate directly from the solid source, creating a cloud of vapor.
Line-of-Sight Transport
Once vaporized, the atoms travel in a straight path from the source to the substrate. This is known as line-of-sight deposition. Anything not in this direct path will not be coated, a factor that has significant implications for coating complex shapes.
Condensation and Film Growth
When the hot vapor atoms strike the cooler substrate, they rapidly lose energy and condense back into a solid state. The film grows atom by atom as more vapor arrives. The temperature of the substrate is often controlled to improve the film's adhesion and uniformity.
Common Methods for Generating Vapor
The "heating" part of the process can be accomplished in several ways, with the choice of method depending on the material being deposited and the desired film properties.
Resistance Thermal Evaporation
This is the simplest and most common method. A high electrical current is passed through a heat-resistant crucible or "boat" (often made of tungsten or molybdenum) that holds the source material. The resistance causes the boat to heat up, which in turn heats the material to its evaporation point.
Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
For materials with very high melting points, an electron beam is used. A high-energy beam of electrons is magnetically guided to strike the source material, creating a localized spot of intense heat that causes evaporation. This method offers high purity as only the material itself is heated, not a surrounding crucible.
Other Heating Techniques
More specialized applications may use other methods. Inductive heating uses an RF coil to heat the crucible, while laser ablation and electric arc methods use focused energy to vaporize the source material.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Evaporation
Like any technical process, evaporation PVD has clear advantages and limitations that make it suitable for some applications but not others.
Key Advantage: Speed and Simplicity
Compared to other PVD techniques like sputtering, evaporation is often faster and mechanically simpler. This can lead to higher throughput and lower equipment costs, making it a cost-effective choice for many applications.
The Limitation: Line-of-Sight Coverage
The straight-line path of vapor atoms is the primary drawback. It makes uniformly coating complex, three-dimensional parts very difficult without sophisticated substrate rotation. Areas not in the direct line of sight will receive little to no coating, a phenomenon known as shadowing.
The Challenge: Alloy and Compound Deposition
Evaporating materials with multiple elements can be challenging. If the elements have different vapor pressures, one may evaporate more quickly than the others, resulting in a film whose chemical composition does not match the source material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for material, geometry, and performance.
- If your primary focus is speed and cost-efficiency for simple geometries: Thermal evaporation is often the ideal choice for depositing thin layers of metals like aluminum, silver, or gold.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-purity films of high-melting-point materials: Electron beam evaporation provides the necessary energy and control to vaporize ceramics or refractory metals.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D parts with perfect uniformity: You may need to consider an alternative PVD process like sputtering, which does not have the same line-of-sight limitation.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles allows you to select the right deposition technique not just for the material, but for the specific demands of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Heating a material in a vacuum until it vaporizes and condenses on a substrate. |
| Key Methods | Resistance Thermal Evaporation, Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation. |
| Primary Advantage | High deposition speed and simplicity for metals like Al, Ag, Au. |
| Main Limitation | Line-of-sight deposition; challenging for complex 3D parts. |
Ready to achieve high-purity, efficient thin-film deposition? The right PVD equipment is critical to your success. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including evaporation systems for depositing metals and high-melting-point materials. Our experts can help you select the ideal solution for your specific materials and throughput needs. Contact our team today to discuss how our evaporation systems can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the process of thermal evaporation in PVD? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What is thermal evaporation used to deposit? A Guide to Metals, Compounds, and Key Applications
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- What is vacuum thermal evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition



















