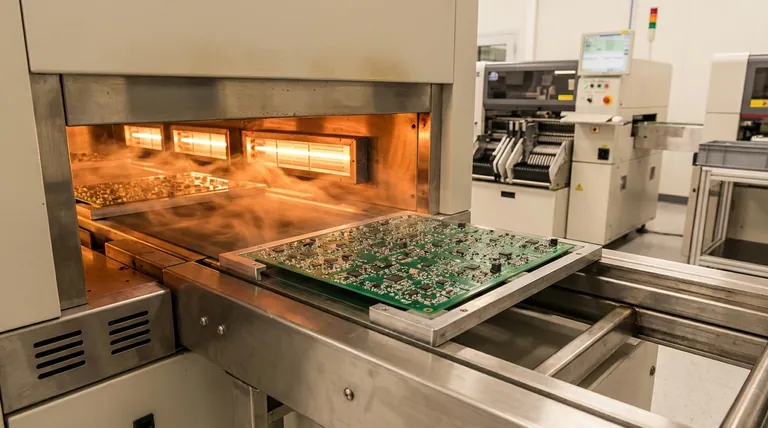
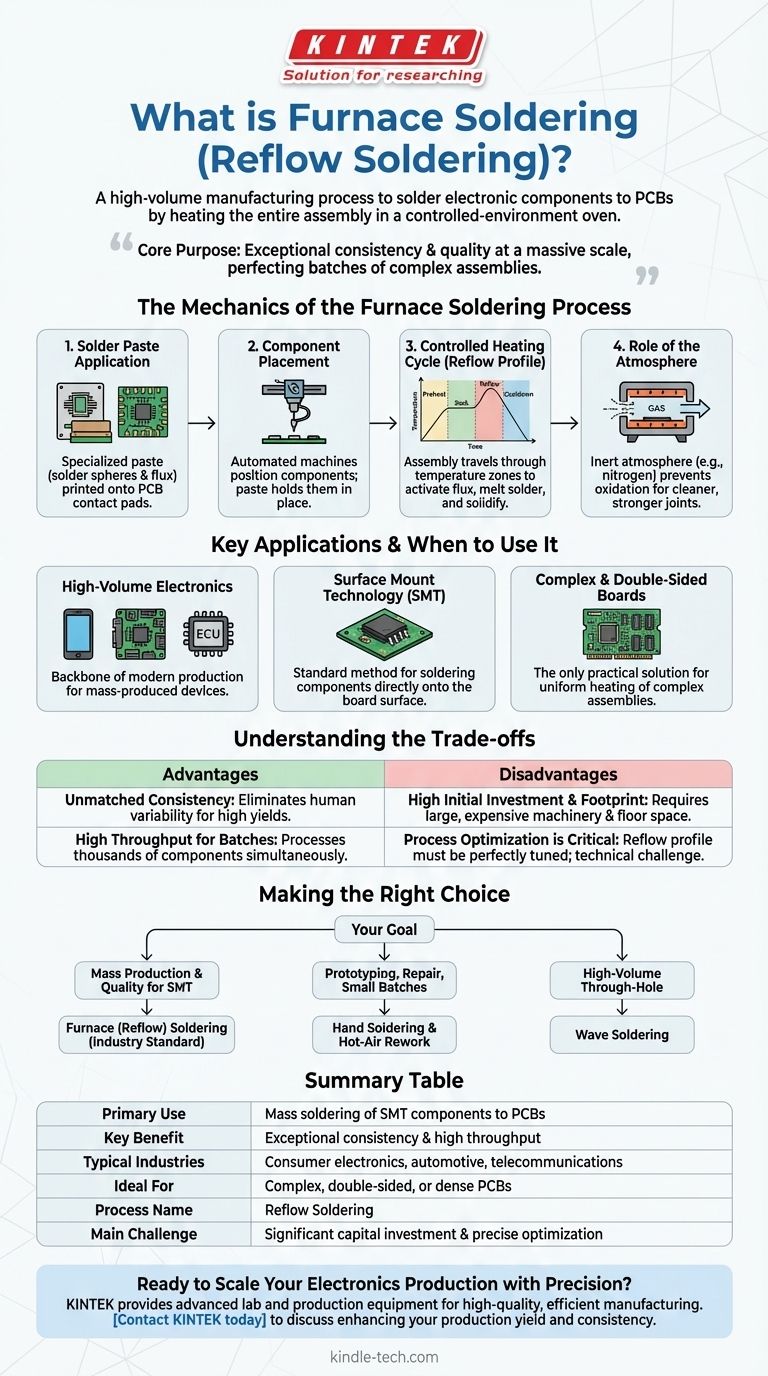
In essence, furnace soldering is a high-volume manufacturing process used to solder electronic components to a printed circuit board (PCB) by heating the entire assembly in a controlled-environment oven. This method, more commonly known as reflow soldering, uses precisely applied solder paste which melts during the heating cycle, creating thousands of reliable electrical connections simultaneously.
The core purpose of furnace soldering is not just to join components, but to do so with exceptional consistency and quality at a massive scale. It trades the speed of a single joint for the efficiency of perfecting an entire batch of complex assemblies at once.

The Mechanics of the Furnace Soldering Process
Furnace soldering is a multi-stage process where precision at each step is critical to the final outcome. The furnace itself is simply the tool for the most crucial stage: the controlled heating cycle.
Step 1: Solder Paste Application
Before any heating occurs, a specialized solder paste—a mixture of microscopic solder spheres and flux—is printed onto the contact pads of the circuit board. This is typically done with a stencil, ensuring a precise amount of paste is deposited exactly where it's needed.
Step 2: Component Placement
Automated "pick-and-place" machines then position the electronic components onto the board. The sticky nature of the solder paste is sufficient to hold the components in place as the board is transferred to the furnace.
Step 3: The Controlled Heating Cycle (Reflow Profile)
This is the heart of the process. The assembly moves through the furnace on a conveyor belt, passing through several zones with different temperatures. This carefully managed temperature curve is called a reflow profile.
- Preheat: Gently raises the board's temperature to activate the flux and prevent thermal shock.
- Soak (or Thermal Soak): Allows the entire assembly, including large and small components, to reach a uniform temperature.
- Reflow: The temperature is rapidly increased above the solder's melting point. The solder spheres turn to liquid, "reflowing" to form metallurgical bonds.
- Cooldown: The assembly is cooled in a controlled manner to solidify the solder joints without creating defects.
Step 4: The Role of the Atmosphere
Many industrial soldering furnaces use a controlled, inert atmosphere, typically by pumping in nitrogen gas. This displaces oxygen, preventing oxidation of the components and solder during the high-temperature reflow stage, resulting in cleaner, stronger, and more reliable solder joints.
Key Applications and When to Use It
While the term "furnace" has broad applications in material science, its use in soldering is highly specific to the electronics industry.
High-Volume Electronics Manufacturing
Furnace soldering is the backbone of modern electronics production. It is used for nearly all mass-produced devices, including motherboards, smartphones, graphics cards, and automotive control units.
Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
This process is the standard and most effective method for soldering Surface Mount Devices (SMDs). These components lack the long leads of older "through-hole" parts and are designed to be mounted directly onto the surface of a PCB, making furnace reflow a perfect fit.
Complex and Double-Sided Boards
For boards with a high density of components or parts mounted on both sides, furnace soldering is the only practical solution. It uniformly heats the entire assembly, something that is impossible to achieve reliably with manual methods like hand soldering.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing furnace soldering involves weighing its distinct advantages against its significant operational requirements.
Advantage: Unmatched Consistency
By heating the entire board with a scientifically developed reflow profile, furnace soldering eliminates the human variability of hand soldering. This results in extremely high yields and consistent quality across millions of joints.
Advantage: High Throughput for Batches
While a single reflow cycle can take several minutes, the furnace processes hundreds or thousands of components on each board simultaneously. When run continuously, its throughput for mass production is immense.
Disadvantage: High Initial Investment and Footprint
Reflow ovens are large, complex, and expensive pieces of industrial machinery. They require significant factory floor space and a substantial capital investment, making them unsuitable for hobbyists or small-scale prototyping.
Disadvantage: Process Optimization is Critical
Developing the correct reflow profile is a technical challenge. The profile must be perfectly tuned for the specific PCB's mass, the components used, and the type of solder paste. An incorrect profile can destroy an entire batch of expensive assemblies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a soldering method depends entirely on your project's scale, complexity, and budget.
- If your primary focus is mass production and quality for SMT: Furnace (reflow) soldering is the non-negotiable industry standard.
- If your primary focus is prototyping, repair, or small batches: Hand soldering and hot-air rework stations are far more practical and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is soldering through-hole components in high volume: Wave soldering, a different process where the board passes over a wave of molten solder, is often the more specialized and efficient choice.
Ultimately, understanding the principles of furnace soldering allows you to select the right manufacturing process based on scale, quality, and cost.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Mass soldering of Surface Mount Technology (SMT) components to PCBs |
| Key Benefit | Exceptional consistency and high throughput for batch processing |
| Typical Industries | Consumer electronics, automotive, telecommunications |
| Ideal For | High-volume production of complex, double-sided, or dense PCBs |
| Process Name | Reflow Soldering |
| Main Challenge | Requires significant capital investment and precise process optimization |
Ready to Scale Your Electronics Production with Precision?
Furnace soldering is the cornerstone of reliable, high-volume electronics manufacturing. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab and production equipment necessary to achieve this level of quality and efficiency. Whether you are scaling up your assembly line or optimizing your reflow process, our expertise in lab equipment and consumables is tailored to meet the rigorous demands of modern electronics manufacturing.
Let us help you ensure every solder joint is perfect. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your production yield and consistency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process



















