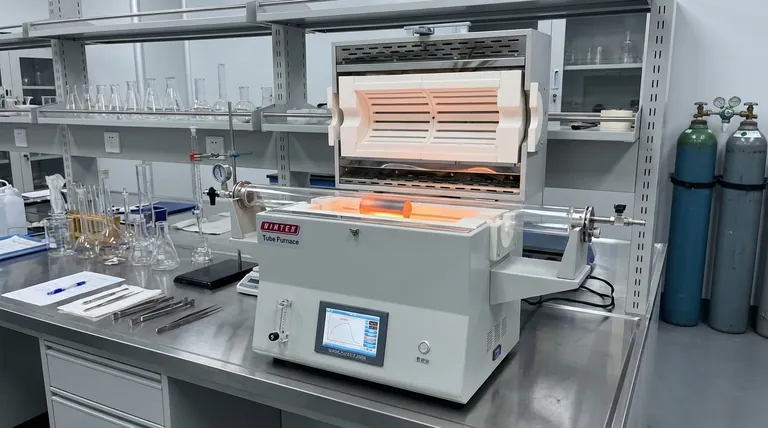
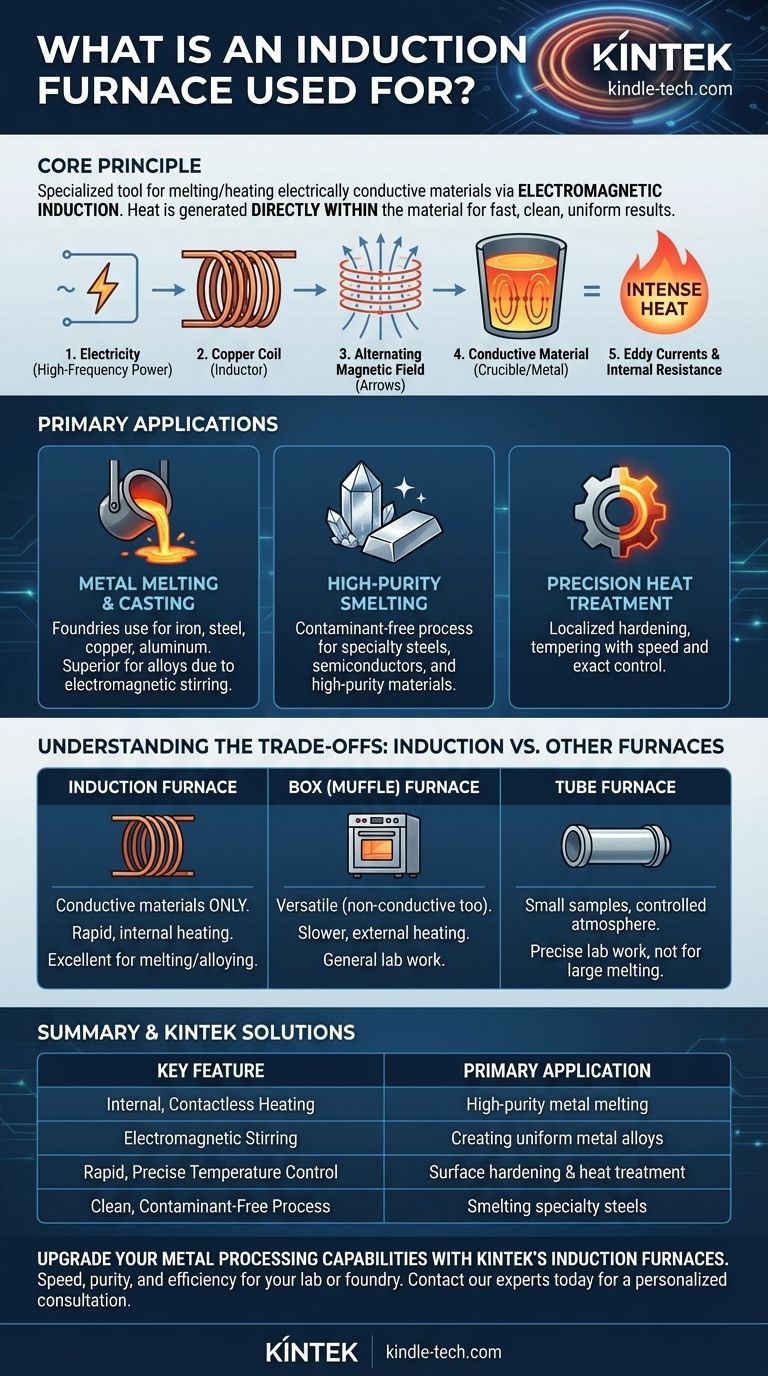
In essence, an induction furnace is a specialized tool used for melting or heating electrically conductive materials, most commonly metals. It operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, using a powerful, alternating magnetic field to generate heat directly within the material itself, leading to exceptionally fast, clean, and uniform results.
An induction furnace is not just another type of oven. Its unique ability to heat materials from the inside out using electromagnetism—without direct contact or flames—makes it the preferred choice for high-purity metal melting, alloying, and precision heat treatment.

How Induction Heating Works: The Core Principle
To understand what an induction furnace is used for, you must first understand its unique heating method, which sets it apart from conventional box or tube furnaces.
From Electricity to a Magnetic Field
An induction furnace uses a high-frequency power supply connected to a copper coil, known as an inductor. When electricity flows through this coil, it generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within the coil.
Generating "Eddy Currents"
When an electrically conductive material (like a piece of steel or a crucible of scrap metal) is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces circular electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
Internal Resistance Creates Heat
The metal's natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents generates immense heat. This is the induction electrothermal effect—the material effectively becomes its own heating element, heating rapidly and uniformly from within.
The Result: Uniformity and Purity
This internal heating process also creates a natural stirring effect in molten metal, which is invaluable for creating homogenous metal alloys. Furthermore, since no external heating elements or combustion byproducts come into contact with the material, it is an exceptionally clean process.
Primary Applications of Induction Furnaces
The unique characteristics of induction heating make these furnaces ideal for specific industrial and scientific tasks.
Metal Melting and Casting
This is the most common use. Foundries use induction furnaces to melt everything from iron and steel to copper, aluminum, and precious metals. The speed, efficiency, and electromagnetic stirring make them superior for producing high-quality castings and alloys with consistent composition.
High-Purity Smelting
Because the process is free from contaminants like carbon that can be introduced by arc furnaces or fuel-fired furnaces, induction is the go-to method for producing specialty steels, silicon for semiconductors, and other high-purity materials where chemical composition is critical.
Precision Heat Treatment
Induction can be used for surface hardening, tempering, or annealing specific areas of a metal part. By controlling the shape of the inductor coil and the frequency of the power supply, heat can be applied to a precise location with incredible speed and control, without affecting the rest of the component.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Induction vs. Other Furnaces
While powerful, an induction furnace is not a universal solution. Its purpose becomes clearer when compared to other common furnace types.
Induction vs. Box (Muffle) Furnaces
A box furnace heats the atmosphere within a chamber, which then slowly transfers heat to the object inside. This is slower and less energy-efficient but highly versatile, as it can heat non-conductive materials like ceramics or be used for ashing samples. Induction furnaces only work with conductive materials.
Induction vs. Tube Furnaces
Tube furnaces are typically used in laboratories for processing small samples in a tightly controlled atmosphere. While they can perform tasks like annealing or sintering, they do so through external heating and are not designed for the large-scale, rapid melting that is the primary strength of an induction furnace.
Key Limitations of Induction
The most significant limitation is that the material being heated must be electrically conductive. Additionally, the initial capital cost for the specialized power supply and control systems is often higher than for simpler furnace designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating technology requires matching the tool to the specific objective.
- If your primary focus is melting metals for casting or creating alloys: An induction furnace is the superior choice for its unmatched speed, cleanliness, and homogenizing stirring effect.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work or heat-treating non-conductive materials: A box or muffle furnace offers greater material versatility and is better suited for these tasks.
- If your primary focus is processing small components or powders in a controlled atmosphere: A tube furnace is specifically designed for this type of precise, small-scale laboratory work.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental difference between internal (induction) and external (conventional) heating is the key to selecting the right furnace for your goal.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Primary Application |
|---|---|
| Internal, Contactless Heating | High-purity metal melting (steel, copper, aluminum) |
| Electromagnetic Stirring | Creating uniform metal alloys |
| Rapid, Precise Temperature Control | Surface hardening and localized heat treatment |
| Clean, Contaminant-Free Process | Smelting specialty steels and semiconductor materials |
Upgrade your metal processing capabilities with KINTEK's induction furnaces.
Whether you're melting metals for casting, creating precise alloys, or performing controlled heat treatment, our induction heating solutions deliver the speed, purity, and efficiency your lab or foundry requires.
We specialize in providing the right equipment for your specific needs:
- For metal melting and alloying: Our induction furnaces offer rapid heating and electromagnetic stirring for superior results.
- For precision heat treatment: Achieve localized hardening or annealing with exact temperature control.
Let KINTEK, your lab equipment partner, help you optimize your process. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how our induction furnaces can bring value to your operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process



















