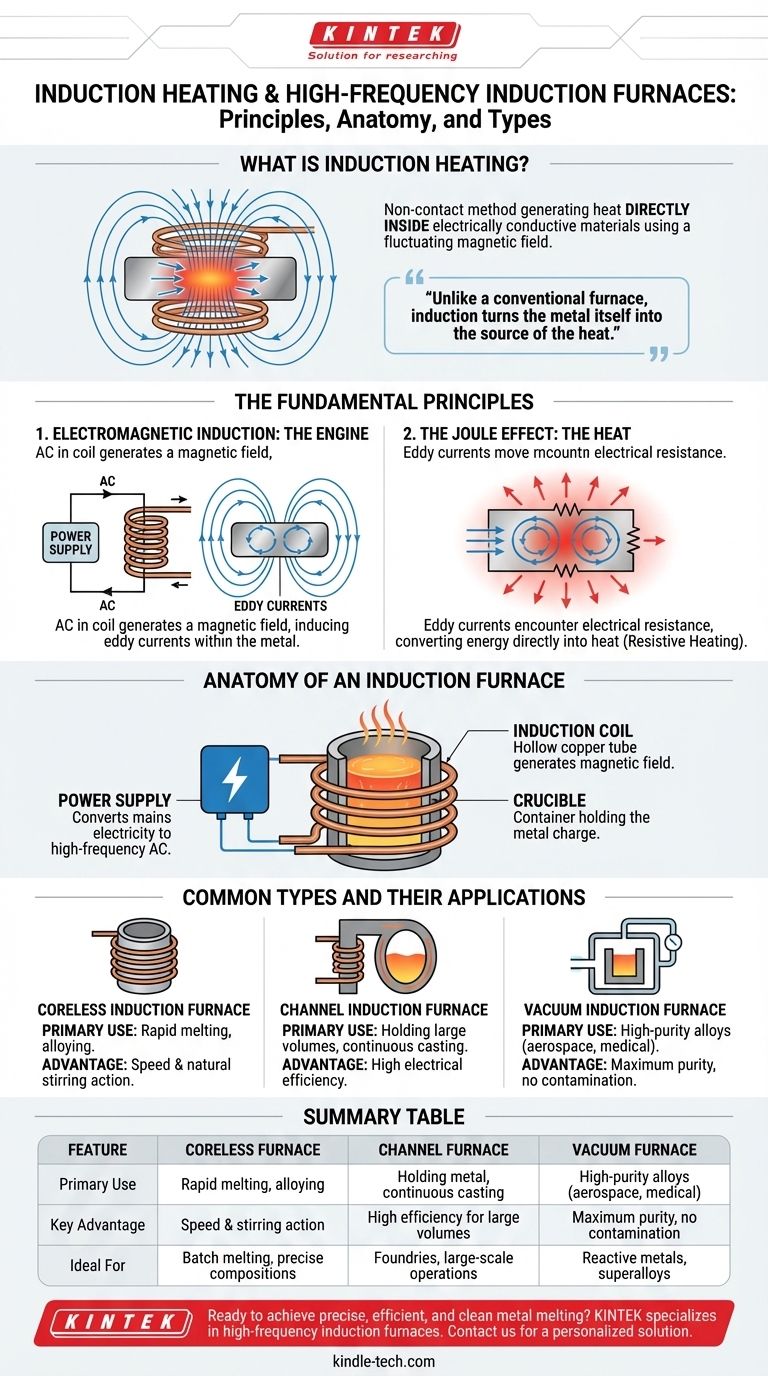
In essence, induction heating is a highly controlled, non-contact method for heating electrically conductive materials. It works by using a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field to generate heat directly inside the material itself. A high-frequency induction furnace is a device that applies this principle to melt metals and create precise alloys, offering speed and purity that traditional heating methods cannot match.
The core concept to grasp is that induction heating turns the metal itself into the source of the heat. Unlike a conventional furnace that heats the outside of a material, induction generates heat from within, leading to rapid, efficient, and clean melting.
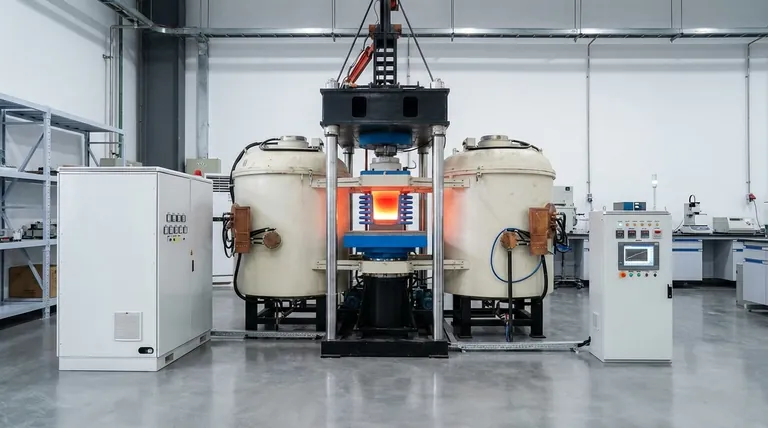

The Fundamental Principles of Induction Heating
To understand an induction furnace, you must first understand the two core physics principles that make it possible. These phenomena work together to convert electrical energy into thermal energy with remarkable efficiency.
Electromagnetic Induction: The Engine
An alternating current (AC) is passed through a copper coil. This flow of electricity generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space around and within the coil.
When a conductive material, such as a piece of metal, is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces circulating electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
The Joule Effect: The Heat
The induced eddy currents are not able to flow through the metal without opposition. The material's inherent electrical resistance impedes the flow of these currents.
This opposition converts the electrical energy of the eddy currents directly into heat. This phenomenon, known as the Joule effect or resistive heating, is what causes the metal's temperature to rise rapidly and eventually melt.
Anatomy of an Induction Furnace
While designs vary, nearly all induction furnaces share the same fundamental components that apply these physical principles.
The Induction Coil
This is typically a hollow copper tube wound into a coil that surrounds the material to be melted. The high-frequency alternating current from the power supply flows through this coil, creating the necessary magnetic field. Water is often circulated through the hollow coil to keep it from overheating.
The Crucible
The crucible is the refractory-lined container that holds the metal charge. It is placed within the induction coil but does not touch it. Depending on the design, the crucible can be made of conductive or non-conductive materials.
The Power Supply
This unit converts mains electricity into the high-frequency, high-current AC power required to drive the induction coil. The frequency is a critical parameter that can be adjusted to control the heating depth and stirring effect within the molten metal.
Common Types and Their Applications
Not all induction furnaces are the same. The specific design is chosen based on the application, from small-batch specialty alloys to large-scale foundry operations.
Coreless Induction Furnaces
This is the most common design, where the coil directly surrounds the crucible containing the metal charge. They are highly versatile and excellent for rapidly melting a wide range of metals. The high frequencies used often create a natural stirring action that helps ensure a homogenous alloy.
Channel (or Core-Type) Furnaces
This design functions more like a transformer. A primary coil is wound around an iron core, and a loop of molten metal acts as the secondary circuit. Heat generated in this "channel" circulates into the main bath of metal. These furnaces are extremely efficient for holding large volumes of molten metal at a specific temperature.
Vacuum Induction Furnaces
For producing the highest purity metals and alloys, the entire melting process is conducted inside a vacuum chamber. This prevents the molten metal from reacting with oxygen, nitrogen, and other gases in the air, which is critical for reactive metals or high-performance superalloys.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The type of induction furnace you use is dictated entirely by the desired outcome. The technology's flexibility allows it to be tailored to very specific metallurgical needs.
- If your primary focus is rapid melting and compositional precision: A coreless high-frequency furnace provides the speed and stirring action needed for creating exact alloys.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of metal or continuous casting: A channel furnace's high electrical efficiency makes it the ideal choice for maintaining temperature over long periods.
- If your primary focus is maximum material purity for aerospace or medical alloys: A vacuum induction furnace is the only method that guarantees protection from atmospheric contamination.
Understanding these operational principles allows you to select the precise tool to achieve your metallurgical objective.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Coreless Furnace | Channel Furnace | Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Rapid melting, alloying | Holding metal, continuous casting | High-purity alloys (aerospace, medical) |
| Key Advantage | Speed & stirring action | High efficiency for large volumes | Maximum purity, no contamination |
| Ideal For | Batch melting, precise compositions | Foundries, large-scale operations | Reactive metals, superalloys |
Ready to achieve precise, efficient, and clean metal melting? KINTEK specializes in high-frequency induction furnaces for laboratories and production facilities. Whether you need the rapid melting of a coreless furnace, the holding efficiency of a channel furnace, or the ultimate purity of a vacuum furnace, our experts will help you select the perfect equipment for your metallurgical goals. Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the primary role of the Vacuum Hot Pressing Sintering Furnace? Prepare High-Purity W-Si Alloy Targets
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results
- Why is the vacuum system of a Vacuum Hot Pressing furnace critical for ODS ferritic stainless steel performance?
- How does a Vacuum Hot Press Sintering Furnace (VHPS) produce high-density high-entropy alloys? Expert Insights
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity



















