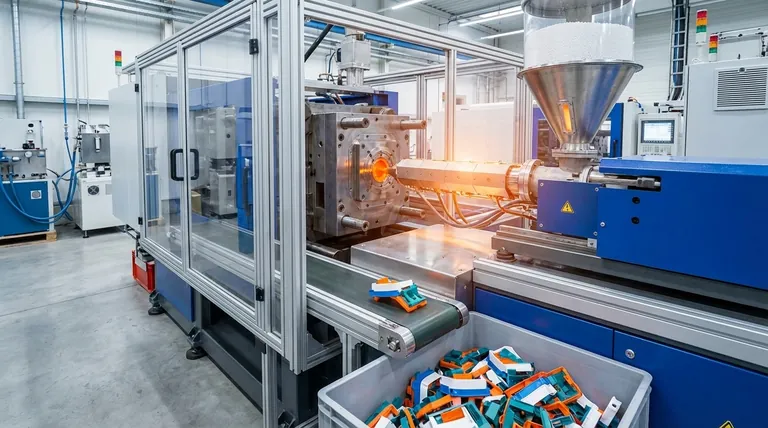
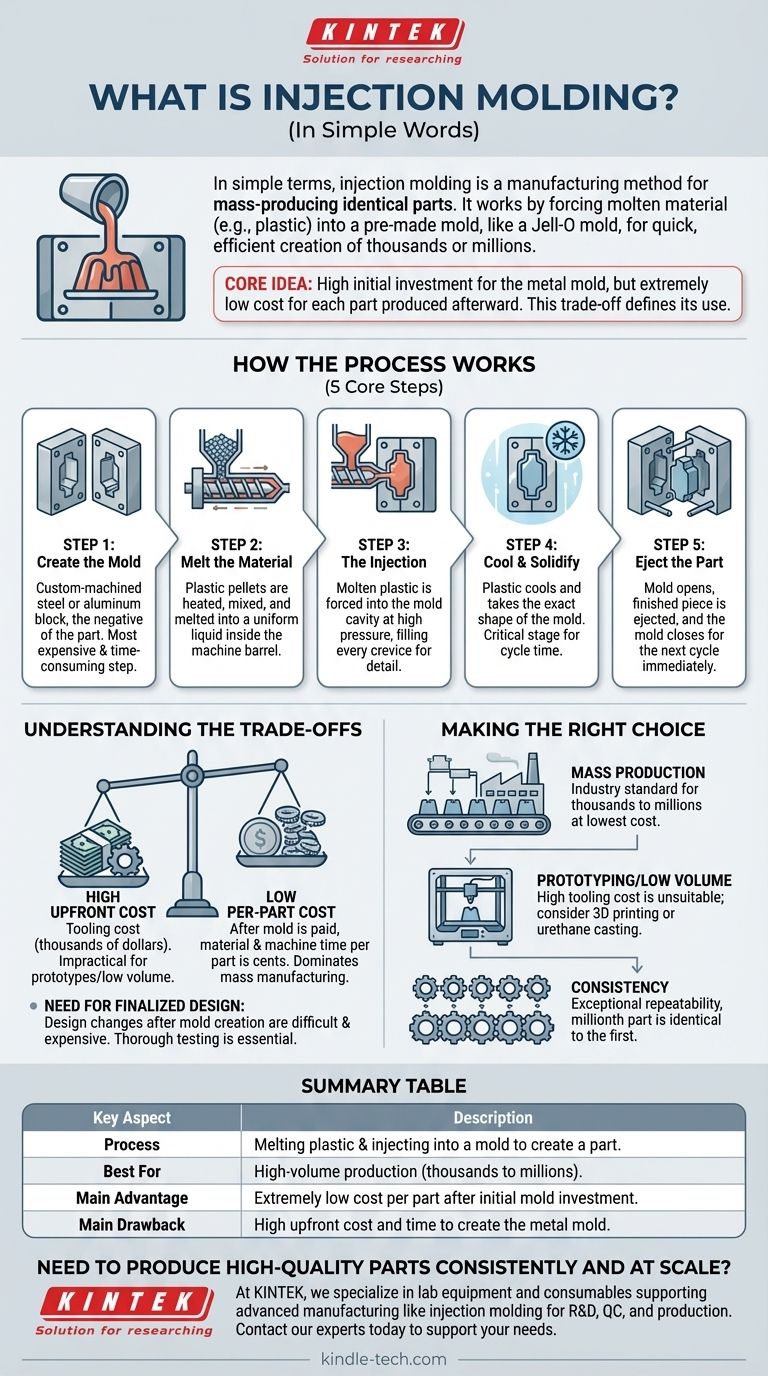
In simple terms, injection molding is a manufacturing method for mass-producing identical parts. It works by forcing molten material, most commonly plastic, into a pre-made mold, much like how a Jell-O mold is filled to create a specific shape. This process allows for the creation of thousands or even millions of the same item quickly and efficiently.
The core idea to remember is that injection molding involves a high initial investment to create the metal mold, but it results in an extremely low cost for each individual part produced afterward. It is the fundamental trade-off that defines its use in manufacturing.

How Does the Process Actually Work?
Understanding injection molding is best done by looking at its core steps. The cycle is fast, often taking only seconds to complete, which is why it's so effective for high-volume production.
Step 1: Creating the Mold
Everything begins with the mold, also known as the tool or die. This is a highly precise, custom-machined block of metal, typically steel or aluminum, that is the negative of the part you want to create. This is by far the most expensive and time-consuming part of the entire process.
Step 2: Melting the Material
Small plastic pellets are fed from a hopper into the barrel of the injection molding machine. Inside, a large screw heats, mixes, and melts these pellets into a uniform molten liquid.
Step 3: The Injection
The molten plastic is then forced forward under extremely high pressure, injecting it into the empty cavity of the closed mold. The machine fills every crevice of the mold to ensure the part is complete and detailed.
Step 4: Cooling and Solidifying
Once the mold is filled, the plastic begins to cool and solidify, taking on the exact shape of the mold's interior. This cooling stage is a critical part of the cycle time.
Step 5: Ejecting the Part
After the part has hardened sufficiently, the mold opens, and the finished piece is pushed out by ejector pins. The mold then closes again, ready for the next cycle to begin immediately.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Injection molding is an incredibly powerful process, but it is not the right solution for every project. The decision to use it is almost always an economic one, governed by a few key principles.
The High Upfront Cost
The primary drawback is the tooling cost. Designing and machining a high-quality steel mold can cost thousands, or even tens of thousands, of dollars. This makes it completely impractical for one-off prototypes or very small production runs.
The Low Per-Part Cost
The benefit directly counters the drawback. Once the mold is paid for, the cost of the raw material and machine time per part is incredibly low, often just a few cents. This economy of scale is why it dominates mass manufacturing.
The Need for Finalized Design
Because the mold is made of metal, making changes to the part design after the tool is created is extremely difficult and expensive. The design must be thoroughly tested and finalized before committing to mold production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use injection molding depends entirely on your project's volume and budget.
- If your primary focus is mass production: Injection molding is the industry standard for creating thousands to millions of identical parts at the lowest possible cost per unit.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or low volume: The high tooling cost makes injection molding unsuitable; consider alternatives like 3D printing or urethane casting.
- If your primary focus is consistency: This process offers exceptional repeatability, ensuring that the millionth part is virtually identical to the first.
Ultimately, injection molding is the engine of modern manufacturing, turning a single perfect design into millions of physical objects with precision and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Melting plastic and injecting it into a mold to create a part. |
| Best For | High-volume production (thousands to millions of parts). |
| Main Advantage | Extremely low cost per part after initial mold investment. |
| Main Drawback | High upfront cost and time to create the metal mold. |
Need to produce high-quality parts consistently and at scale?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables that support advanced manufacturing processes like injection molding. Whether you're in R&D, quality control, or production, our solutions help ensure material integrity and process efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and manufacturing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What is molding technique? A Guide to High-Volume, Complex Part Manufacturing
- What are the parameters to be considered for selecting the thin wall molding machine? Key Specs for High-Speed Production
- What is short capacity of injection Moulding machine? Optimize Your Shot Size for Flawless Parts
- What is a positive of injection moulding? Achieve High-Volume Production with Unmatched Efficiency
- What is the manufacturing process of rubber molding? Injection, Compression, or Transfer Molding?



















