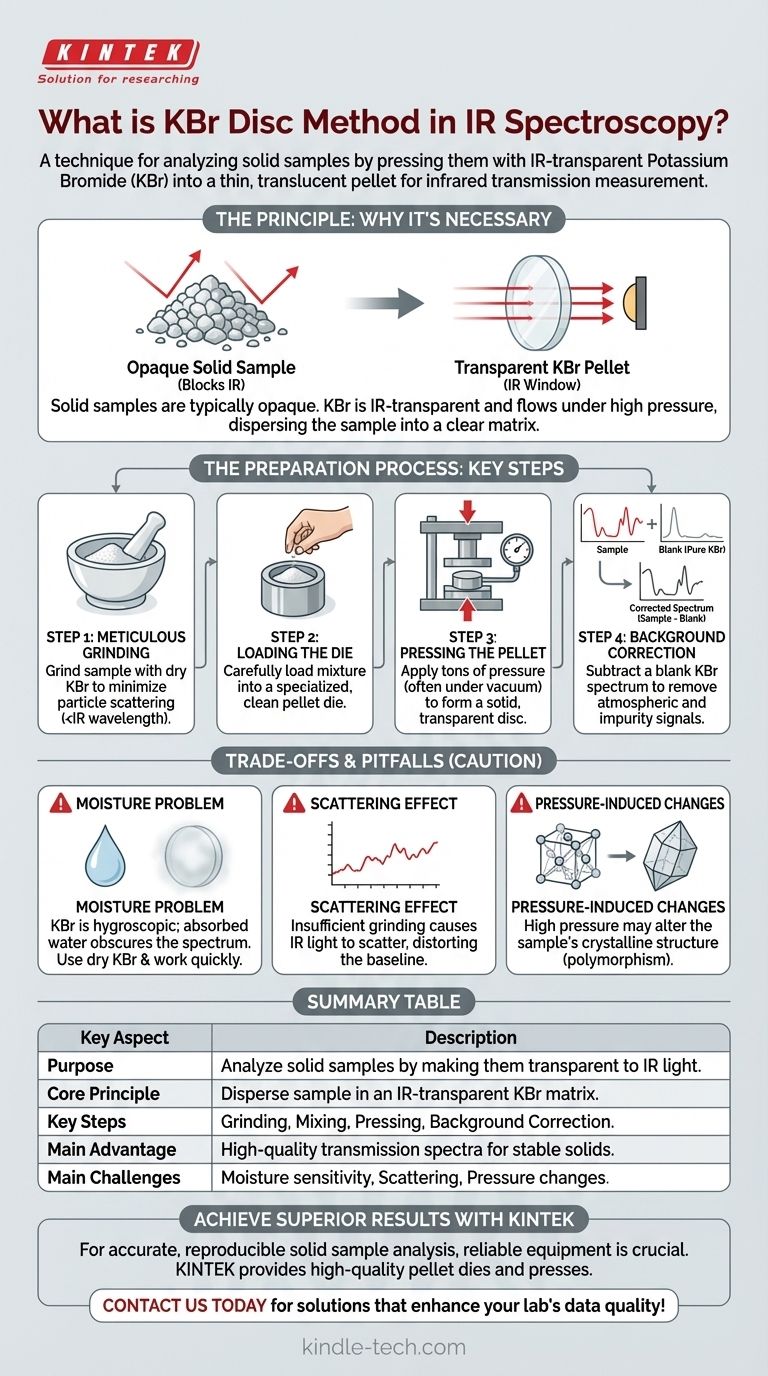
In short, the KBr disc method is a common sample preparation technique used in infrared (IR) spectroscopy to analyze solid samples. It involves finely grinding a small amount of the solid sample with potassium bromide (KBr) powder and then compressing the mixture under high pressure to form a thin, transparent disc or pellet. This pellet can then be placed directly in the path of the spectrometer's infrared beam for analysis.
The core challenge in analyzing solid samples with traditional IR spectroscopy is that they are typically opaque. The KBr method overcomes this by dispersing the sample within a KBr matrix, which is transparent to infrared light, effectively turning an opaque powder into a translucent window for measurement.
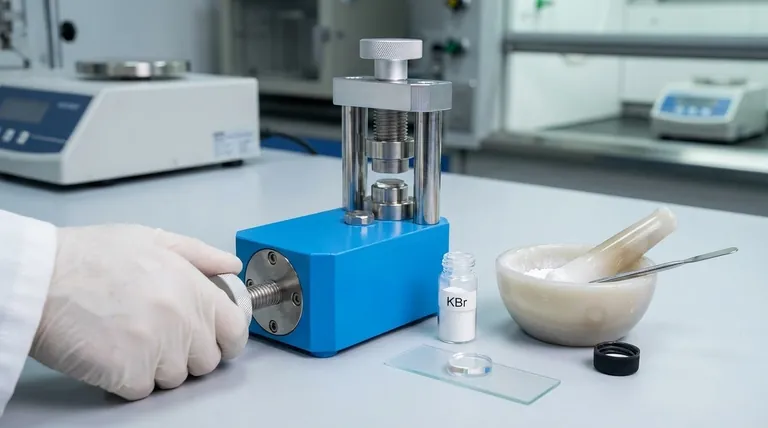

The Principle: Why This Method is Necessary
Why Solids Need a Special Approach
Infrared spectroscopy works by passing a beam of IR light through a sample and measuring which wavelengths are absorbed. For this to work, the sample must be at least partially transparent to the light.
Most solid materials, especially in powdered form, are opaque and will simply block or scatter the IR beam, making a standard transmission measurement impossible.
The Unique Role of Potassium Bromide (KBr)
The KBr method cleverly exploits the physical properties of alkali halides like potassium bromide. KBr is an ideal matrix material for two key reasons:
- IR Transparency: It does not absorb light in the mid-infrared region, so it provides a clear "window" to see the sample's own absorption peaks.
- Plasticity Under Pressure: When subjected to immense pressure, KBr powder flows and fuses into a solid, glass-like sheet, trapping the sample particles within it.
Creating the Analytical Window
By grinding the sample into extremely fine particles and dispersing them evenly throughout the KBr powder, you create a homogeneous mixture. When pressed, this forms a solid disc where the sample is suspended in the transparent KBr matrix, allowing the IR beam to pass through and interact with the sample molecules.
The Preparation Process: Key Steps for a Quality Spectrum
Step 1: Meticulous Grinding
The sample is mixed with a much larger amount of pure, dry KBr powder. The mixture is then ground extensively in an agate mortar and pestle.
The goal is to reduce the sample's particle size to be smaller than the wavelength of the IR radiation being used. This prevents the light from scattering off the particles, which would distort the resulting spectrum.
Step 2: Loading the Die
A small amount of the finely ground mixture is carefully loaded into a specialized pellet die. It is crucial that the die is immaculately clean, as any contaminants will appear in the final spectrum.
Step 3: Pressing the Pellet
The die is placed into a hydraulic press, and a force of several tons is applied. This immense pressure causes the KBr to plasticize and form the solid, transparent pellet.
Often, this is done under a vacuum. The vacuum helps remove trapped air and, more importantly, any residual moisture, which can interfere with the measurement.
Step 4: Background Correction
Before measuring the sample pellet, a "blank" is often run. This can be an empty beam path or, ideally, a pellet made from pure KBr only.
This background spectrum is then subtracted from the sample's spectrum to electronically remove any interfering signals from atmospheric CO2, water vapor, or impurities in the KBr itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
The Moisture Problem
Potassium bromide is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs water from the atmosphere. This absorbed water creates a very broad and strong absorption peak in the spectrum, which can easily obscure important features of the actual sample. Using dried KBr and preparing the pellet quickly is critical.
The Scattering Effect (Christiansen Effect)
If the sample is not ground finely enough, the particles will scatter the IR light rather than absorb it. This leads to a distorted baseline and can make it difficult to accurately identify the true absorption peaks. Proper grinding is the only solution.
Pressure-Induced Changes
The high pressure used to form the pellet can sometimes alter the crystalline structure (polymorphism) of the sample material. This means the resulting spectrum may not perfectly represent the sample in its original state.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Choosing the correct sampling method is essential for obtaining meaningful data.
- If your primary focus is a high-quality transmission spectrum of a stable solid: The KBr disc method is a classic, powerful, and cost-effective choice when performed correctly.
- If your sample is sensitive to pressure or moisture: Consider alternative, non-destructive methods like Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR), which analyzes the sample surface directly with minimal preparation.
- If you need to perform quantitative analysis: Be aware that the KBr method requires extremely precise control over pellet thickness and sample concentration to achieve reproducible results.
Mastering this technique provides a reliable way to unlock the chemical fingerprint of a wide range of solid materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | To analyze solid samples in IR spectroscopy by making them transparent to IR light. |
| Core Principle | Disperse a fine powder sample in a potassium bromide (KBr) matrix, which is transparent to IR radiation. |
| Key Steps | Grinding, mixing with KBr, pressing into a pellet under high pressure, and background correction. |
| Main Advantage | Provides high-quality transmission spectra for stable solid materials. |
| Main Challenges | Moisture sensitivity (KBr is hygroscopic), particle scattering, and potential pressure-induced changes. |
Ready to achieve superior results in your solid sample analysis?
The KBr disc method is a fundamental technique for reliable IR spectroscopy. For accurate and reproducible results, having the right equipment is crucial. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables, including reliable pellet dies and presses, to support your sample preparation needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and data quality. Let our experts help you select the perfect equipment for your application.
Get in touch with our team now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press contribute to the molding phase of Cu/WC? Precision Compacts for Composite Success
- What does the working principle of a hydraulic press depend on? Harness Pascal's Law for Immense Force
- Which mechanism is used in a press machine? Harnessing Hydraulic Power for Maximum Force
- Why is stable pressure control necessary for epoxy resin preforms? Achieving High-Density Insulation Excellence
- Why is precise pressure control necessary for LATP densification? Optimize Density Without Cracking Your Material
- What is the capacities of a hydraulic press? From 1-Ton Lab Presses to 10,000+ Ton Industrial Giants
- Can hydraulic systems that run too hot or too cold cause severe problems over time? Yes, and here's how to prevent it.
- Why is a hydraulic press used to apply 380 MPa to battery bilayers? Achieve Superior Density & Safety



















