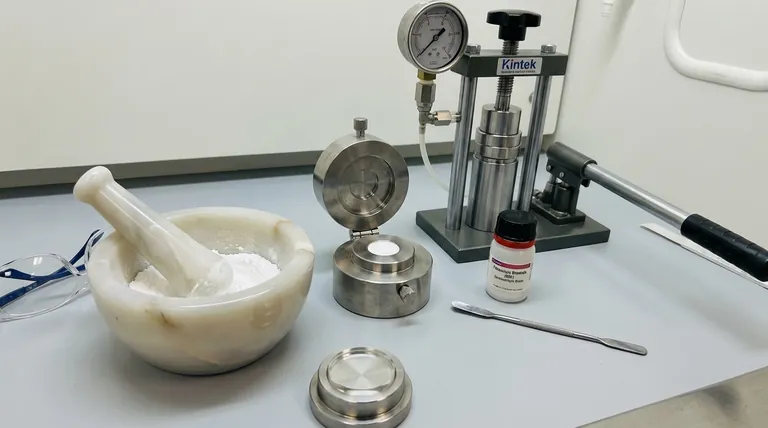
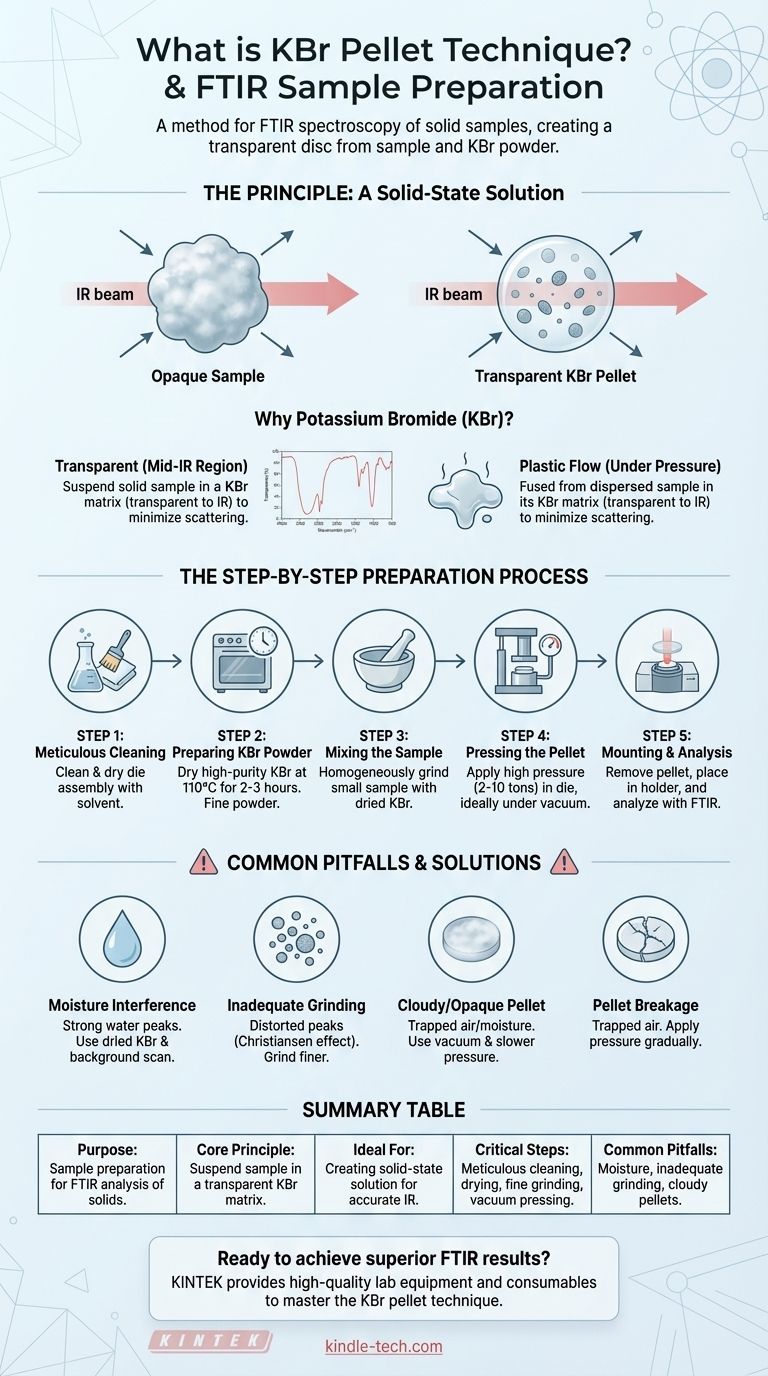
The KBr pellet technique is a widely used sample preparation method for performing Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy on solid samples. The process involves intimately mixing a small amount of a solid sample with finely ground potassium bromide (KBr) powder. This mixture is then compressed under high pressure in a die to form a small, thin, transparent disc or "pellet" that can be analyzed by an IR beam.
The core principle is to suspend the solid sample within a matrix (KBr) that is transparent to infrared radiation. This creates a solid-state "solution," minimizing light scattering and allowing the spectrometer's IR beam to pass through and interact primarily with the sample, not the matrix.

The Principle Behind the Pellet
FTIR spectroscopy works by passing infrared light through a sample to see which frequencies are absorbed. While analyzing gases and liquids is straightforward, solid samples are often opaque and scatter light, making direct analysis difficult. The KBr pellet method elegantly solves this problem.
Why Potassium Bromide (KBr)?
Potassium bromide is the ideal material for this technique for two key reasons. First, KBr is transparent across most of the mid-infrared region, meaning it does not have significant absorption bands that would interfere with the sample's spectrum.
Second, alkali halides like KBr have a unique physical property: under immense pressure, they become plastic and flow, fusing together to form a solid, glass-like sheet.
The Goal: A Solid-State Solution
By finely grinding the sample and dispersing it within the KBr powder, you create a homogeneous mixture. When pressed, the KBr forms a solid matrix that effectively "dissolves" the sample particles, holding them in place for analysis. This uniform dispersion is critical for obtaining a clear and accurate spectrum.
The Step-by-Step Preparation Process
Achieving a high-quality pellet requires a methodical and precise approach. Each step is designed to minimize contamination and physical imperfections that can ruin an analysis.
Step 1: Meticulous Cleaning
Before you begin, all parts of the pellet die assembly must be thoroughly cleaned. A solvent like chloroform is often used to remove any residual sample or dirt, followed by drying with a clean tissue.
Step 2: Preparing the KBr Powder
The KBr powder must be of high purity and, most importantly, completely dry. It should be ground to a fine powder (around 200 mesh) to ensure it mixes well with the sample.
Crucially, the powder must be dried in an oven at approximately 110°C for two to three hours to remove any adsorbed water, which has strong IR absorption bands that can obscure the sample's spectrum.
Step 3: Mixing the Sample
A small amount of the solid sample is ground with a portion of the dried KBr powder using an agate mortar and pestle. The goal is to reduce the sample's particle size and ensure it is homogeneously distributed throughout the KBr.
Step 4: Pressing the Pellet
The ground mixture is carefully transferred into the cavity of the pellet die. The die is assembled and placed in a hydraulic press, where a load of several tons (typically 2 to 10 tons) is applied.
For the best results, this pressing should be done under vacuum. The vacuum removes trapped air and any final traces of moisture, which helps create a perfectly clear, transparent pellet that won't easily crack.
Step 5: Mounting and Analysis
Once the pressure is released, the transparent pellet is removed from the die. It is often retained within a stainless steel collar, which can then be placed into a sample holder that fits directly into the spectrometer's sample compartment for analysis.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
The quality of the final spectrum is entirely dependent on the quality of the pellet. Several common issues can arise, but they are easily preventable with care.
The Problem of Moisture
Water is the primary enemy of this technique. If the KBr is not thoroughly dried, strong water absorption peaks will appear in your spectrum. Always use freshly dried KBr and perform a background measurement with a KBr-only pellet to help correct for any residual moisture or scattering.
Inadequate Grinding and Mixing
If the sample particles are too large or not evenly mixed, they will scatter the infrared light. This effect, known as the Christiansen effect, results in a sloping baseline and distorted peaks, making the spectrum difficult to interpret.
Cloudy or Opaque Pellets
A pellet that appears cloudy or opaque is a sign of trapped air or moisture. This is most often caused by applying pressure too quickly or not using an adequate vacuum during the pressing stage. A good pellet should be almost perfectly transparent.
Pellet Breakage
Pellets that crack or shatter easily are also typically a result of trapped air. Applying pressure gradually and using a good vacuum allows air to escape, resulting in a mechanically stable pellet.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Mastering this technique is about controlling variables to produce a reliable result. Your focus will determine which steps to prioritize.
- If your primary focus is maximum clarity and transparency: Concentrate on extremely fine grinding of the sample and KBr, thorough drying, and using a high vacuum during pressing.
- If your primary focus is minimizing spectral interference: Prioritize using high-purity, spectroscopic-grade KBr and always run a background scan using a blank KBr pellet.
- If your primary focus is reproducibility: Standardize your sample-to-KBr ratio, grinding time, and the exact pressure and duration used for every pellet you make.
Properly executed, the KBr pellet technique is a powerful and fundamental tool for the infrared analysis of solid materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Sample preparation for FTIR analysis of solids. |
| Core Principle | Suspend sample in a transparent KBr matrix to minimize light scattering. |
| Ideal For | Creating a solid-state "solution" for accurate infrared spectroscopy. |
| Critical Steps | Meticulous cleaning, drying KBr, fine grinding, homogeneous mixing, high-pressure pressing (often under vacuum). |
| Common Pitfalls | Moisture interference, inadequate grinding (causes baseline distortion), cloudy pellets from trapped air. |
Ready to achieve superior FTIR results?
The KBr pellet technique is fundamental for accurate solid sample analysis. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need to master this method, from reliable hydraulic presses and pellet dies to high-purity KBr powder.
Let our expertise enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy



















