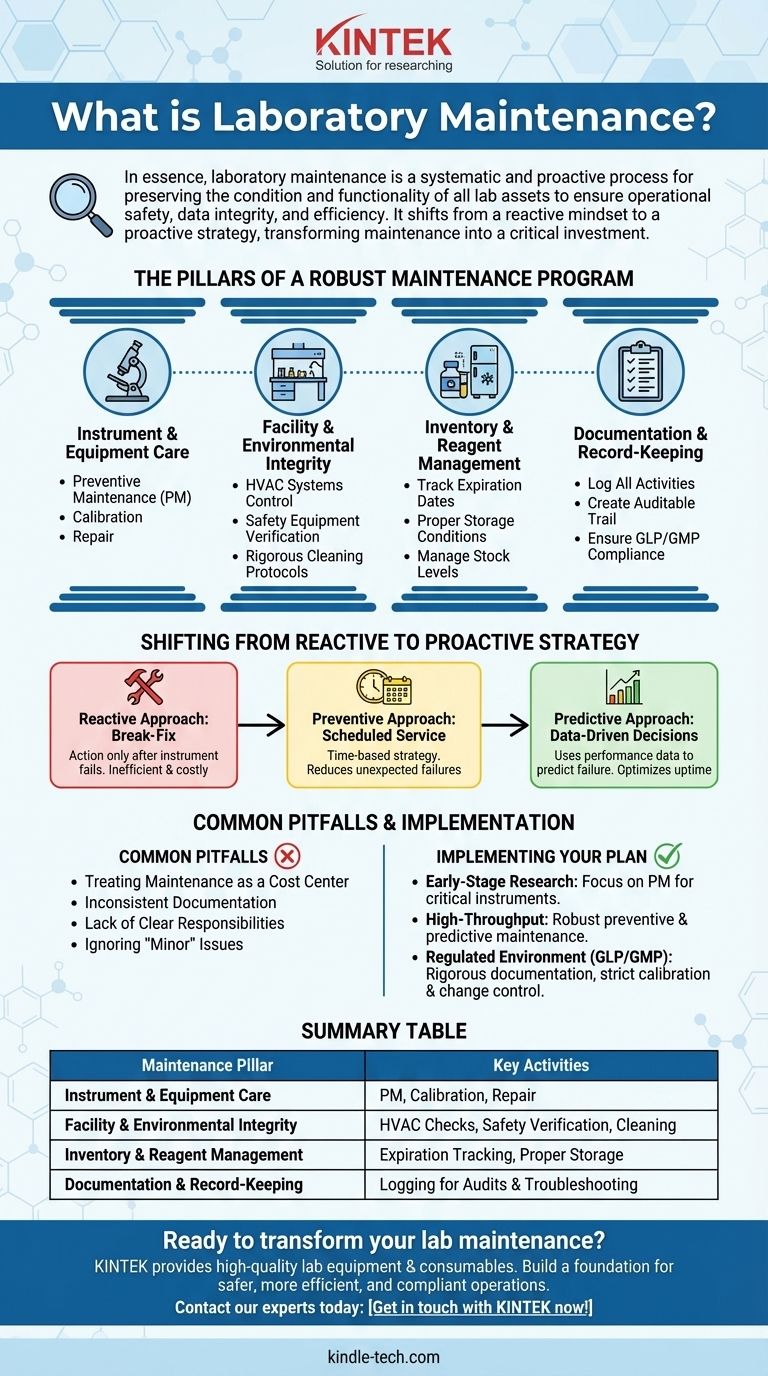
In essence, laboratory maintenance is a systematic and proactive process for preserving the condition and functionality of all lab assets, including instruments, facilities, and safety equipment. It involves a scheduled combination of cleaning, inspection, calibration, repair, and record-keeping to ensure operational safety, data integrity, and efficiency.
The core principle is to shift from a reactive mindset of fixing things when they break to a proactive strategy that prevents failures before they happen. This transforms maintenance from a costly chore into a critical investment in reliable and reproducible results.
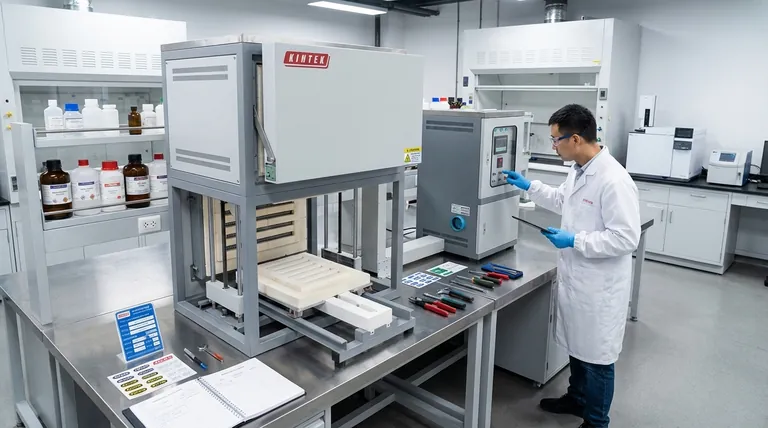

The Pillars of a Robust Maintenance Program
Effective laboratory maintenance isn't just about fixing a broken centrifuge. It's a holistic system built on several key pillars that work together to ensure the entire environment is controlled, safe, and fit for purpose.
Instrument and Equipment Care
This is the most visible aspect of lab maintenance. It ensures that the tools you rely on for data generation are performing to specification.
Key activities include preventive maintenance (PM), which involves scheduled service like cleaning optics or replacing seals, and calibration, which verifies the instrument's accuracy against a known standard.
Facility and Environmental Integrity
The physical space of the lab is as critical as the equipment within it. This pillar focuses on the infrastructure that supports your work.
This includes maintaining HVAC systems to control temperature and air quality, verifying the function of safety equipment like fume hoods and emergency showers, and implementing rigorous cleaning protocols to prevent contamination.
Inventory and Reagent Management
Your results are only as good as the materials you use. Proper maintenance of consumables is vital for reproducibility.
This involves tracking expiration dates, ensuring proper storage conditions for sensitive reagents, and managing stock levels to prevent unexpected shortages that can disrupt workflows.
Documentation and Record-Keeping
If it isn’t documented, it didn’t happen. Meticulous records are the backbone of a defensible and compliant maintenance program.
Every maintenance activity, from a simple cleaning to a major repair, must be logged. This creates an auditable trail that is essential for quality control, troubleshooting, and regulatory compliance (e.g., GLP/GMP).
Shifting from a Reactive to a Proactive Strategy
The maturity of a lab's maintenance program can be judged by how it approaches problems. The goal is to move up the hierarchy from simply reacting to issues to actively preventing them.
The Reactive Approach: "Break-Fix"
This is the most basic level of maintenance. Action is only taken after an instrument fails.
While necessary for unexpected breakdowns, relying solely on this method is inefficient, costly, and leads to significant downtime. It can also compromise ongoing experiments and jeopardize data quality.
The Preventive Approach: Scheduled Service
This is a time-based strategy where maintenance tasks are performed at regular intervals, regardless of the equipment's current condition.
Examples include annual pipette calibrations or quarterly filter changes. This approach significantly reduces unexpected failures and is the foundation of most effective maintenance programs.
The Predictive Approach: Data-Driven Decisions
This is the most advanced strategy, using performance data and monitoring to predict when a failure is likely to occur.
For instance, tracking a pump's pressure signature over time can indicate a developing leak before it becomes catastrophic. This minimizes unnecessary maintenance while still preventing failures, optimizing both uptime and resource allocation.
Common Pitfalls That Undermine Lab Operations
Even with good intentions, maintenance programs can fail due to common and avoidable mistakes. Recognizing these pitfalls is the first step toward building a resilient system.
Treating Maintenance as a Cost Center
Viewing maintenance as a pure expense rather than an investment is a critical error. The cost of a single failed experiment or instrument failure almost always outweighs the cost of a preventive program.
Inconsistent Documentation
Sporadic or incomplete maintenance logs make it impossible to track performance trends, troubleshoot effectively, or pass an audit. A system is only as good as its records.
Lack of Clear Responsibilities
When no single person or team is assigned responsibility for a task, it often gets overlooked. A successful program requires clearly defined roles for every piece of equipment and every protocol.
Ignoring "Minor" Issues
Small problems, like a frayed power cord or a slightly noisy motor, are often ignored until they escalate into major failures. A culture of proactive reporting is essential for catching these issues early.
Implementing Your Maintenance Plan
The right maintenance strategy depends on your lab's specific goals, workload, and regulatory requirements. A scalable plan is key.
- If your primary focus is early-stage research: Begin with a solid preventive maintenance schedule for critical instruments like pipettes, balances, and pH meters, coupled with clear cleaning and safety check protocols.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening or diagnostics: Implement a robust preventive program with a centralized digital tracking system and consider predictive maintenance for high-cost, high-use automated systems to maximize uptime.
- If your primary focus is working in a regulated (GLP/GMP) environment: Your program must be built on rigorous, auditable documentation, strict calibration and validation schedules, and formal change control procedures for all equipment.
Ultimately, a well-maintained laboratory is a prerequisite for trustworthy science.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Pillar | Key Activities |
|---|---|
| Instrument & Equipment Care | Preventive maintenance, calibration, repair |
| Facility & Environmental Integrity | HVAC checks, safety equipment verification, cleaning protocols |
| Inventory & Reagent Management | Expiration tracking, proper storage, stock management |
| Documentation & Record-Keeping | Logging all activities for audits and troubleshooting |
Ready to transform your lab maintenance from a reactive chore into a proactive investment?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables your maintenance program relies on. From precision instruments requiring regular calibration to durable consumables with traceable lot numbers, our products are designed for reliability and ease of maintenance.
Let us help you build a foundation for safer, more efficient, and fully compliant laboratory operations. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and ensure your data's integrity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the effect of pressure on sputtering? Control Film Density and Quality
- What are some disadvantages of powder metallurgy? Size, Strength, and Complexity Limitations
- What role does a laboratory magnetic stirrer play in the acidification pretreatment of aluminum sludge? Speed Recovery
- What is target in sputtering? The Essential Source Material for Thin-Film Deposition
- Why is high-power ultrasound utilized for MOFs in MMMs? Unlock Superior Gas Separation & Uniform Dispersion
- What is furnace soldering? A High-Volume Process for Joining Components
- Is natural or synthetic graphite better? Choosing the Right Material for Your Application
- What is the most common metal used for blacksmithing? Start with Mild Steel for Forging Success



















