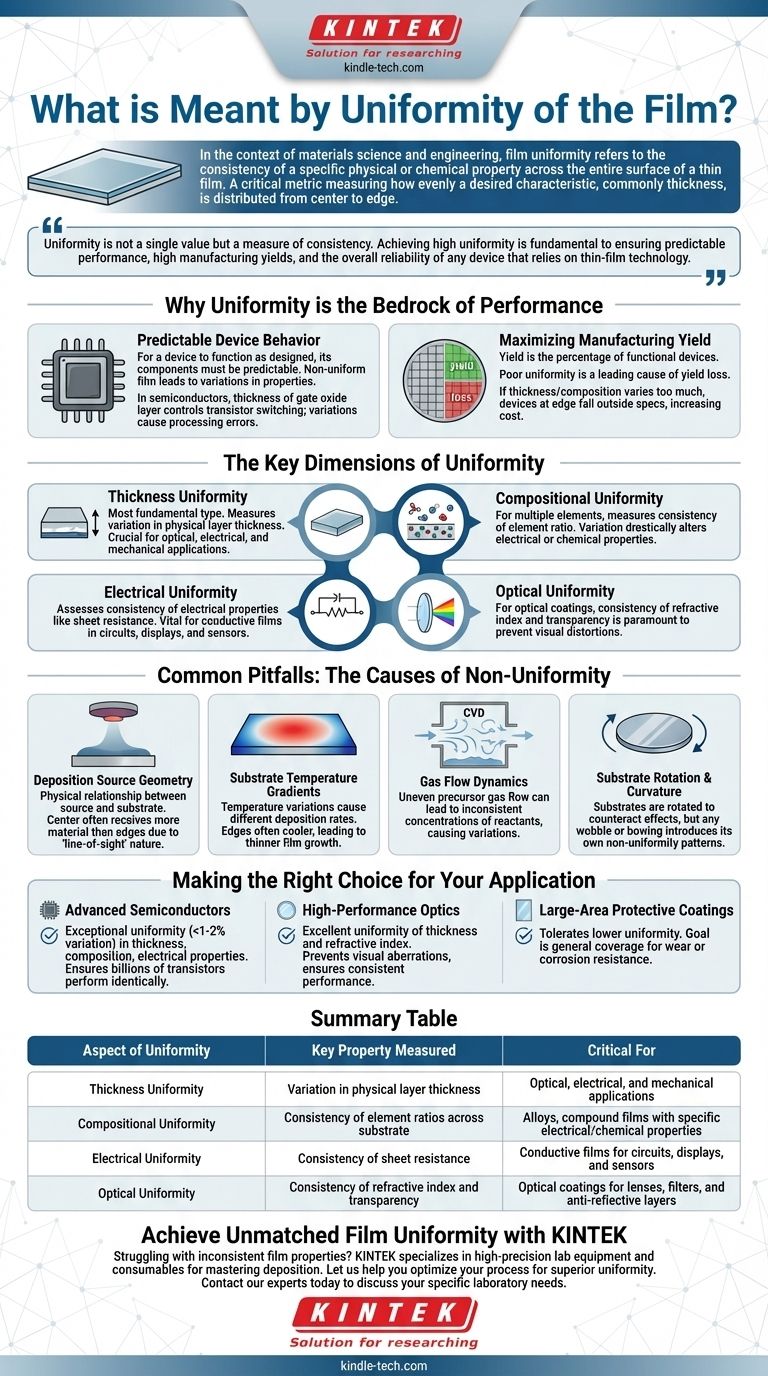
In the context of materials science and engineering, film uniformity refers to the consistency of a specific physical or chemical property across the entire surface of a thin film. It is a critical metric that measures how evenly a desired characteristic, most commonly thickness, is distributed from the center to the edge of a substrate.
Uniformity is not a single value but a measure of consistency. Achieving high uniformity is fundamental to ensuring predictable performance, high manufacturing yields, and the overall reliability of any device that relies on thin-film technology.
Why Uniformity is the Bedrock of Performance
In nearly every application of thin films—from microchips to eyeglasses—inconsistency is a direct cause of failure or poor performance. Uniformity is the primary indicator of a well-controlled and repeatable manufacturing process.
Predictable Device Behavior
For a device to function as designed, its components must be predictable. A non-uniform film leads to variations in properties across a single device or from one device to another on the same wafer.
In semiconductors, for example, the thickness of a gate oxide layer directly controls the transistor's switching characteristics. If this film is not uniform, transistors across the chip will behave differently, leading to processing errors.
Maximizing Manufacturing Yield
Yield is the percentage of functional devices produced from a single manufacturing run (e.g., on a silicon wafer). Poor film uniformity is a leading cause of yield loss.
If a film's thickness or composition varies too much, devices at the edge of the wafer may fall outside of acceptable performance specifications, rendering them useless and driving up the cost per functional chip.
The Key Dimensions of Uniformity
While thickness is the most commonly discussed metric, uniformity applies to any critical film property that can be measured and mapped across a surface.
Thickness Uniformity
This is the most fundamental type. It measures the variation in the physical thickness of the deposited layer. It is crucial for optical, electrical, and mechanical applications.
Compositional Uniformity
For films made of multiple elements (alloys or compounds), this measures how consistent the ratio of those elements is across the substrate. A variation in composition can drastically alter a film's electrical or chemical properties.
Electrical Uniformity
This assesses the consistency of electrical properties, such as sheet resistance. It is vital for conductive films used in integrated circuits, transparent conductors for displays, and sensor electrodes.
Optical Uniformity
For optical coatings, the uniformity of properties like refractive index and transparency is paramount. Inconsistent optical properties on a lens, for example, would result in visible distortions or color variations.
Common Pitfalls: The Causes of Non-Uniformity
Achieving high uniformity requires precise control over the film deposition process. Non-uniformity is not random; it is typically a systematic outcome of the deposition environment.
Deposition Source Geometry
The physical relationship between the material source (e.g., a sputtering target) and the substrate is critical. The "line-of-sight" nature of many deposition techniques means the center of the substrate often receives more material than the edges.
Substrate Temperature Gradients
Temperature variations across the substrate can cause different reaction or deposition rates. The edges of a substrate holder are often cooler than the center, leading to thinner film growth in those areas.
Gas Flow Dynamics
In chemical vapor deposition (CVD), the flow of precursor gases must be carefully managed. Turbulent or uneven flow can lead to inconsistent concentrations of reactants across the surface, causing variations in film growth.
Substrate Rotation and Curvature
To counteract these effects, substrates are almost always rotated during deposition. However, any wobble in the rotation or curvature (bowing) of the substrate itself can introduce its own patterns of non-uniformity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The required level of uniformity is dictated entirely by the end-use application. Understanding your primary goal is key to setting the right process specifications.
- If your primary focus is advanced semiconductors: You require exceptional uniformity (often <1-2% variation) in thickness, composition, and electrical properties to ensure billions of transistors perform identically.
- If your primary focus is high-performance optics: You need excellent uniformity of thickness and refractive index to prevent visual aberrations and ensure consistent anti-reflective or filtering performance.
- If your primary focus is large-area protective coatings: You can often tolerate lower uniformity, as the goal is general coverage for wear or corrosion resistance rather than micro-scale device performance.
Ultimately, controlling film uniformity is about mastering the deposition process to deliver consistent, reliable performance where it matters most.
Summary Table:
| Aspect of Uniformity | Key Property Measured | Critical For |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness Uniformity | Variation in physical layer thickness | Optical, electrical, and mechanical applications |
| Compositional Uniformity | Consistency of element ratios across the substrate | Alloys and compound films with specific electrical/chemical properties |
| Electrical Uniformity | Consistency of sheet resistance and other electrical properties | Conductive films for circuits, displays, and sensors |
| Optical Uniformity | Consistency of refractive index and transparency | Optical coatings for lenses, filters, and anti-reflective layers |
Achieve Unmatched Film Uniformity with KINTEK
Struggling with inconsistent film properties that impact your device performance and manufacturing yield? KINTEK specializes in providing high-precision lab equipment and consumables designed to master the deposition process. Whether you are working on semiconductors, optical coatings, or protective layers, our solutions help you deliver the consistent, reliable results your application demands.
Let us help you optimize your process for superior uniformity. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your thin-film technology.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- How does biomass work as a renewable energy? A Carbon-Neutral Power Source Explained
- Which institutions have adjusted their ULT freezer set points to -70°C? Save Energy Without Risking Samples
- What are environmental impacts of biomass? Balancing Sustainability with Potential Harm
- What role does an open reactor play in the SHS process? Enhance Your Surface Coatings Today
- What is the sputtering voltage of a magnetron? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- What is the necessity of a low-temperature drying step in Cu-TiO2 thin film preparation? Ensure Structural Integrity
- What is a normal heat treatment? Achieve Uniform & Predictable Metal Properties
- What gas emissions come from pyrolysis? Turning Waste into Energy and Carbon Sequestration



















